Python RegEx: re.match(), re.search(), re.findall() with Example
What is Regular Expression in Python?
A Regular Expression (RE) in a programming language is a special text string used for describing a search pattern. It is extremely useful for extracting information from text such as code, files, log, spreadsheets or even documents.
While using the Python regular expression the first thing is to recognize is that everything is essentially a character, and we are writing patterns to match a specific sequence of characters also referred as string. Ascii or latin letters are those that are on your keyboards and Unicode is used to match the foreign text. It includes digits and punctuation and all special characters like $#@!%, etc.
For instance, a Python regular expression could tell a program to search for specific text from the string and then to print out the result accordingly. Expression can include
- Text matching
- Repetition
- Branching
- Pattern-composition etc.
Regular expression or RegEx in Python is denoted as RE (REs, regexes or regex pattern) are imported through re module. Python supports regular expression through libraries. RegEx in Python supports various things like Modifiers, Identifiers, and White space characters.
| Identifiers | Modifiers | White space characters | Escape required |
|---|---|---|---|
| \d= any number (a digit) | \d represents a digit.Ex: \d{1,5} it will declare digit between 1,5 like 424,444,545 etc. | \n = new line | . + * ? [] $ ^ () {} | \ |
| \D= anything but a number (a non-digit) | + = matches 1 or more | \s= space | |
| \s = space (tab,space,newline etc.) |
? = matches 0 or 1 | \t =tab | |
| \S= anything but a space | * = 0 or more | \e = escape | |
| \w = letters ( Match alphanumeric character, including “_”) | $ match end of a string | \r = carriage return | |
| \W =anything but letters ( Matches a non-alphanumeric character excluding “_”) | ^ match start of a string | \f= form feed | |
| . = anything but letters (periods) | | matches either or x/y | —————– | |
| \b = any character except for new line | [] = range or “variance” | —————- | |
| \. | {x} = this amount of preceding code | —————– |
Regular Expression(RE) Syntax
import re
- “re” module included with Python primarily used for string searching and manipulation
- Also used frequently for web page “Scraping” (extract large amount of data from websites)
We will begin the expression tutorial with this simple exercise by using the expressions (w+) and (^).
Example of w+ and ^ Expression
- “^”: This expression matches the start of a string
- “w+“: This expression matches the alphanumeric character in the string
Here we will see a Python RegEx Example of how we can use w+ and ^ expression in our code. We cover the function re.findall() in Python, later in this tutorial but for a while we simply focus on \w+ and \^ expression.
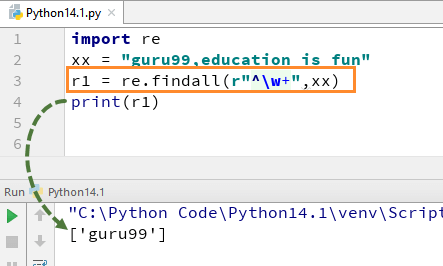
For example, for our string “guru99, education is fun” if we execute the code with w+ and^, it will give the output “guru99”.
import re xx = "guru99,education is fun" r1 = re.findall(r"^\w+",xx) print(r1)
Remember, if you remove +sign from the w+, the output will change, and it will only give the first character of the first letter, i.e., [g]
Example of \s expression in re.split function
- “s”: This expression is used for creating a space in the string
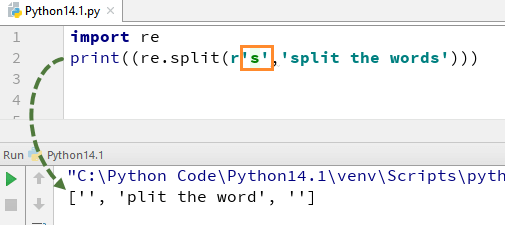
To understand how this RegEx in Python works, we begin with a simple Python RegEx Example of a split function. In the example, we have split each word using the “re.split” function and at the same time we have used expression \s that allows to parse each word in the string separately.
When you execute this code it will give you the output [‘we’, ‘are’, ‘splitting’, ‘the’, ‘words’].
Now, let see what happens if you remove “\” from s. There is no ‘s’ alphabet in the output, this is because we have removed ‘\’ from the string, and it evaluates “s” as a regular character and thus split the words wherever it finds “s” in the string.
Similarly, there are series of other Python regular expression that you can use in various ways in Python like \d,\D,$,\.,\b, etc.
Here is the complete code
import re xx = "guru99,education is fun" r1 = re.findall(r"^\w+", xx) print((re.split(r'\s','we are splitting the words'))) print((re.split(r's','split the words')))
Next, we will going to see the types of methods that are used with regular expression in Python.
Using regular expression methods
The “re” package provides several methods to actually perform queries on an input string. We will see the methods of re in Python:
- re.match()
- re.search()
- re.findall()
Note: Based on the regular expressions, Python offers two different primitive operations. The match method checks for a match only at the beginning of the string while search checks for a match anywhere in the string.
re.match()
re.match() function of re in Python will search the regular expression pattern and return the first occurrence. The Python RegEx Match method checks for a match only at the beginning of the string. So, if a match is found in the first line, it returns the match object. But if a match is found in some other line, the Python RegEx Match function returns null.
