Python readline() Method with Examples
What is Python readline?
Python readline() is a file method that helps to read one complete line from the given file. It has a trailing newline (“\n”) at the end of the string returned.
You can also make use of the size parameter to get a specific length of the line. The size parameter is optional, and by default, the entire line will be returned.
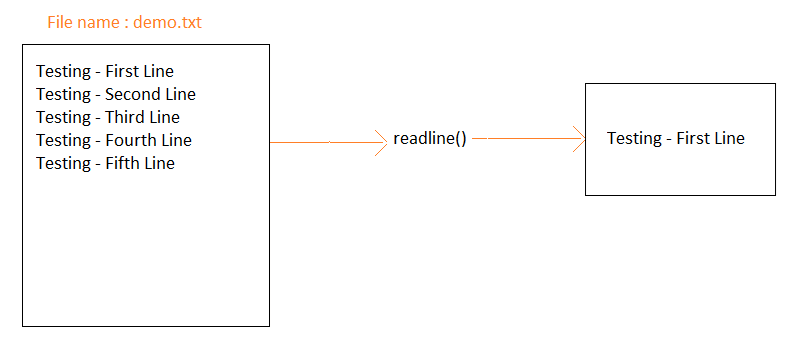
The flow of readline() is well understood in the screenshot shown below:
You have a file demo.txt, and when readline() is used, it returns the very first line from demo.txt.
Characteristic of Python readline()
Here, are important characteristics of Python read line:
- Python readline() method reads only one complete line from the file given.
- It appends a newline (“\n”) at the end of the line.
- If you open the file in normal read mode, readline() will return you the string.
- If you open the file in binary mode, readline() will return you binary object.
- You can give size as an argument to readline(), and it will get you the line as per the size given inclusive of the newline. By default, the size is 0, and it returns the entire line.
Syntax
file.readline(size)
Parameters
size: (optional) Here, you can specify the number, an integer value to readline(). It will get the string of that size. By default, the value of size is -1, and hence the entire string is returned.
ReturnValue
The readline() method returns the line from the file given.
Example: To read the first line using readline()
Here will understand how to read the line from the file given using the readline() method. We are going to make use of demo.txt file here to read the contents.
The file contents of demo.txt are as follows:
demo.txt
Testing - FirstLine Testing - SecondLine Testing - Third Line Testing - Fourth Line Testing - Fifth Line
The following are the steps to read a line from the file demo.txt.
Step 1) First, open the file using the file open() method, as shown below:
myfile = open("demo.txt", "r")
The open() method takes the first parameter as the name of the file, and the second parameter is the mode is while you want to open. Right now, we have used “r”, which means the file will open in read mode.
Step 2) Use the readline() method to read the line from the file demo.txt as shown below:
myline = myfile.readline()
Step 3) The line read is stored inside myline. Let us now print the line to see the details:
print(myline)
Step 4) Once the reading is done, close the file using close() method as shown below:
myfile.close()
The entire code is as follows:
myfile = open("demo.txt", "r")
myline = myfile.readline()
print(myline)
myfile.close()
Output:
Testing - FirstLine
Example: Using size argument in readline()
We have seen how to read the entire line from the file given. You can also make use of the size parameter to get only the required length of the line.
The given example has the size parameter given as 10. The first line will be fetched, and it will return the line with characters from 0 to 10.
We are going to make use of demo.txt file used earlier. Save the file demo.txt and use the location of the demo.txt inside open() function.
myfile = open("demo.txt", "r")
myline = myfile.readline(10)
print(myline)
myfile.close()
Output:
Testing -
Basic File IO in Python
The basic file IO in Python to open a file for reading or writing is the built-in open() function. The two important arguments that goes in open() function are the file path, which is a string, and the mode that specifies whether the file is meant for reading or writing. The mode argument is a string.
Syntax:
open("file path", "mode")
Following are the modes available that can be used with open() method:
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| R | This will open() the file in read mode. |
| W | Using w, you can write to the file. |
| a | Using a with open() will open the file in write mode, and the contents will be appended at the end. |
| rb | The rb mode will open the file for binary data reading. |
| wb | The wb mode will open the file for writing binary data. |
Since we need the file for reading, we are going to make use of read mode i.e. (r).
