XPath Contains: Text, Following Sibling & Ancestor in Selenium
🚀 Smart Summary
XPath Contains, Sibling, and Ancestor in Selenium enable precise web element identification using structured relationships and text patterns. These XPath functions enhance automation reliability, flexibility, and maintainability in complex DOM hierarchies.
What is XPath Contains?
XPath contains is a function within an XPath expression, which is used to search for the web elements that contain a particular text. We can extract all the elements that match the given text value using the XPath contains() function throughout the webpage. Contains in XPath has the ability to find the element with partial text.
Example – contains text
Here we are searching an anchor .contains text as ‘SAP M’.
"//h4/a[contains(text(),'SAP M')]"
NOTE: You can practice the following XPath exercise on this https://demo.guru99.com/test/selenium-xpath.html
If a simple XPath is not able to find a complicated web element for our test script, we need to use the functions from the XPath 1.0 library. With the combination of these functions, we can create a more specific XPath.
👉 Enroll for Free Live Selenium Testing Project
Following Sibling in XPath
A Sibling in Selenium Webdriver is a function used to fetch a web element that is a sibling to the parent element. If the parent element is known, then the web element can be easily found or located, which can use the sibling attribute of the XPath expression in Selenium WebDriver.
Sibling in XPath Example:
Here, on the basis of the sibling element of ‘a’ we are finding ‘h4’
"//div[@class='canvas- graph']//a[@href='/accounting.html'][i[@class='icon-usd']]/following-sibling::h4"
Ancestor: To find an element on the basis of the parent element, we can use the ancestor attribute of XPath.
Let’s understand these 3 functions using an example –
Test Steps:
Note: Since the date of creation of the tutorial, the Homepage of Guru99 has been updated, so use the demo site instead to run tests
- Go to https://demo.guru99.com/test/guru99home/
- In the section ‘A few of our most popular courses’, search all Web Elements that are siblings of a WebElement whose text is ‘SELENIUM’
- We will find elements using XPath text contains, ancestor, and sibling functions.
USING Contains Text and XPath Sibling
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.List;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
// If you prefer WebDriverManager (optional):
// import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager;
public class SiblingAndParentInXpath_Chrome {
@Test
public void testSiblingAndParentInXpath() {
// === Option A: Use local ChromeDriver binary path ===
// Update this path to your chromedriver location:
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "C:\\chromedriver.exe");
// === Option B: Use WebDriverManager (uncomment next line and remove Option A lines) ===
// WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
// Add any flags you need, e.g. headless:
// options.addArguments("--headless=new");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(options);
try {
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(Duration.ofSeconds(10));
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.get("https://demo.guru99.com/test/guru99home/");
// Find all siblings (divs) next to the 'SELENIUM' tile within
// the "A few of our most popular courses" section.
// Steps encoded in XPath:
// 1) Locate the H2 that contains the section title
// 2) Move to its parent DIV
// 3) Inside it, locate the link with text 'SELENIUM'
// 4) From the SELENIUM tile's parent DIV, get following sibling tiles
List<WebElement> dateBox = driver.findElements(By.xpath(
"//h2[contains(., 'A few of our most popular courses')]/parent::div" +
"//a[normalize-space(.)='SELENIUM']/parent::div" +
"/following-sibling::div[contains(@class,'rt-grid-2')]"
));
// Print the text of each sibling element
for (WebElement el : dateBox) {
System.out.println(el.getText());
}
} finally {
driver.quit();
}
}
}
Output will be like:
XPath Ancestor in Selenium
XPath Ancestor in Selenium is a function used to find the ancestor of a specific element at the specified layer. The level of ancestor to be returned or the level of the ancestor relative to the level of the member can be explicitly specified. It returns the number of hierarchical steps from the ancestor, locating the specified ancestor that the user wants.
Now, suppose we need to Search All elements in the ‘Popular course’ section with the help of the ancestor of the anchor whose text is ‘SELENIUM’
Here our xpath query will be like
"//div[.//a[text()='SELENIUM']]/ancestor::div[@class='rt-grid-2 rt-omega']/following-sibling::div"
Complete Code
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.List;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class AncestorInXpath_Chrome {
@Test
public void testAncestorInXpath() {
// Set path to your ChromeDriver executable
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "C:\\chromedriver.exe");
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(options);
try {
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(Duration.ofSeconds(10));
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.get("https://demo.guru99.com/test/guru99home/");
// Search all elements in 'Popular course' section
// using the ancestor of the 'SELENIUM' link
List <WebElement> dateBox = driver.findElements(
By.xpath("//div[.//a[text()='SELENIUM']]/ancestor::div[@class='rt-grid-2 rt-omega']/following-sibling::div")
);
// Print all sibling elements of the 'SELENIUM' tile
for (WebElement element : dateBox) {
System.out.println(element.getText());
}
} finally {
driver.quit();
}
}
}
Output will look like-
Using AND and OR
By using AND and OR, you can put 2 conditions in our XPath expression.
- In case of AND, both 2 conditions should be true, then only it finds the element.