For example, consider the following code of Python re.match() function. The expression “w+” and “\W” will match the words starting with letter ‘g’ and thereafter, anything which is not started with ‘g’ is not identified. To check match for each element in the list or string, we run the forloop in this Python re.match() Example.
re.search(): Finding Pattern in Text
re.search() function will search the regular expression pattern and return the first occurrence. Unlike Python re.match(), it will check all lines of the input string. The Python re.search() function returns a match object when the pattern is found and “null” if the pattern is not found
How to use search()?
In order to use search() function, you need to import Python re module first and then execute the code. The Python re.search() function takes the “pattern” and “text” to scan from our main string
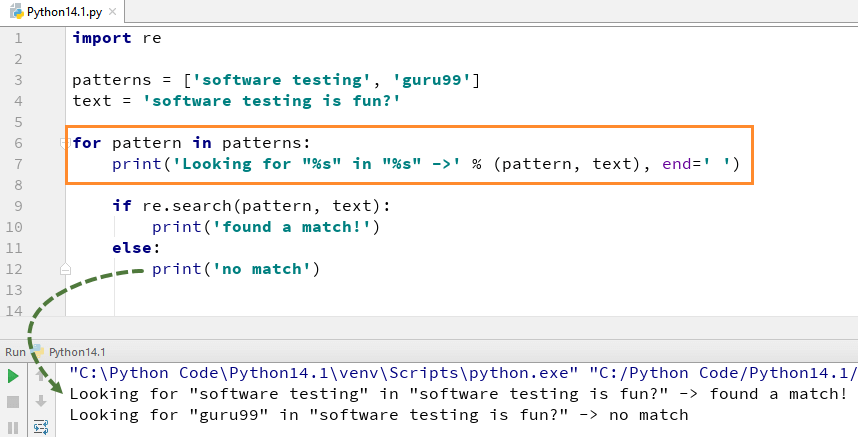
For example here we look for two literal strings “Software testing” “guru99”, in a text string “Software Testing is fun”. For “software testing” we found the match hence it returns the output of Python re.search() Example as “found a match”, while for word “guru99” we could not found in string hence it returns the output as “No match”.
re.findall()
findall() module is used to search for “all” occurrences that match a given pattern. In contrast, search() module will only return the first occurrence that matches the specified pattern. findall() will iterate over all the lines of the file and will return all non-overlapping matches of pattern in a single step.
How to Use re.findall() in Python?
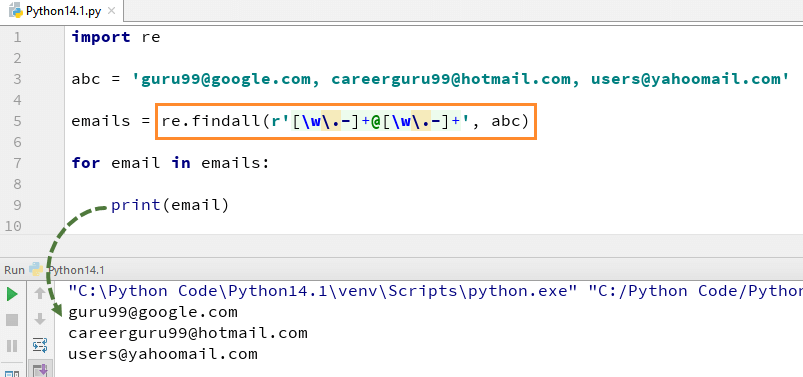
Here we have a list of e-mail addresses, and we want all the e-mail addresses to be fetched out from the list, we use the method re.findall() in Python. It will find all the e-mail addresses from the list.
Here is the complete code for Example of re.findall()
import re
list = ["guru99 get", "guru99 give", "guru Selenium"]
for element in list:
z = re.match("(g\w+)\W(g\w+)", element)
if z:
print((z.groups()))
patterns = ['software testing', 'guru99']
text = 'software testing is fun?'
for pattern in patterns:
print('Looking for "%s" in "%s" ->' % (pattern, text), end=' ')
if re.search(pattern, text):
print('found a match!')
else:
print('no match')
abc = 'guru99@google.com, careerguru99@hotmail.com, users@yahoomail.com'
emails = re.findall(r'[\w\.-]+@[\w\.-]+', abc)
for email in emails:
print(email)
Python Flags
Many Python Regex Methods and Regex functions take an optional argument called Flags. This flags can modify the meaning of the given Python Regex pattern. To understand these we will see one or two example of these Flags.
