iOS App Testing Tutorial: Manual & Automation
What is iOS App Testing?
iOS App Testing is a testing process in which an iOS application is tested on real Apple devices to check whether it works as expected or not for specific user actions like installation time, user interface, user experience, appearance, behaviour, functionality, load time, performance, App Store listing, OS version support, etc.
Why iOS App Testing?
iOS App Testing is required because iOS is Apple’s platform for mobile applications which was released on June 29, 2007. Unlike Android, Apple doesn’t license iOS for installation on non-Apple hardware. iOS and iOS applications can be only installed on Apple devices hence, your iOS App must be compatible with iOS versions and iOS devices.
This is the common question when developer create an iOS application.
It doesn’t matter how much time you invest in design and implementation, mistakes are inevitable, and bugs will appear. There are some common bugs on the iOS application. As shown in below figure.
Application crashing
One of the most frustrating problems, when using Apple’s devices, is that an application may crash frequently during execution. Many times the app crashes because there’s some bugs or memory leak in apps.
Application incompatibilities
Your iOS application may run perfectly on current iOS version, but if iOS is upgraded, it may not work due to incompatibility issues.
Security vulnerability
A Security vulnerability in iOS allows the hacker to attack your iOS devices, steal your private information. Until now, severe iPhone security vulnerabilities are discovered in different iOS versions.
Memory leaks
Memory leaks are blocks of allocated memory that the program no longer uses. Memory leaks cause your iOS application to crash.
They are bugs and should always be fixed.
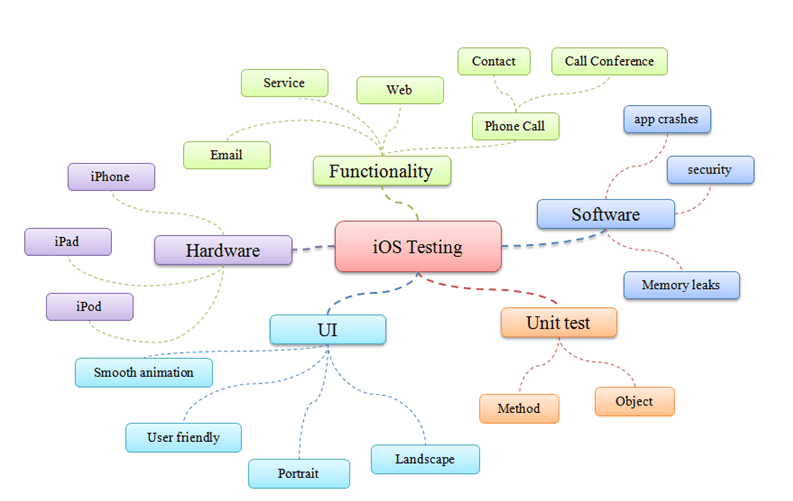
iOS testing MindMap
As shown in the above figure, iOS Testing MindMap shows all the items which tester should consider when conduct testing on iOS.
iOS Application Testing Checklist
This checklist is specifically designed to test the characteristics of iOS mobile applications. Obviously, it tests only generic application characteristics and not the functionality of it.
- Check the installation time taken by the application onto the device. Make sure that application is installed within an acceptable time.
- Once the application is installed, check whether the application has app icon and name. Also, make sure that both icon and name are self-explanatory reflecting the core intention of the application.
- Launch the application and check whether splash screen is displayed.
- Check the splash screen timeout and time taken to load home screen. The Home screen of the application should load within an acceptable time. If the Home screen only takes more time to load, then there is more chance for the user to quit or even uninstall the application itself. Also, check how the contents are loaded in Home screen.
- The main function of the application should be apparent immediately. It should speak for itself.
- Check whether the app supports both landscape and portrait orientations. If so, check the app in both orientations. The application’s user interface should get set accordingly.
- Without an internet connection, launch the application. Make sure that app behaves as designed/desired. There is a chance that the application may crash on launching it or may just display a blank screen.
- If the application uses location services, then check whether location permission alert is displayed or not. This alert should be prompted to the user only once.
- If the application sends push notifications, then check whether push notification permission alert is displayed or not. This alert should also be prompted to the user only once.
