Stemming and Lemmatization in Python NLTK with Examples
What is Stemming and Lemmatization in Python NLTK?
Stemming and Lemmatization in Python NLTK are text normalization techniques for Natural Language Processing. These techniques are widely used for text preprocessing. The difference between stemming and lemmatization is that stemming is faster as it cuts words without knowing the context, while lemmatization is slower as it knows the context of words before processing.
What is Stemming?
Stemming is a method of normalization of words in Natural Language Processing. It is a technique in which a set of words in a sentence are converted into a sequence to shorten its lookup. In this method, the words having the same meaning but have some variations according to the context or sentence are normalized.
In another word, there is one root word, but there are many variations of the same words. For example, the root word is “eat” and it’s variations are “eats, eating, eaten and like so”. In the same way, with the help of Stemming in Python, we can find the root word of any variations.
For example
He was riding. He was taking the ride.
In the above two sentences, the meaning is the same, i.e., riding activity in the past. A human can easily understand that both meanings are the same. But for machines, both sentences are different. Thus it became hard to convert it into the same data row. In case we do not provide the same data-set, then machine fails to predict. So it is necessary to differentiate the meaning of each word to prepare the dataset for machine learning. And here stemming is used to categorize the same type of data by getting its root word.
Let’s implement this with a Python program.NLTK has an algorithm named as “PorterStemmer”. This algorithm accepts the list of tokenized word and stems it into root word.
Program for understanding Stemming
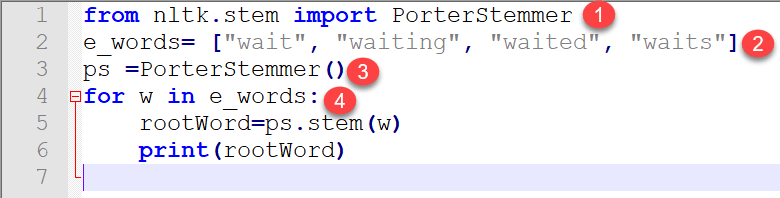
from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer
e_words= ["wait", "waiting", "waited", "waits"]
ps =PorterStemmer()
for w in e_words:
rootWord=ps.stem(w)
print(rootWord)
Output:
wait wait wait wait
Code Explanation:
- There is a stem module in NLTk which is imported. If ifyou import the complete module, then the program becomes heavy as it contains thousands of lines of codes. So from the entire stem module, we only imported “PorterStemmer.”
- We prepared a dummy list of variation data of the same word.
- An object is created which belongs to class nltk.stem.porter.PorterStemmer.
- Further, we passed it to PorterStemmer one by one using “for” loop. Finally, we got output root word of each word mentioned in the list.
From the above explanation, it can also be concluded that stemming is considered as an important preprocessing step because it removed redundancy in the data and variations in the same word. As a result, data is filtered which will help in better machine training.
Now we pass a complete sentence and check for its behavior as an output.
Program:
from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize, word_tokenize sentence="Hello Guru99, You have to build a very good site and I love visiting your site." words = word_tokenize(sentence) ps = PorterStemmer() for w in words: rootWord=ps.stem(w) print(rootWord)
Output:
hello guru99 , you have build a veri good site and I love visit your site
Code Explanation:
- Package PorterStemer is imported from module stem
- Packages for tokenization of sentence as well as words are imported
- A sentence is written which is to be tokenized in the next step.
- Word tokenization stemming lemmatization is implemented in this step.
- An object for PorterStemmer is created here.
- Loop is run and stemming of each word is done using the object created in the code line 5
Conclusion:
Stemming is a data-preprocessing module. The English language has many variations of a single word. These variations create ambiguity in machine learning training and prediction. To create a successful model, it’s vital to filter such words and convert to the same type of sequenced data using stemming. Also, this is an important technique to get row data from a set of sentence and removal of redundant data also known as normalization.
What is Lemmatization?