Various flags used in Python includes
| Syntax for Regex Flags | What does this flag do |
|---|---|
| [re.M] | Make begin/end consider each line |
| [re.I] | It ignores case |
| [re.S] | Make [ . ] |
| [re.U] | Make { \w,\W,\b,\B} follows Unicode rules |
| [re.L] | Make {\w,\W,\b,\B} follow locale |
| [re.X] | Allow comment in Regex |
Example of re.M or Multiline Flags
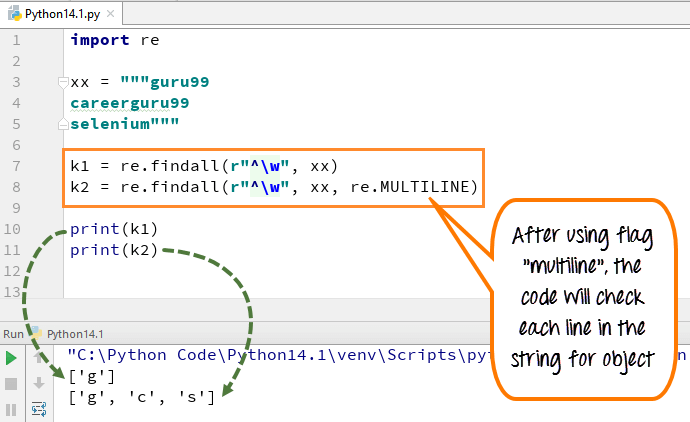
In multiline the pattern character [^] match the first character of the string and the beginning of each line (following immediately after the each newline). While expression small “w” is used to mark the space with characters. When you run the code the first variable “k1” only prints out the character ‘g’ for word guru99, while when you add multiline flag, it fetches out first characters of all the elements in the string.
Here is the code
import re xx = """guru99 careerguru99 selenium""" k1 = re.findall(r"^\w", xx) k2 = re.findall(r"^\w", xx, re.MULTILINE) print(k1) print(k2)
- We declared the variable xx for string ” guru99…. careerguru99….selenium”
- Run the code without using flags multiline, it gives the output only ‘g’ from the lines
- Run the code with flag “multiline”, when you print ‘k2’ it gives the output as ‘g’, ‘c’ and ‘s’
- So, the difference we can see after and before adding multi-lines in above example.
Likewise, you can also use other Python flags like re.U (Unicode), re.L (Follow locale), re.X (Allow Comment), etc.
Python 2 Example
Above codes are Python 3 examples, If you want to run in Python 2 please consider following code.
# Example of w+ and ^ Expression
import re
xx = "guru99,education is fun"
r1 = re.findall(r"^\w+",xx)
print r1
# Example of \s expression in re.split function
import re
xx = "guru99,education is fun"
r1 = re.findall(r"^\w+", xx)
print (re.split(r'\s','we are splitting the words'))
print (re.split(r's','split the words'))
# Using re.findall for text
import re
list = ["guru99 get", "guru99 give", "guru Selenium"]
for element in list:
z = re.match("(g\w+)\W(g\w+)", element)
if z:
print(z.groups())
patterns = ['software testing', 'guru99']
text = 'software testing is fun?'
for pattern in patterns:
print 'Looking for "%s" in "%s" ->' % (pattern, text),
if re.search(pattern, text):
print 'found a match!'
else:
print 'no match'
abc = 'guru99@google.com, careerguru99@hotmail.com, users@yahoomail.com'
emails = re.findall(r'[\w\.-]+@[\w\.-]+', abc)
for email in emails:
print email
# Example of re.M or Multiline Flags
import re
xx = """guru99
careerguru99
selenium"""
k1 = re.findall(r"^\w", xx)
k2 = re.findall(r"^\w", xx, re.MULTILINE)
print k1
print k2
Test your Python Knowledge
1. Which method is used to find all occurrences of a pattern in a string?
- re.search()
- re.match()
- re.findall()
- re.split()
2. What does the \d character class represent in regular expressions?
- Any digit (0-9)
- Any non-digit character
- Any whitespace character
- Any letter or number
3. Which function would you use to split a string based on spaces?
- re.split(r’\s’, string)
- re.findall(r’\w+’, string)
- re.match(r’\s+’, string)
- re.split(r’\w+’, string)
4. What is the main difference between re.match() and re.search()?
- re.match() looks for a pattern at the start of a string, while re.search() looks for a pattern anywhere in the string.
- re.match() returns all matches, while re.search() returns the first match.
- re.search() is faster than re.match().
- Both functions behave the same way.
Summary
A regular expression in a programming language is a special text string used for describing a search pattern. It includes digits and punctuation and all special characters like $#@!%, etc. Expression can include literal
- Text matching
- Repetition
- Branching
- Pattern-composition etc.
In Python, a regular expression is denoted as RE (REs, regexes or regex pattern) are embedded through Python re module.
- “re” module included with Python primarily used for string searching and manipulation
- Also used frequently for webpage “Scraping” (extract large amount of data from websites)
- Regular Expression Methods include re.match(),re.search()& re.findall()
- Other Python RegEx replace methods are sub() and subn() which are used to replace matching strings in re
- Python Flags Many Python Regex Methods and Regex functions take an optional argument called Flags
- This flags can modify the meaning of the given Regex pattern
- Various Python flags used in Regex Methods are re.M, re.I, re.S, etc.