Hadoop & Mapreduce Examples: Create First Program in Java
In this tutorial, you will learn to use Hadoop with MapReduce Examples. The input data used is SalesJan2009.csv. It contains Sales related information like Product name, price, payment mode, city, country of client etc. The goal is to Find out Number of Products Sold in Each Country.
First Hadoop MapReduce Program
Now in this MapReduce tutorial, we will create our first Java MapReduce program:
Ensure you have Hadoop installed. Before you start with the actual process, change user to ‘hduser’ (id used while Hadoop configuration, you can switch to the userid used during your Hadoop programming config ).
su - hduser_
Step 1)
Create a new directory with name MapReduceTutorial as shwon in the below MapReduce example
sudo mkdir MapReduceTutorial
Give permissions
sudo chmod -R 777 MapReduceTutorial
SalesMapper.java
package SalesCountry;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.*;
public class SalesMapper extends MapReduceBase implements Mapper <LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, OutputCollector <Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
String valueString = value.toString();
String[] SingleCountryData = valueString.split(",");
output.collect(new Text(SingleCountryData[7]), one);
}
}
SalesCountryReducer.java
package SalesCountry;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.*;
public class SalesCountryReducer extends MapReduceBase implements Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public void reduce(Text t_key, Iterator<IntWritable> values, OutputCollector<Text,IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
Text key = t_key;
int frequencyForCountry = 0;
while (values.hasNext()) {
// replace type of value with the actual type of our value
IntWritable value = (IntWritable) values.next();
frequencyForCountry += value.get();
}
output.collect(key, new IntWritable(frequencyForCountry));
}
}
SalesCountryDriver.java
package SalesCountry;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.*;
public class SalesCountryDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JobClient my_client = new JobClient();
// Create a configuration object for the job
JobConf job_conf = new JobConf(SalesCountryDriver.class);
// Set a name of the Job
job_conf.setJobName("SalePerCountry");
// Specify data type of output key and value
job_conf.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job_conf.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// Specify names of Mapper and Reducer Class
job_conf.setMapperClass(SalesCountry.SalesMapper.class);
job_conf.setReducerClass(SalesCountry.SalesCountryReducer.class);
// Specify formats of the data type of Input and output
job_conf.setInputFormat(TextInputFormat.class);
job_conf.setOutputFormat(TextOutputFormat.class);
// Set input and output directories using command line arguments,
//arg[0] = name of input directory on HDFS, and arg[1] = name of output directory to be created to store the output file.
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job_conf, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job_conf, new Path(args[1]));
my_client.setConf(job_conf);
try {
// Run the job
JobClient.runJob(job_conf);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Check the file permissions of all these files
and if ‘read’ permissions are missing then grant the same-
Step 2)
Export classpath as shown in the below Hadoop example
export CLASSPATH="$HADOOP_HOME/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-client-core-2.2.0.jar:$HADOOP_HOME/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-client-common-2.2.0.jar:$HADOOP_HOME/share/hadoop/common/hadoop-common-2.2.0.jar:~/MapReduceTutorial/SalesCountry/*:$HADOOP_HOME/lib/*"
Step 3)
Compile Java files (these files are present in directory Final-MapReduceHandsOn). Its class files will be put in the package directory
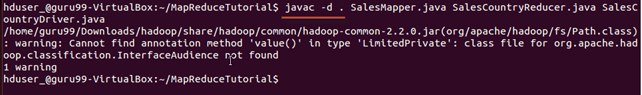
javac -d . SalesMapper.java SalesCountryReducer.java SalesCountryDriver.java
This warning can be safely ignored.
This compilation will create a directory in a current directory named with package name specified in the java source file (i.e. SalesCountry in our case) and put all compiled class files in it.
Step 4)
Create a new file Manifest.txt
sudo gedit Manifest.txt
add following lines to it,
Main-Class: SalesCountry.SalesCountryDriver
SalesCountry.SalesCountryDriver is the name of main class. Please note that you have to hit enter key at end of this line.
Step 5)
Create a Jar file
jar cfm ProductSalePerCountry.jar Manifest.txt SalesCountry/*.class
Check that the jar file is created
Step 6)
Start Hadoop
$HADOOP_HOME/sbin/start-dfs.sh
$HADOOP_HOME/sbin/start-yarn.sh
Step 7)
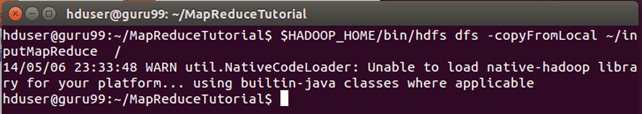
Copy the File SalesJan2009.csv into ~/inputMapReduce
Now Use below command to copy ~/inputMapReduce to HDFS.
