How to Create EC2 Instance in AWS: Step by Step Tutorial
What is Amazon EC2 Instance?
An EC2 instance is nothing but a virtual server in Amazon Web services terminology. It stands for Elastic Compute Cloud. It is a web service where an AWS subscriber can request and provision a compute server in AWS cloud.
An on-demand EC2 instance is an offering from AWS where the subscriber/user can rent the virtual server per hour and use it to deploy his/her own applications.
The instance will be charged per hour with different rates based on the type of the instance chosen. AWS provides multiple instance types for the respective business needs of the user.
Thus, you can rent an instance based on your own CPU and memory requirements and use it as long as you want. You can terminate the instance when it’s no more used and save on costs. This is the most striking advantage of an on-demand instance- you can drastically save on your CAPEX.
Let us see in detail how to launch an on-demand EC2 instance in AWS Cloud.
Login and access to AWS services
Step 1) In this step,
- Login to your AWS account and go to the AWS Services tab at the top left corner.
- Here, you will see all of the AWS Services categorized as per their area viz. Compute, Storage, Database, etc. For creating an EC2 instance, we have to choose Computeà EC2 as in the next step.
- Open all the services and click on EC2 under Compute services. This will launch the dashboard of EC2.
Here is the EC2 dashboard. Here you will get all the information in gist about the AWS EC2 resources running.
Step 2) On the top right corner of the EC2 dashboard, choose the AWS Region in which you want to provision the EC2 server.
Here we are selecting N. Virginia. AWS provides 10 Regions all over the globe.
Step 3) In this step
- Once your desired Region is selected, come back to the EC2 Dashboard.
- Click on ‘Launch Instance’ button in the section of Create Instance (as shown below).
- Instance creation wizard page will open as soon as you click ‘Launch Instance’.
Choose AMI
Step 1) In this step we will do,
- You will be asked to choose an AMI of your choice. (An AMI is an Amazon Machine Image. It is a template basically of an Operating System platform which you can use as a base to create your instance). Once you launch an EC2 instance from your preferred AMI, the instance will automatically be booted with the desired OS. (We will see more about AMIs in the coming part of the tutorial).
- Here we are choosing the default Amazon Linux (64 bit) AMI.
Choose EC2 Instance Types
Step 1) In the next step, you have to choose the type of instance you require based on your business needs.
- We will choose t2.micro instance type, which is a 1vCPU and 1GB memory server offered by AWS.
- Click on “Configure Instance Details” for further configurations
- In the next step of the wizard, enter details like no. of instances you want to launch at a time.
- Here we are launching one instance.
Configure Instance
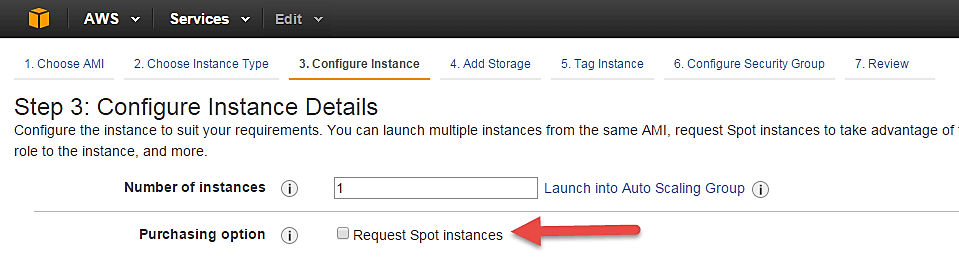
Step 1) No. of instances- you can provision up to 20 instances at a time. Here we are launching one instance.
Step 2) Under Purchasing Options, keep the option of ‘Request Spot Instances’ unchecked as of now. (This is done when we wish to launch Spot instances instead of on-demand ones. We will come back to Spot instances in the later part of the tutorial).
Step 3) Next, we have to configure some basic networking details for our EC2 server.
- You have to decide here, in which VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) you want to launch your instance and under which subnets inside your VPC. It is better to determine and plan this prior to launching the instance. Your AWS architecture set-up should include IP ranges for your subnets etc. pre-planned for better management. (We will see how to create a new VPC in Networking section of the tutorial.