Read a File Line-by-Line in Python
The readline() method helps to read just one line at a time, and it returns the first line from the file given.
Here, we will make use of readline() to read all the lines from the file given. The file that will read is demo.txt. The contents of the file are:
Save the file demo.txt and use the location of demo.txt inside open() function.
Testing - FirstLine Testing - SecondLine Testing - Third Line Testing - Fourth Line Testing - Fifth Line
Using readline() inside while-loop will take care of reading all the lines present in the file demo.txt.
myfile = open("demo.txt", "r")
myline = myfile.readline()
while myline:
print(myline)
myline = myfile.readline()
myfile.close()
Output:
Testing - FirstLine Testing - SecondLine Testing - Third Line Testing - Fourth Line Testing - Fifth Line
How to read all lines in a file at once?
To read all the lines from a given file, you can make use of Python readlines() function. The specialty of Python readlines() function is to read all the contents from the given file and save the output in a list.
The readlines() function reads until the End of the file, making use of readline() function internally and returns a list with all the lines read from the file.
Here is a working example to read all the lines from the file using readlines().
The file that we are going to make use of to read is test.txt. The contents of the file test.txt are as follows:
test.txt: Save the file test.txt and use the location of test.txt inside open() function.
Line No 1 Line No 2 Line No 3 Line No 4 Line No 5
myfile = open("test.txt", "r")
mylist = myfile.readlines()
print(mylist)
myfile.close()
Output:
['Line No 1\n', 'Line No 2\n', 'Line No 3\n', 'Line No 4\n', 'Line No 5']
How to read a File line-by-line using for loop?
Following are the steps to read a line-by-line from a given file using for-loop:
Step 1) First, open the file using Python open() function in read mode.
Step 2) The open() function will return a file handler. Use the file handler inside your for-loop and read all the lines from the given file line-by-line.
Step 3) Once done, close the file handler using the close() function.
Here is a working example of using for-loop to read line-by-line from a given file. The file that we are going to use here is test.txt.
The contents of test.txt are as shown below. Save the file test.txt and use the location of test.txt inside an open() function.
Line No 1 Line No 2 Line No 3 Line No 4 Line No 5
myfile = open("test.txt", "r")
for line in myfile:
print(line)
myfile.close()
Output:
Line No 1 Line No 2 Line No 3 Line No 4 Line No 5
How to read a File line-by-line using a while loop?
You can make use of a while loop and read the contents from the given file line-by-line. To do that, first, open the file in read mode using open() function. The file handler returned from open(), use it inside while –loop to read the lines.
Python readline() function is used inside while-loop to read the lines. In the case of for-loop, the loop terminates when the end of the file is encountered. But the same is not the case with a while-loop, and you need to keep a check to see if the file is done reading. So once the readline() function returns an empty string, you can make use of the break statement to terminate from the while –loop.
Here is a working example to read a file line by line using a while-loop.
The file that we are going to make use is test.txt .Save the file test.txt and use the location of test.txt inside open() function.
Line No 1 Line No 2 Line No 3 Line No 4 Line No 5
myfile = open("test.txt", "r")
while myfile:
line = myfile.readline()
print(line)
if line == "":
break
myfile.close()
Output:
Line No 1 Line No 2 Line No 3 Line No 4 Line No 5
Summary
- Python readline() is a file method that helps to read one complete line from the given file. It has a trailing newline (“\n”) at the end of the string returned.
- You can also make use of the size parameter to get a specific length of the line. The size parameter is optional, and by default, the entire line will be returned.
- The readline() method helps to read just one line at a time, and it returns the first line from the file given. We will make use of readline() to read all the lines from the file given.
- To read all the lines from a given file, you can make use of Python readlines() function. The specialty of Python readlines() function is that it reads all the contents from the given file and saves the output in a list.
- The readlines() function reads till the End of the file making use of readline() function internally and returns a list that has all the lines read from the file.
- It is possible to read a file line by line using for loop. To do that, first, open the file using Python open() function in read mode. The open() function will return a file handler. Use the file handler inside your for-loop and read all the lines from the given file line by line. Once done,close the file handler using close() function.
- You can make use of a while loop and read the contents from the given file line by line. To do that, first, open the file in read mode using open() function. The file handler returned from open(), use it inside while –loop to read the lines. Python readline() function is used inside while-loop to read the lines.