$HADOOP_HOME/bin/hdfs dfs -copyFromLocal ~/inputMapReduce /
We can safely ignore this warning.
Verify whether a file is actually copied or not.
$HADOOP_HOME/bin/hdfs dfs -ls /inputMapReduce
Step 8)
Run MapReduce job
$HADOOP_HOME/bin/hadoop jar ProductSalePerCountry.jar /inputMapReduce /mapreduce_output_sales
This will create an output directory named mapreduce_output_sales on HDFS. Contents of this directory will be a file containing product sales per country.
Step 9)
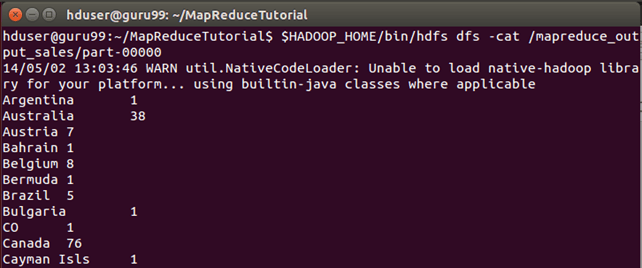
The result can be seen through command interface as,
$HADOOP_HOME/bin/hdfs dfs -cat /mapreduce_output_sales/part-00000
Results can also be seen via a web interface as-
Open r in a web browser.
Now select ‘Browse the filesystem’ and navigate to /mapreduce_output_sales
Open part-r-00000
Explanation of SalesMapper Class
In this section, we will understand the implementation of SalesMapper class.
1. We begin by specifying a name of package for our class. SalesCountry is a name of our package. Please note that output of compilation, SalesMapper.class will go into a directory named by this package name: SalesCountry.
Followed by this, we import library packages.
Below snapshot shows an implementation of SalesMapper class-
Sample Code Explanation:
1. SalesMapper Class Definition-
public class SalesMapper extends MapReduceBase implements Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
Every mapper class must be extended from MapReduceBase class and it must implement Mapper interface.
2. Defining ‘map’ function-
public void map(LongWritable key,
Text value,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException
The main part of Mapper class is a ‘map()’ method which accepts four arguments.
At every call to ‘map()’ method, a key-value pair (‘key’ and ‘value’ in this code) is passed.
‘map()’ method begins by splitting input text which is received as an argument. It uses the tokenizer to split these lines into words.
String valueString = value.toString();
String[] SingleCountryData = valueString.split(",");
Here, ‘,’ is used as a delimiter.
After this, a pair is formed using a record at 7th index of array ‘SingleCountryData’ and a value ‘1’.
output.collect(new Text(SingleCountryData[7]), one);
We are choosing record at 7th index because we need Country data and it is located at 7th index in array ‘SingleCountryData’.
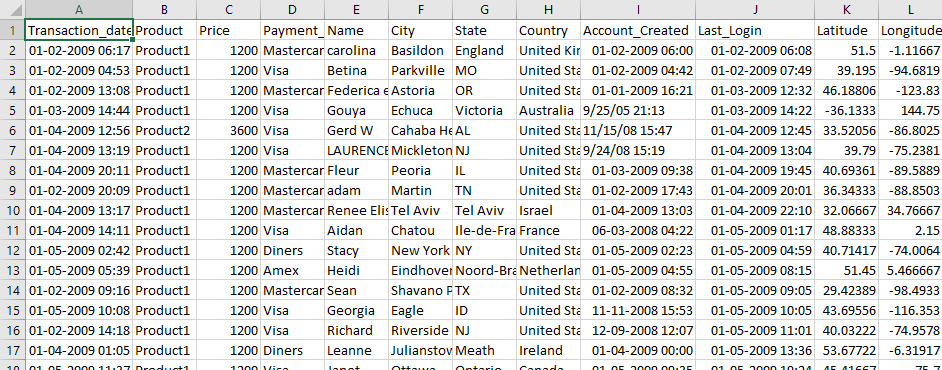
Please note that our input data is in the below format (where Country is at 7th index, with 0 as a starting index)-
Transaction_date,Product,Price,Payment_Type,Name,City,State,Country,Account_Created,Last_Login,Latitude,Longitude
An output of mapper is again a key-value pair which is outputted using ‘collect()’ method of ‘OutputCollector’.
