Python Matrix: Transpose, Multiplication, NumPy Arrays Examples
What is Python Matrix?
A Python matrix is a specialized two-dimensional rectangular array of data stored in rows and columns. The data in a matrix can be numbers, strings, expressions, symbols, etc. Matrix is one of the important data structures that can be used in mathematical and scientific calculations.
How do Python Matrices work?
The data inside the two-dimensional array in matrix format looks as follows:
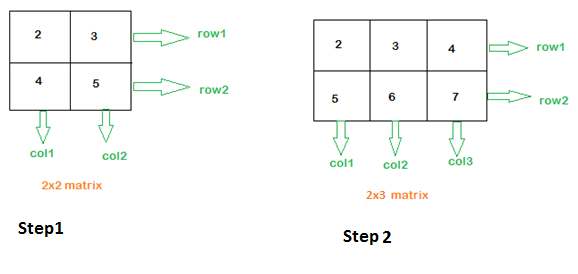
Step 1) It shows a 2×2 matrix. It has two rows and 2 columns. The data inside the matrix are numbers. The row1 has values 2,3, and row2 has values 4,5. The columns, i.e., col1, have values 2,4, and col2 has values 3,5.
Step 2) It shows a 2×3 matrix. It has two rows and three columns. The data inside the first row, i.e., row1, has values 2,3,4, and row2 has values 5,6,7. The columns col1 has values 2,5, col2 has values 3,6, and col3 has values 4,7.
So similarly, you can have your data stored inside the nxn matrix in Python. A lot of operations can be done on a matrix-like addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
Python does not have a straightforward way to implement a matrix data type.
The python matrix makes use of arrays, and the same can be implemented.
- Create a Python Matrix using the nested list data type
- Create Python Matrix using Arrays from Python Numpy package
Create Python Matrix using a nested list data type
In Python, the arrays are represented using the list data type. So now will make use of the list to create a python matrix.
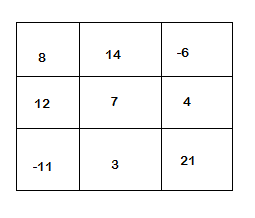
We will create a 3×3 matrix, as shown below:
- The matrix has 3 rows and 3 columns.
- The first row in a list format will be as follows: [8,14,-6]
- The second row in a list will be: [12,7,4]
- The third row in a list will be: [-11,3,21]
The matrix inside a list with all the rows and columns is as shown below:
List = [[Row1],
[Row2],
[Row3]
...
[RowN]]
So as per the matrix listed above the list type with matrix data is as follows:
M1 = [[8, 14, -6], [12,7,4], [-11,3,21]]
To read data inside Python Matrix using a list.
We will make use of the matrix defined above. The example will read the data, print the matrix, display the last element from each row.
Example: To print the matrix
M1 = [[8, 14, -6],
[12,7,4],
[-11,3,21]]
#To print the matrix
print(M1)
Output:
The Matrix M1 = [[8, 14, -6], [12, 7, 4], [-11, 3, 21]]
Example 2: To read the last element from each row
M1 = [[8, 14, -6],
[12,7,4],
[-11,3,21]]
matrix_length = len(M1)
#To read the last element from each row.
for i in range(matrix_length):
print(M1[i][-1])
Output:
-6 4 21
Example 3: To print the rows in the Matrix
M1 = [[8, 14, -6],
[12,7,4],
[-11,3,21]]
matrix_length = len(M1)
#To print the rows in the Matrix
for i in range(matrix_length):
print(M1[i])
Output:
[8, 14, -6] [12, 7, 4] [-11, 3, 21]
Adding Matrices Using Nested List
We can easily add two given matrices. The matrices here will be in the list form. Let us work on an example that will take care to add the given matrices.
Matrix 1:
M1 = [[8, 14, -6],
[12,7,4],
[-11,3,21]]
Matrix 2 :
M2 = [[3, 16, -6],
[9,7,-4],
[-1,3,13]]
Last will initialize a matrix that will store the result of M1 + M2.
Matrix 3 :
M3 = [[0,0,0],
[0,0,0],
[0,0,0]]
Example: Adding Matrices
To add, the matrices will make use of a for-loop that will loop through both the matrices given.