- Launch the application, quit it and relaunch. Check whether app behaves as designed/desired
- Close the application by tapping over Home button of the device and open the app again. Check whether the app works as designed/desired.
- Once installed, check whether the app is listed in iPhone’s settings app.
- After the application is made live, check whether the application can be found in “App Store.” There will be supported OS version for the application. So, make sure the application can be found in those supported OS version device’s “App Store.” Also, the application should not be listed in unsupported OS version device’s “App Store.”
- Check whether the application goes to sleep mode when running in the background to prevent battery drain.
- If the performance of the application is slow or whenever contents are loading, check whether there is a progress status icon (“Loading…”), preferably with a specific message.
- Search the application with its name in device search bar. Check whether the app is listed
- Check whether the appearance of buttons that perform standard actions are not altered in the app (for instance: refresh, organize, trash, Reply, back, etc.)
- Check whether standard buttons are not used for other functions then that they are normally used for
iOS Testing Strategy
The below figure introduces some common types of iOS testing strategy.
Automated testing
Automated testing is the most advantages of iOS testing. It enables you to detect the bug and performance issues quickly. The benefits of automated testing as shown below:
- Automated testing can run on multiple devices, saving your time
- Automated testing can target SDKs. You can run test on different SDK versions
- Automated testing increase your productivity of testing, save your cost of software development
- There are many open source Testing frameworks support automated testing on iOS
Unit testing with OCUnit
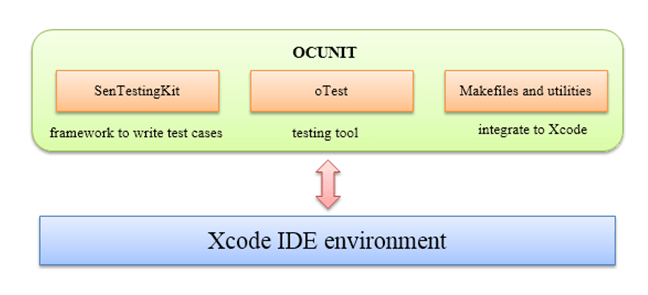
When the original iOS SDK was released, it lacked Unit Testing capabilities. So Apple has brought back the OCUnit unit test solution in iOS SDK version 2.2.
OCUnit is a testing framework for C- Objective in the Mac OS. The biggest advantages of an OCUnit framework are the tight integration into XCode development environment as shown below.
Some of the benefits of OCUnit are shown in below figure.
UI Testing with UIAutomation
UI Automation is a JavaScript library provided by Apple Inc, which can be used to perform an automated test on real devices and on iOS Simulator. This framework is added to iOS SDK4.0. Using UI Automation, you can automate testing the application not only on the simulator but also the real device.
UIAutomation brings you these benefits:
- Reduce effort on Manual Testing
- Use less your memory to execute all your tests
- Simplify your UI testing procedure ( just push one or three buttons and run full your test suites)
UIAutomation instrument works from scripts, which are written in JavaScript. It simulates user events on target iOS application.
UIAutomation Cons vs.Pros
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Good support for gesture and rotation | It’s not open source, less support from the developer |
| 2. | Can run UIAutomation tests on the device, not the only simulator. | Can’t integrate with other tools extremely well |
| 3. | Developed by JavaScript, it is a popular programming language. |
The above figure represents some common classes in UIAutomation framework.
- The UIAElement class is the super class for all user interface elements in the context of the Automation
- The UIATarget class represents the high-level user interface elements of the system under test
- The UIALogger class provides test and error information on retrieval functionality
- The UIAActivityViewclass allows access to, and control of, activity views within your app.
- The UIAActionSheet class allows access to, and control of, action sheets within your app.
- User Event Action
- UISlider class
- UIAButton class
- UIAKey class
- UIAKeyboard class
Other Automated testing frameworks
- Frank: Automated Acceptance Test framework for iPhone and iPad
- KIF : is an iOS integration test framework. It allows for easy automation of iOS apps by leveraging the accessibility attributes that the OS makes available for those with visual disabilities.
Manual testing
Exploratory Testing
It is a testing without a formal test plan. Exploratory Testing is low cost testing method, but it can miss the potential bugs in your iOS application.
