How to Create (Write) Text File in Python
Python File Handling
In Python, there is no need for importing external library to read and write files. Python provides an inbuilt function for creating, writing, and reading files.
How to Open a Text File in Python
To open a file, you need to use the built-in open function. The Python file open function returns a file object that contains methods and attributes to perform various operations for opening files in Python.
Syntax of Python open file function
file_object = open("filename", "mode")
Here,
- filename: gives name of the file that the file object has opened.
- mode: attribute of a file object tells you which mode a file was opened in.
More details of these modes are explained below
How to Create a Text File in Python
With Write to file Python, you can create a .text files (guru99.txt) by using the code, we have demonstrated here:
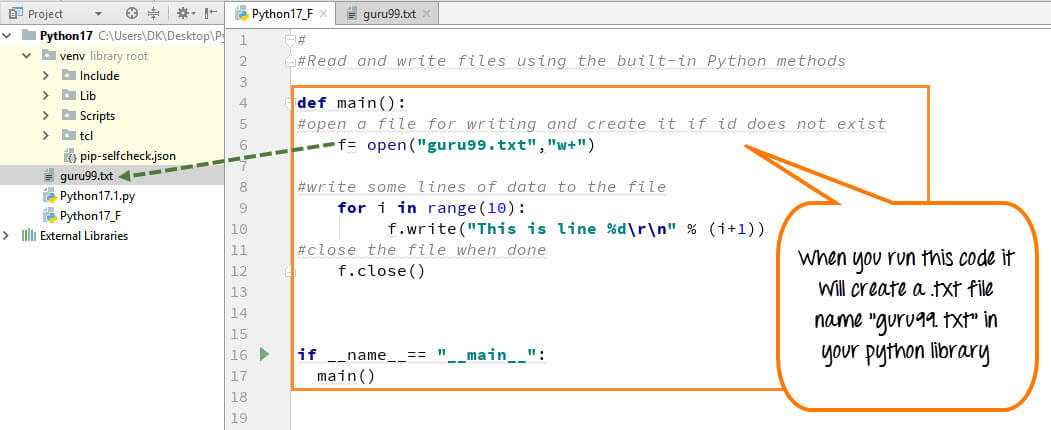
Step 1) Open the .txt file
f= open("guru99.txt","w+")
- We declared the variable “f” to open a file named guru99.txt. Open takes 2 arguments, the file that we want to open and a string that represents the kinds of permission or operation we want to do on the file
- Here, we used “w” letter in our argument, which indicates Python write to file and it will create file in Python if it does not exist in library
- Plus sign indicates both read and write for Python create file operation.
Step 2) Enter data into the file
for i in range(10):
f.write("This is line %d\r\n" % (i+1))
- We have a for loop that runs over a range of 10 numbers.
- Using the write function to enter data into the file.
- The output we want to iterate in the file is “this is line number”, which we declare with Python write file function and then percent d (displays integer)
- So basically we are putting in the line number that we are writing, then putting it in a carriage return and a new line character
Step 3) Close the file instance
f.close()
- This will close the instance of the file guru99.txt stored
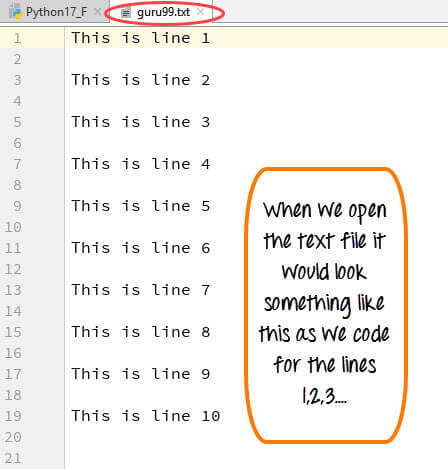
Here is the result after code execution for create text file in Python example:
When you click on your text file in our case “guru99.txt” it will look something like this
How to Append Text File in Python
You can also append/add a new text to the already existing file or a new file.