- Subnetting should also be pre-planned. E.g.: If it’s a web server you should place it in the public subnet and if it’s a DB server, you should place it in a private subnet all inside your VPC.
Below,
- Network section will give a list of VPCs available in our platform.
- Select an already existing VPC
- You can also create a new VPC
Here I have selected an already existing VPC where I want to launch my instance.
Step 4) In this step,
- A VPC consists of subnets, which are IP ranges that are separated for restricting access.
- Below,
- Under Subnets, you can choose the subnet where you want to place your instance.
- I have chosen an already existing public subnet.
- You can also create a new subnet in this step.
- Once your instance is launched in a public subnet, AWS will assign a dynamic public IP to it from their pool of IPs.
Step 5) In this step,
- You can choose if you want AWS to assign it an IP automatically, or you want to do it manually later. You can enable/ disable ‘Auto assign Public IP’ feature here likewise.
- Here we are going to assign this instance a static IP called as EIP (Elastic IP) later. So we keep this feature disabled as of now.
Step 6) In this step,
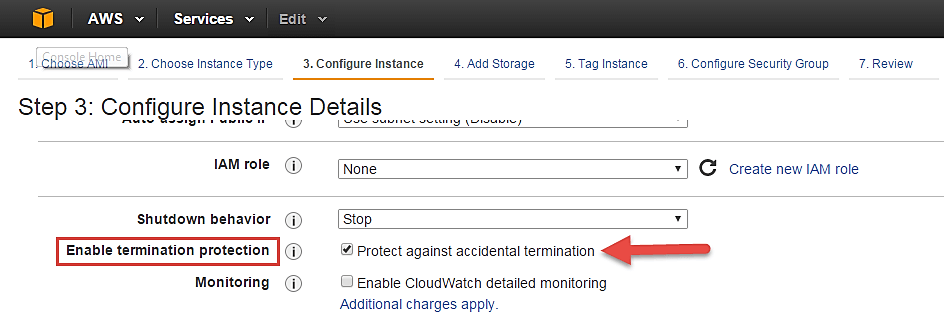
- In the following step, keep the option of IAM role ‘None’ as of now. We will visit the topic of IAM role in detail in IAM services.
Step 7) In this step, you have to do following things
- Shutdown Behavior – when you accidently shut down your instance, you surely don’t want it to be deleted but stopped.
- Here we are defining my shutdown behavior as Stop.
Step 8) In this step,
- In case, you have accidently terminated your instance, AWS has a layer of security mechanism. It will not delete your instance if you have enabled accidental termination protection.
- Here we are checking the option for further protecting our instance from accidental termination.
Step 9) In this step,
- Under Monitoring- you can enable Detailed Monitoring if your instance is a business critical instance. Here we have kept the option unchecked. AWS will always provide Basic monitoring on your instance free of cost. We will visit the topic of monitoring in AWS Cloud Watch part of the tutorial.
- Under Tenancy- select the option if shared tenancy. If your application is a highly secure application, then you should go for dedicated capacity. AWS provides both options.
Step 10) In this step,
- Click on ‘Add Storage’ to add data volumes to your instance in next step.
Add Storage
Step 1) In this step we do following things,
- In the Add Storage step, you’ll see that the instance has been automatically provisioned a General Purpose SSD root volume of 8GB. ( Maximum volume size we can give to a General Purpose volume is 16GB)
- You can change your volume size, add new volumes, change the volume type, etc.
- AWS provides 3 types of EBS volumes- Magnetic, General Purpose SSD, Provisioned IOPs. You can choose a volume type based on your application’s IOPs needs.
Tag Instance
Step 1) In this step
- you can tag your instance with a key-value pair. This gives visibility to the AWS account administrator when there are lot number of instances.
- The instances should be tagged based on their department, environment like Dev/SIT/Prod. Etc. this gives a clear view of the costing on the instances under one common tag.