Explanation of SalesCountryReducer Class
In this section, we will understand the implementation of SalesCountryReducer class.
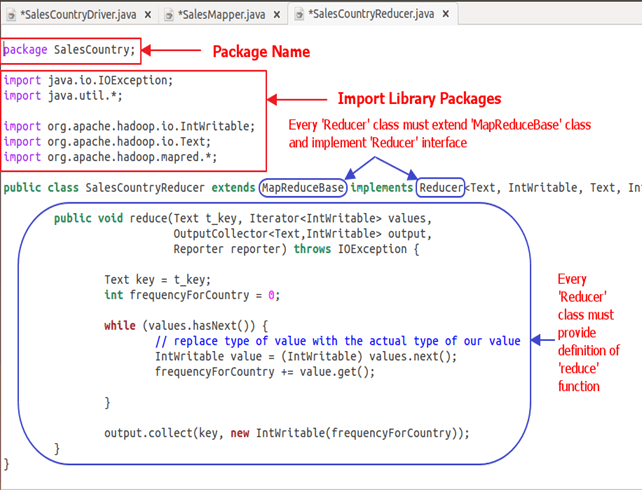
1. We begin by specifying a name of the package for our class. SalesCountry is a name of out package. Please note that output of compilation, SalesCountryReducer.class will go into a directory named by this package name: SalesCountry.
Followed by this, we import library packages.
Below snapshot shows an implementation of SalesCountryReducer class-
Code Explanation:
1. SalesCountryReducer Class Definition-
public class SalesCountryReducer extends MapReduceBase implements Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
Here, the first two data types, ‘Text’ and ‘IntWritable’ are data type of input key-value to the reducer.
Output of mapper is in the form of <CountryName1, 1>, <CountryName2, 1>. This output of mapper becomes input to the reducer. So, to align with its data type, Text and IntWritable are used as data type here.
The last two data types, ‘Text’ and ‘IntWritable’ are data type of output generated by reducer in the form of key-value pair.
Every reducer class must be extended from MapReduceBase class and it must implement Reducer interface.
2. Defining ‘reduce’ function-
public void reduce( Text t_key,
Iterator<IntWritable> values,
OutputCollector<Text,IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
An input to the reduce() method is a key with a list of multiple values.
For example, in our case, it will be-
<United Arab Emirates, 1>, <United Arab Emirates, 1>, <United Arab Emirates, 1>,<United Arab Emirates, 1>, <United Arab Emirates, 1>, <United Arab Emirates, 1>.
This is given to reducer as <United Arab Emirates, {1,1,1,1,1,1}>
So, to accept arguments of this form, first two data types are used, viz., Text and Iterator<IntWritable>. Text is a data type of key and Iterator<IntWritable> is a data type for list of values for that key.
The next argument is of type OutputCollector<Text,IntWritable> which collects the output of reducer phase.
reduce() method begins by copying key value and initializing frequency count to 0.
Text key = t_key;
int frequencyForCountry = 0;
Then, using ‘while’ loop, we iterate through the list of values associated with the key and calculate the final frequency by summing up all the values.
while (values.hasNext()) {
// replace type of value with the actual type of our value
IntWritable value = (IntWritable) values.next();
frequencyForCountry += value.get();
}
Now, we push the result to the output collector in the form of key and obtained frequency count.
Below code does this-
output.collect(key, new IntWritable(frequencyForCountry));
Explanation of SalesCountryDriver Class
In this section, we will understand the implementation of SalesCountryDriver class
1. We begin by specifying a name of package for our class. SalesCountry is a name of out package. Please note that output of compilation, SalesCountryDriver.class will go into directory named by this package name: SalesCountry.
Here is a line specifying package name followed by code to import library packages.
2. Define a driver class which will create a new client job, configuration object and advertise Mapper and Reducer classes.
The driver class is responsible for setting our MapReduce job to run in Hadoop. In this class, we specify job name, data type of input/output and names of mapper and reducer classes.
3. In below code snippet, we set input and output directories which are used to consume input dataset and produce output, respectively.
arg[0] and arg[1] are the command-line arguments passed with a command given in MapReduce hands-on, i.e.,
$HADOOP_HOME/bin/hadoop jar ProductSalePerCountry.jar /inputMapReduce /mapreduce_output_sales
4. Trigger our job
Below code start execution of MapReduce job-
try {
// Run the job
JobClient.runJob(job_conf);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}