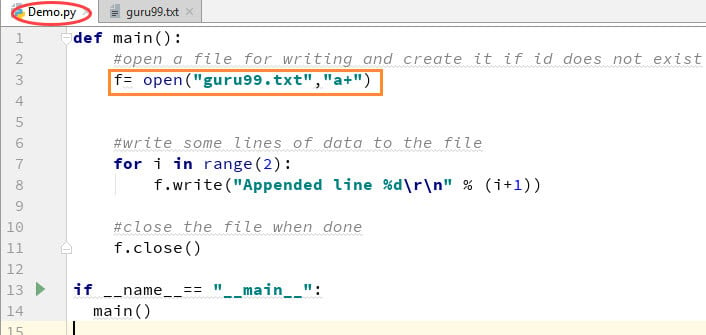
Step 1)
f=open("guru99.txt", "a+")
Once again if you could see a plus sign in the code, it indicates that it will create a new file if it does not exist. But in our case we already have the file, so we are not required to create a new file for Python append to file operation.
Step 2)
for i in range(2):
f.write("Appended line %d\r\n" % (i+1))
This will write data into the file in append mode.
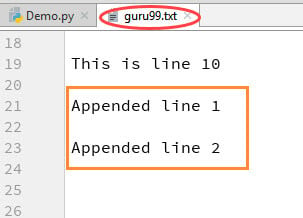
You can see the output in “guru99.txt” file. The output of the code is that earlier file is appended with new data by Python append to file operation.
How to Read Files in Python
You can read a file in Python by calling .txt file in a “read mode”(r).
Step 1) Open the file in Read mode
f=open("guru99.txt", "r")
Step 2) We use the mode function in the code to check that the file is in open mode. If yes, we proceed ahead
if f.mode == 'r':
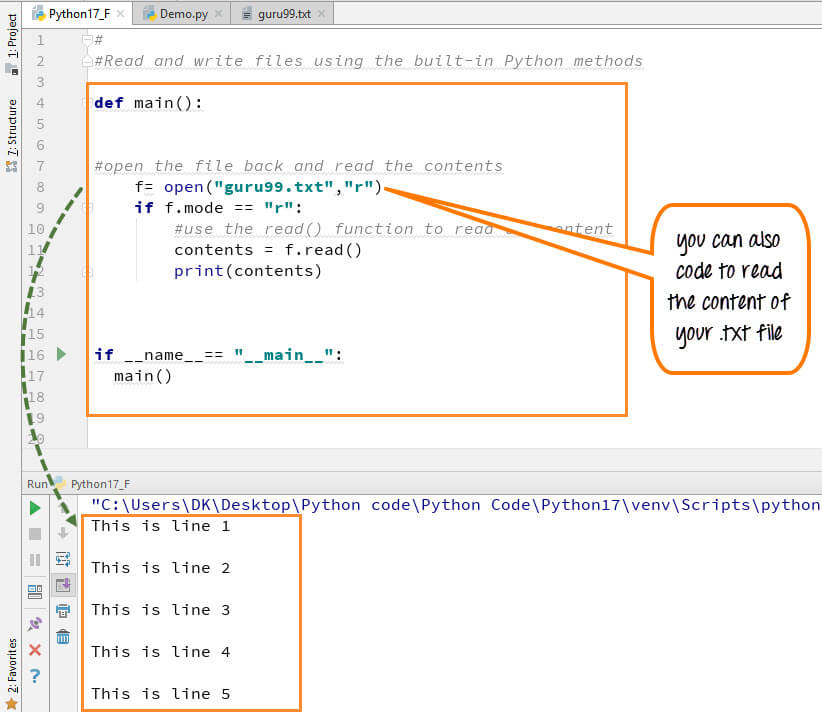
Step 3) Use f.read to read file data and store it in variable content for reading files in Python
contents =f.read()
Step 4) Print contents for Python read text file
Here is the output of the read file Python example:
How to Read a File line by line in Python
You can also read your .txt file line by line if your data is too big to read. readlines() code will segregate your data in easy to read mode.