- Here we have tagged the instance as a Dev_Web server 01
- Go to configure Security Groups later
Configure Security Groups
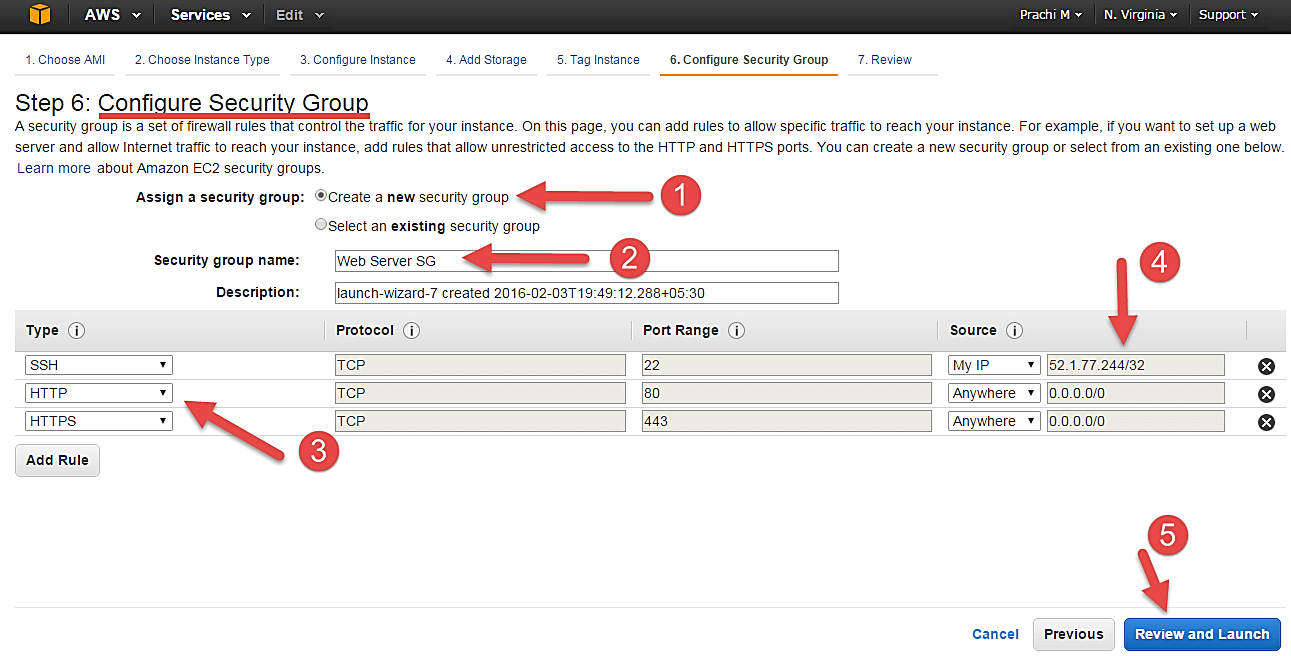
Step 1) In this next step of configuring Security Groups, you can restrict traffic on your instance ports. This is an added firewall mechanism provided by AWS apart from your instance’s OS firewall.
You can define open ports and IPs.
- Since our server is a webserver=, we will do following things
- Creating a new Security Group
- Naming our SG for easier reference
- Defining protocols which we want enabled on my instance
- Assigning IPs which are allowed to access our instance on the said protocols
- Once, the firewall rules are set- Review and launch
Review Instances
Step 1) In this step, we will review all our choices and parameters and go ahead to launch our instance.
Step 2) In the next step you will be asked to create a key pair to login to you an instance. A key pair is a set of public-private keys.
AWS stores the private key in the instance, and you are asked to download the private key. Make sure you download the key and keep it safe and secured; if it is lost you cannot download it again.
- Create a new key pair
- Give a name to your key
- Download and save it in your secured folder
- When you download your key, you can open and have a look at your RSA private key.
Step 3) Once you are done downloading and saving your key, launch your instance.
- You can see the launch status meanwhile.
- You can also see the launch log.