M1 = [[8, 14, -6],
[12,7,4],
[-11,3,21]]
M2 = [[3, 16, -6],
[9,7,-4],
[-1,3,13]]
M3 = [[0,0,0],
[0,0,0],
[0,0,0]]
matrix_length = len(M1)
#To Add M1 and M2 matrices
for i in range(len(M1)):
for k in range(len(M2)):
M3[i][k] = M1[i][k] + M2[i][k]
#To Print the matrix
print("The sum of Matrix M1 and M2 = ", M3)
Output:
The sum of Matrix M1 and M2 = [[11, 30, -12], [21, 14, 0], [-12, 6, 34]]
Multiplication of Matrices using Nested List
To multiply the matrices, we can use the for-loop on both the matrices as shown in the code below:
M1 = [[8, 14, -6],
[12,7,4],
[-11,3,21]]
M2 = [[3, 16, -6],
[9,7,-4],
[-1,3,13]]
M3 = [[0,0,0],
[0,0,0],
[0,0,0]]
matrix_length = len(M1)
#To Multiply M1 and M2 matrices
for i in range(len(M1)):
for k in range(len(M2)):
M3[i][k] = M1[i][k] * M2[i][k]
#To Print the matrix
print("The multiplication of Matrix M1 and M2 = ", M3)
Output:
The multiplication of Matrix M1 and M2 = [[24, 224, 36], [108, 49, -16], [11, 9, 273]]
Create Python Matrix using Arrays from Python Numpy package
The python library Numpy helps to deal with arrays. Numpy processes an array a little faster in comparison to the list.
To work with Numpy, you need to install it first. Follow the steps given below to install Numpy.
Step 1) The command to install Numpy is :
pip install NumPy
Step 2) To make use of Numpy in your code, you have to import it.
import NumPy
Step 3) You can also import Numpy using an alias, as shown below:
import NumPy as np
We are going to make use of array() method from Numpy to create a python matrix.
Example : Array in Numpy to create Python Matrix
import numpy as np M1 = np.array([[5, -10, 15], [3, -6, 9], [-4, 8, 12]]) print(M1)
Output:
[[ 5 -10 15] [ 3 -6 9] [ -4 8 12]]
Matrix Operation using Numpy.Array()
The matrix operation that can be done is addition, subtraction, multiplication, transpose, reading the rows, columns of a matrix, slicing the matrix, etc. In all the examples, we are going to make use of an array() method.
Matrix Addition
To perform addition on the matrix, we will create two matrices using numpy.array() and add them using the (+) operator.
Example:
import numpy as np M1 = np.array([[3, 6, 9], [5, -10, 15], [-7, 14, 21]]) M2 = np.array([[9, -18, 27], [11, 22, 33], [13, -26, 39]]) M3 = M1 + M2 print(M3)
Output:
[[ 12 -12 36] [ 16 12 48] [ 6 -12 60]]
Matrix Subtraction
To perform subtraction on the matrix, we will create two matrices using numpy.array() and subtract them using the (-) operator.
Example:
import numpy as np M1 = np.array([[3, 6, 9], [5, -10, 15], [-7, 14, 21]]) M2 = np.array([[9, -18, 27], [11, 22, 33], [13, -26, 39]]) M3 = M1 - M2 print(M3)
Output:
[[ -6 24 -18] [ -6 -32 -18] [-20 40 -18]]
Matrix Multiplication
First will create two matrices using numpy.arary(). To multiply them will, you can make use of numpy dot() method. Numpy.dot() is the dot product of matrix M1 and M2. Numpy.dot() handles the 2D arrays and perform matrix multiplications.
Example:
import numpy as np M1 = np.array([[3, 6], [5, -10]]) M2 = np.array([[9, -18], [11, 22]]) M3 = M1.dot(M2) print(M3)
Output:
[[ 93 78] [ -65 -310]]
Matrix Transpose
The transpose of a matrix is calculated, by changing the rows as columns and columns as rows. The transpose() function from Numpy can be used to calculate the transpose of a matrix.
Example:
import numpy as np M1 = np.array([[3, 6, 9], [5, -10, 15], [4,8,12]]) M2 = M1.transpose() print(M2)
Output:
[[ 3 5 4] [ 6 -10 8] [ 9 15 12]]
Slicing of a Matrix
Slicing will return you the elements from the matrix based on the start /end index given.
- The syntax for slicing is – [start:end]
- If the start index is not given, it is considered as 0. For example [:5], it means as [0:5].
- If the end is not passed, it will take as the length of the array.
- If the start/end has negative values, it will the slicing will be done from the end of the array.
Before we work on slicing on a matrix, let us first understand how to apply slice on a simple array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16]) print(arr[3:6]) # will print the elements from 3 to 5 print(arr[:5]) # will print the elements from 0 to 4 print(arr[2:]) # will print the elements from 2 to length of the array. print(arr[-5:-1]) # will print from the end i.e. -5 to -2 print(arr[:-1]) # will print from end i.e. 0 to -2
Output:
[ 8 10 12] [ 2 4 6 8 10] [ 6 8 10 12 14 16] [ 8 10 12 14] [ 2 4 6 8 10 12 14]
Now let us implement slicing on matrix . To perform slicing on a matrix
the syntax will be M1[row_start:row_end, col_start:col_end]
- The first start/end will be for the row, i.e to select the rows of the matrix.