- In case of OR, any one of the 2 conditions should be true, then only it finds the element.
Here, our XPath query will be like
Xpath=//*[@type='submit' OR @name='btnReset']
Xpath=//input[@type='submit' and @name='btnLogin']
Test Steps:
- Go to https://demo.guru99.com/v1/
- In this section, we will use the above demo site to search for elements with different functions of XPath.
You will find an element using AND and OR, parent, starts-with, and XPath axes
AND OR Example
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class AND_OR {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WebDriver driver;
WebElement w,x;
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","E://Selenium//Selenium_Jars//chromedriver.exe");
driver= new ChromeDriver();
// Launch the application
driver.get("https://www.guru99.com/");
//Search element using OR in the xpath
w=driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@type='submit' OR @name='btnReset']"));
//Print the text of the element
System.out.println(w.getText());
//Search element using AND in the xpath
x=driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@type='submit' and @name='btnLogin']"));
//Print the text of the searched element
System.out.println(x.getText());
//Close the browser
driver.quit();
}
}
XPath Parent in Selenium
Parent in Selenium is a method used to retrieve the parent node of the current node selected in the web page. It is very useful in situations where you select an element and need to get the parent element using XPath. This method is also used to get the parent’s parent.
Here, our XPath query will be like
Xpath=//*[@id='rt-feature']//parent::div
XPath using Parent
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class Parent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WebDriver driver;
WebElement w;
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","E://Selenium//Selenium_Jars//chromedriver.exe");
driver= new ChromeDriver();
// Launch the application
driver.get("https://www.guru99.com/");
//Search the element by using PARENT
w=driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id='rt-feature']//parent::div"));
//Print the text of the searched element
System.out.println(w.getText());
//Close the browser
driver.quit();
}
}
Starts-with
Using the Starts-with function, you can find the element whose attribute dynamically changes on refresh or other operations like click, submit, etc.
Here our XPath query will be like
Xpath=//label[starts-with(@id,'message')]
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class StartsWith {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WebDriver driver;
WebElement w;
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","E://Selenium//Selenium_Jars//chromedriver.exe");
driver= new ChromeDriver();
// Launch the application
driver.get("https://www.guru99.com/");
//Search the element by using starts-with
w=driver.findElement(By.xpath("//label[starts-with(@id,'message')]"));
//Print the text of the searched element
System.out.println(w.getText());
//Close the browser
driver.quit();
}
}
Xpath axes
By using XPath axes, you can find the dynamic and very complex elements on a web page. XPath axes contain several methods to find an element. Here, will discuss a few methods.
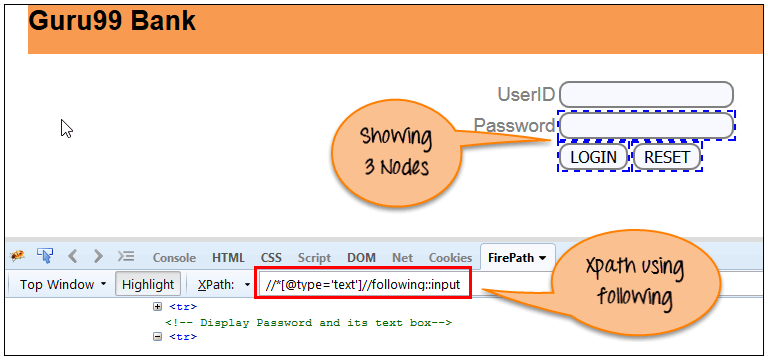
following: This function will return the immediate element of the particular component.
Here our XPath query will be like
Xpath=//*[@type='text']//following::input
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class Following {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WebDriver driver;
WebElement w;
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","E://Selenium//Selenium_Jars//chromedriver.exe");
driver= new ChromeDriver();
// Launch the application
driver.get("https://www.guru99.com/");
//Search the element by using Following method
w=driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@type='text']//following::input"));
//Print the text of the searched element
System.out.println(w.getText());
//Close the browser
driver.quit();
}
}
Preceding: This function will return the preceding element of the particular element.
Here our XPath query will be like
Xpath= //*[@type='submit']//preceding::input

import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class Preceding {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WebDriver driver;
WebElement w;
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","E://Selenium//Selenium_Jars//chromedriver.exe");
driver= new ChromeDriver();
// Launch the application
driver.get("https://www.guru99.com/");
//Search the element by using preceding method
w=driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@type='submit']//preceding::input"));
//Print the searched element
System.out.println(w.getText());
//Close the browser
driver.quit();
}
}
d) Descendant: This function will return the descendant element of the particular element.
Here our XPath query will be like
Xpath= //*[@id='rt-feature']//descendant::a

import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class Descendant {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WebDriver driver;
WebElement w;
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","E://Selenium//Selenium_Jars//chromedriver.exe");
driver= new ChromeDriver();
// Launch the application
driver.get("https://www.guru99.com/");
//Search the element by using descendant method
w=driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id='rt-feature']//descendant::a"));
//Print the searched element
System.out.println(w.getText());
//Close the browser
driver.quit();
}
}