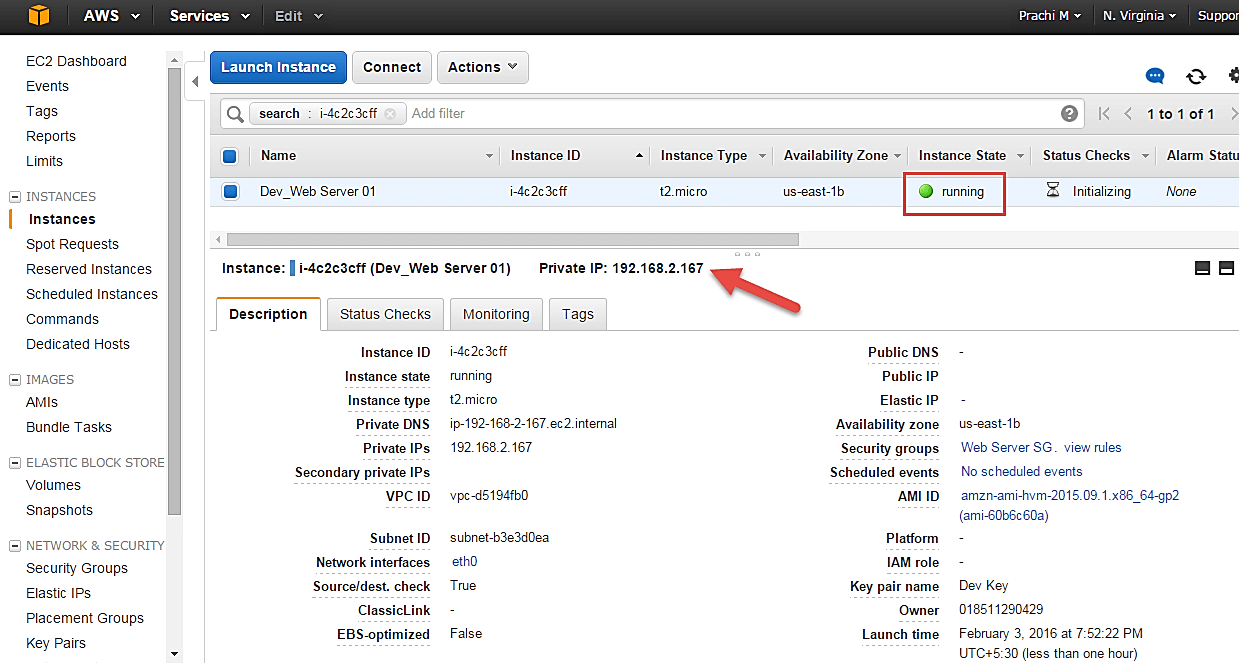
- Click on the ‘Instances’ option on the left pane where you can see the status of the instance as ‘Pending’ for a brief while.
- Once your instance is up and running, you can see its status as ‘Running’ now.
- Note that the instance has received a Private IP from the pool of AWS.
Create a EIP and connect to your instance
An EIP is a static public IP provided by AWS. It stands for Elastic IP. Normally when you create an instance, it will receive a public IP from the AWS’s pool automatically. If you stop/reboot your instance, this public IP will change- it’dynamic. In order for your application to have a static IP from where you can connect via public networks, you can use an EIP.
Step 1) On the left pane of EC2 Dashboard, you can go to ‘Elastic IPs’ as shown below.
Step 2) Allocate a new Elastic IP Address.
Step 3) Allocate this IP to be used in a VPC scope.
- Your request will succeed if you don’t have 5 or more than 5 EIPs already in your account.
Step 4) Now assign this IP to your instance.
- Select the said IP
- Click on Actions -> Associate Address
Step 5) In the next page,
- Search for your instance and
- Associate the IP to it.
Step 6) Come back to your instances screen, you’ll see that your instance has received your EIP.