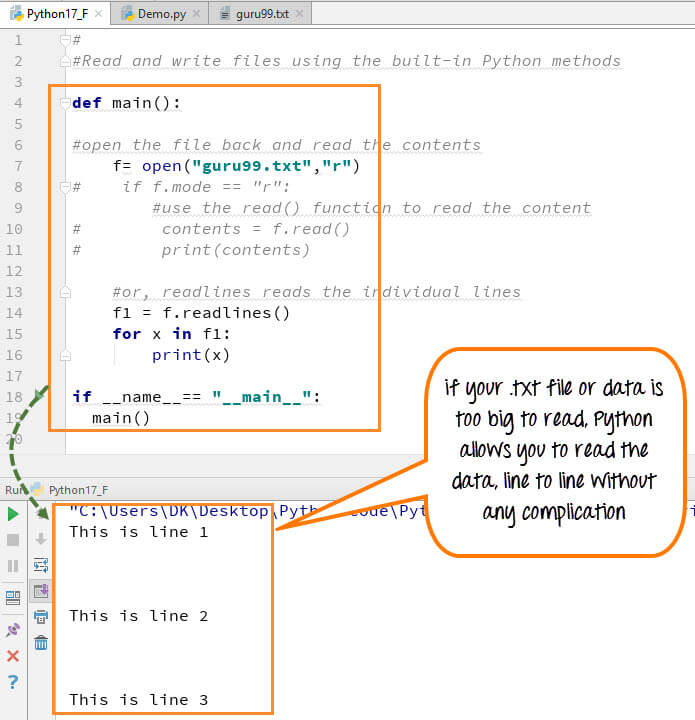
When you run the code (f1=f.readlines()) to read file line by line in Python, it will separate each line and present the file in a readable format. In our case the line is short and readable, the output will look similar to the read mode. But if there is a complex data file which is not readable, this piece of code could be useful.
File Modes in Python
Following are the various File Modes in Python:
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| ‘r’ | This is the default mode. It Opens file for reading. |
| ‘w’ | This Mode Opens file for writing. If file does not exist, it creates a new file. If file exists it truncates the file. |
| ‘x’ | Creates a new file. If file already exists, the operation fails. |
| ‘a’ | Open file in append mode. If file does not exist, it creates a new file. |
| ‘t’ | This is the default mode. It opens in text mode. |
| ‘b’ | This opens in binary mode. |
| ‘+’ | This will open a file for reading and writing (updating) |
Here is the complete code for Python print() to File Example
Python 2 Example
def main():
f= open("guru99.txt","w+")
#f=open("guru99.txt","a+")
for i in range(10):
f.write("This is line %d\r\n" % (i+1))
f.close()
#Open the file back and read the contents
#f=open("guru99.txt", "r")
# if f.mode == 'r':
# contents =f.read()
# print contents
#or, readlines reads the individual line into a list
#fl =f.readlines()
#for x in fl:
#print x
if __name__== "__main__":
main()
Python 3 Example
Below is another Python print() to File Example:
def main():
f= open("guru99.txt","w+")
#f=open("guru99.txt","a+")
for i in range(10):
f.write("This is line %d\r\n" % (i+1))
f.close()
#Open the file back and read the contents
#f=open("guru99.txt", "r")
#if f.mode == 'r':
# contents =f.read()
# print (contents)
#or, readlines reads the individual line into a list
#fl =f.readlines()
#for x in fl:
#print(x)
if __name__== "__main__":
main()
Summary
- Python allows you to read, write and delete files
- Use the function open(“filename”,”w+”) for Python create text file. The + tells the python interpreter for Python open text file with read and write permissions.
- To append data to an existing file or Python print to file operation, use the command open(“Filename”, “a“)
- Use the Python read from file function to read the ENTIRE contents of a file
- Use the readlines function to read the content of the file one by one.