Exploratory Testing Cons vs. Pros
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Less preparation is needed, early detect serious bugs. | Requires high skill of the tester |
| 2. | Don’t need Test Plan speed up the bug detection. | Test coverage is low. It does not guarantee that all your requirements are tested. |
| 3. | Most bugs are discovered early by some sort of exploratory testing | Lack of testing documentation |
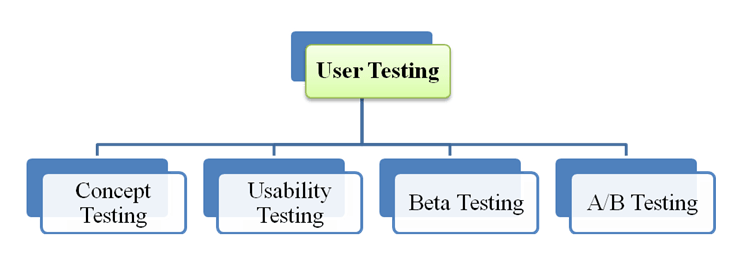
User Testing
User testing is a type of Manual Testing on iOS. The purpose of this testing is to create better apps, not only bug-free apps. Below figure shows four types of User Testing
Concept testing
Evaluate user response to an application idea before releasing to the market. Procedures of concept testing on iOS are described as below
Usability Testing
Usability Testing is a test how easy to use your iOS application. In iOS testing, usability test could be recorded to remember or to share with others.
There is some tools support usability testing on iOS.
TryMyUI mobile user testing apps for Android and iOS.
Delight.io, this tool can capture real user interaction on your iOS apps.
Beta testing
Beta Testing is the integration testing with real data to get final feedback from users. To distribute your apps for beta testing, you have to follow steps below.
–Pre-condition: If you are beta testing a final candidate for a release, be sure to validate the app before distributing it to testers.
–Find tester via service: you collect device IDs from testers and add them to Member Center
–Create ad-hoc distribution: Ad Hoc distribution allows the tester to run your app on their device without need Xcode. This step includes 2 sub-steps
- Create distribution certificates
- Create Ad-hoc provisioning profiles
–Solicit feedback from tester: Tester conduct testing and send bug reports to you. After your app is released, you can get the reports from iTunes connect.
A/B testing
A/B testing is one of the most powerful ways to evaluate the effectiveness of your iOS app. It uses randomized experiments with two devices, A and B.
A/B testing includes three main steps
- Configure a test: Prepared 2 versions of your iOS app (A & B) and test metric
- Test: Test 2 iOS apps versions above on devices simultaneously.
- Analyze: Measure and select better version to release
Following tools support A/B testing on iOS.
- Arise: A/B testing for both iOS and Android. It can be integrated into your iOS app and make the testing process more quickly.
Best practices for A/B testing
- Define the target of your test. Any test is useless without a target.
- Watch end users use your app the first time
- Run one test only per update. It saves your time when conduct testing
- Monitor your test carefully. You can learn experiences from your test by monitoring it.
iOS testing Best practice
Here are some tips you should know when organizing the testing of your iOS application
- Test the application on a real device to get real about performance
- Improve your testing methods, because traditional testing methods are no longer sufficient to coverage all tests on iOS testing
- Using console log to test iOS application. This is an iOS feature includes information from every application on the device.
- Document application bugs using built-in screen short command. It helps developer understand how the bugs occur.
- Crash reporting is useful tools when test your application. They can detect crashes and log detail so you can investigate the bugs easily.
MYTHS about iOS testing
This section examines a few popular myths and realities of iOS testing
Testing application on iOS and Android are the same thing.
iOS and Android are two platforms were developed by Apple Inc and Google. They are totally different. Etc test environments, test frameworks, programming languages.
Test application on iOS Simulator is enough.
iOS Simulator is not strong enough for testing an app. Because iOS Simulator has some limitations:
- Hardware limitations (Camera, Microphone input, Sensor)
- Your app’s UI may appear to run both faster and smoother than on a device
- API Limitations
- Some frameworks unsupported (Media Player, Store Kit, Message UI..)
Everyone will download my apps on the app store because it has many features
The more features your application has, the more bugs you could get. No user will download your application if it still has many defects.

.png)