- The second start/end will be for the column, i.e to select the columns of the matrix.
The matrix M1 tthat we are going to use is as follows:
M1 = np.array([[2, 4, 6, 8, 10],
[3, 6, 9, -12, -15],
[4, 8, 12, 16, -20],
[5, -10, 15, -20, 25]])
There are total 4 rows. The index starts from 0 to 3. The 0th row is the [2,4,6,8,10], 1st row is [3,6,9,-12,-15] followed by 2nd and 3rd.
The matrix M1 has 5 columns. The index starts from 0 to 4.The 0th column has values [2,3,4,5], 1st columns have values [4,6,8,-10] followed by 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th.
Here is an example showing how to get the rows and columns data from the matrix using slicing. In the example, we are printing the 1st and 2nd row, and for columns, we want the first, second, and third column. To get that output we have used: M1[1:3, 1:4]
Example:
import numpy as np
M1 = np.array([[2, 4, 6, 8, 10],
[3, 6, 9, -12, -15],
[4, 8, 12, 16, -20],
[5, -10, 15, -20, 25]])
print(M1[1:3, 1:4]) # For 1:3, it will give first and second row.
#The columns will be taken from first to third.
Output:
[[ 6 9 -12] [ 8 12 16]]
Example : To print all rows and third columns
import numpy as np
M1 = np.array([[2, 4, 6, 8, 10],
[3, 6, 9, -12, -15],
[4, 8, 12, 16, -20],
[5, -10, 15, -20, 25]])
print(M1[:,3]) # This will print all rows and the third column data.
Output:
[ 8 -12 16 -20]
Example: To print the first row and all columns
import numpy as np
M1 = np.array([[2, 4, 6, 8, 10],
[3, 6, 9, -12, -15],
[4, 8, 12, 16, -20],
[5, -10, 15, -20, 25]])
print(M1[:1,]) # This will print first row and all columns
Output:
[[ 2 4 6 8 10]]
Example: To print the first three rows and first 2 columns
import numpy as np
M1 = np.array([[2, 4, 6, 8, 10],
[3, 6, 9, -12, -15],
[4, 8, 12, 16, -20],
[5, -10, 15, -20, 25]])
print(M1[:3,:2])
Output:
[[2 4] [3 6] [4 8]]
Accessing NumPy Matrix
We have seen how slicing works. Taking that into consideration, we will how to get the rows and columns from the matrix.
To print the rows of the matrix
In the example will print the rows of the matrix.
Example:
import numpy as np M1 = np.array([[3, 6, 9], [5, -10, 15], [4,8,12]]) print(M1[0]) #first row print(M1[1]) # the second row print(M1[-1]) # -1 will print the last row
Output:
[3 6 9] [ 5 -10 15] [ 4 8 12]
To get the last row, you can make use of the index or -1. For example, the matrix has 3 rows,
so M1[0] will give you the first row,
M1[1] will give you second row
M1[2] or M1[-1] will give you the third row or last row.
To print the columns of the matrix
import numpy as np
M1 = np.array([[2, 4, 6, 8, 10],
[3, 6, 9, -12, -15],
[4, 8, 12, 16, -20],
[5, -10, 15, -20, 25]])
print(M1[:,0]) # Will print the first Column
print(M1[:,3]) # Will print the third Column
print(M1[:,-1]) # -1 will give you the last column
Output:
[2 3 4 5] [ 8 -12 16 -20] [ 10 -15 -20 25]
Summary
- A Python matrix is a specialized two-dimensional rectangular array of data stored in rows and columns. The data in a matrix can be numbers, strings, expressions, symbols, etc. Matrix is one of the important data structures that can be used in mathematical and scientific calculations.
- Python does not have a straightforward way to implement a matrix data type. Python matrix can be created using a nested list data type and by using the numpy library.
- The python library Numpy helps to deal with arrays. Numpy processes an array a little faster in comparison to the list.
- The matrix operation that can be done is addition, subtraction, multiplication, transpose, reading the rows, columns of a matrix, slicing the matrix, etc.
- To add two matrices, you can make use of numpy.array() and add them using the (+) operator.
- To multiply them will, you can make use of the numpy dot() method. Numpy.dot() is the dot product of matrix M1 and M2. Numpy.dot() handles the 2D arrays and perform matrix multiplications.
- The transpose of a matrix is calculated by changing the rows as columns and columns as rows. The transpose() function from Numpy can be used to calculate the transpose of a matrix.
- Slicing of a matrix will return you the elements based on the start /end index given.