Lemmatization in NLTK is the algorithmic process of finding the lemma of a word depending on its meaning and context. Lemmatization usually refers to the morphological analysis of words, which aims to remove inflectional endings. It helps in returning the base or dictionary form of a word known as the lemma.
The NLTK Lemmatization method is based on WorldNet’s built-in morph function. Text preprocessing includes both stemming as well as lemmatization. Many people find the two terms confusing. Some treat these as the same, but there is a difference between stemming vs lemmatization. Lemmatization is preferred over the former because of the below reason.
Why is Lemmatization better than Stemming?
Stemming algorithm works by cutting the suffix from the word. In a broader sense cuts either the beginning or end of the word.
On the contrary, Lemmatization is a more powerful operation, and it takes into consideration morphological analysis of the words. It returns the lemma which is the base form of all its inflectional forms. In-depth linguistic knowledge is required to create dictionaries and look for the proper form of the word. Stemming is a general operation while lemmatization is an intelligent operation where the proper form will be looked in the dictionary. Hence, lemmatization helps in forming better machine learning features.
Code to distinguish between Lemmatization and Stemming
Stemming Code:
import nltk
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
porter_stemmer = PorterStemmer()
text = "studies studying cries cry"
tokenization = nltk.word_tokenize(text)
for w in tokenization:
print("Stemming for {} is {}".format(w,porter_stemmer.stem(w)))
Output::
Stemming for studies is studi Stemming for studying is studi Stemming for cries is cri Stemming for cry is cri
Lemmatization Code:
import nltk
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
wordnet_lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
text = "studies studying cries cry"
tokenization = nltk.word_tokenize(text)
for w in tokenization:
print("Lemma for {} is {}".format(w, wordnet_lemmatizer.lemmatize(w)))
Output:
Lemma for studies is study Lemma for studying is studying Lemma for cries is cry Lemma for cry is cry
Discussion of Output
If you look stemming for studies and studying, output is same (studi) but NLTK lemmatizer provides different lemma for both tokens study for studies and studying for studying. So when we need to make feature set to train machine, it would be great if lemmatization is preferred.
Use Case of Lemmatizer
Lemmatizer minimizes text ambiguity. Example words like bicycle or bicycles are converted to base word bicycle. Basically, it will convert all words having the same meaning but different representation to their base form. It reduces the word density in the given text and helps in preparing the accurate features for training machine. Cleaner the data, the more intelligent and accurate your machine learning model, will be. NLTK Lemmatizer will also saves memory as well as computational cost.
Real Time example showing use of Wordnet Lemmatization and POS Tagging in Python
from nltk.corpus import wordnet as wn from nltk.stem.wordnet import WordNetLemmatizer from nltk import word_tokenize, pos_tag from collections import defaultdict tag_map = defaultdict(lambda : wn.NOUN) tag_map['J'] = wn.ADJ tag_map['V'] = wn.VERB tag_map['R'] = wn.ADV text = "guru99 is a totally new kind of learning experience." tokens = word_tokenize(text) lemma_function = WordNetLemmatizer() for token, tag in pos_tag(tokens): lemma = lemma_function.lemmatize(token, tag_map[tag[0]]) print(token, "=>", lemma)
Code Explanation
- Firstly, the corpus reader wordnet is imported.
- WordNetLemmatizer is imported from wordnet.
- Word tokenize as well as parts of speech tag are imported from nltk.
- Default Dictionary is imported from collections.
- Dictionary is created where pos_tag (first letter) are the key values whose values are mapped with the value from wordnet dictionary. We have taken the only first letter as we will use it later in the loop.
- Text is written and is tokenized.
- Object lemma_function is created which will be used inside the loop.
- Loop is run and lemmatize will take two arguments one is token and other is a mapping of pos_tag with wordnet value.
Output:
guru99 => guru99 is => be totally => totally new => new kind => kind of => of learning => learn experience => experience . => .
Python Lemmatization has a close relation with wordnet dictionary, so it is essential to study this topic, so we keep this as the next topic.