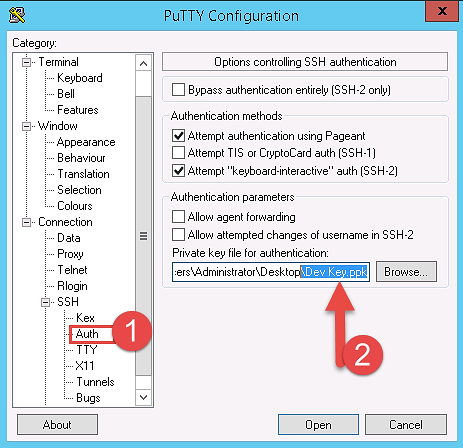
Step 7) Now open putty from your programs list and add your same EIP in there as below.
Step 8) In this step,
Add your private key in putty for secure connection
- Go to Auth
- Add your private key in .ppk (putty private key) format. You will need to convert pem file from AWS to ppk using puttygen
Once done click on “Open” button
- Once you connect, you will successfully see the Linux prompt.
- Please note that the machine you are connecting from should be enabled on the instance Security Group for SSH (like in the steps above).
Once you become familiar with the above steps for launching the instance, it becomes a matter of 2 minutes to launch the same!
You can now use your on-demand EC2 server for your applications.
What is Spot Instance?
A spot Instance is an offering from AWS; it allows an AWS business subscriber to bid on unused AWS compute capacity. The hourly price for a Spot instance is decided by AWS, and it fluctuates depending on the supply and demand for Spot instances.
Your Spot instance runs whenever your bid exceeds the current market price. The price of a spot instance varies based on the instance type and the Availability Zone in which the instance can be provisioned.
When your bid price exceeds the market spot price of the instance called as the ‘spot price,’ your instance stays running. When the spot price overshoots the bid price, AWS will terminate your instance automatically. Therefore, it is necessary to plan the spot instances in your application architecture carefully.
Create a Spot Request
In order to launch a spot instance, you have to first create a Spot Request.
Follow the steps below to create a Spot Request.
- On the EC2 Dashboard select ‘Spot Requests’ from the left pane under Instances.
- Click on the button ‘Request Spot Instances” as shown below.
Spot instance launch wizard will open up. You can now go ahead with selecting the parameters and the instance configuration.
Find Instance Types
The first step for spot instance is to “Find instance types.”
Step 1) Select an AMI- an AMI is a template consisting of the OS platform and software to be installed in the instance. Select your desired AMI from the existing list. We are selecting Amazon Linux AMI for this tutorial.
Step 2) Capacity Unit- a Capacity Unit is your application requirement. You may decide to launch an instance based on the instance type, vCPU or custom configuration like your choice of vCPU/memory/storage requirements. Here we are selecting an Instance.
If you wish to customize the capacity, you can add your choice of
- vCPU,
- Memory and
- Instance storage as below.
Step 3) Target Capacity depicts how many spot instances you wish to maintain in your request. Here we are selecting one.
Step 4) Bid Price – this is the maximum price we are ready to pay for the instance. We are going to set a particular price per instance/hour. This is the simplest to calculate based on our business requirement. We will see ahead how we should determine the bid price so that our bid price always remains high and doesn’t exceed the spot price so that our instance keeps running.
just below the bid price you can see a button of Pricing History. Click on that as shown below.
Here in Pricing History, we can see a graph depicting instance pricing trends with historical data. You can select the parameters and get an idea of the pricing of our desired instance over a period of time.
- Select the product. We have selected our Linux AMI.
- Select the instance type. We have selected m3.medium.
- Note the average prices for over a day here.
Thus, from the chart below, we can see that the instance type that we are planning to provision lies in the pricing range of $0.01xx, and it seems that Availability Zone ‘us-east 1a’ has the lowest price.
cont. to step 4.
So let’s come back to our step of quoting a bid price.
For the sake of maintaining our instance always available and if it falls within our budget, we can quote a higher bid price. Here we have quoted a slightly higher price of $0.05.
You can see some trends in the wizard itself.
- Note the instance types section
- Select the instance type that we are planning to provision
- Note the price that we are planning to bid. % of on-demand shows us that our quoted price is 75% of the on-demand price for the same instance type. This means we are saving 25% per hour as compared to an on-demand instance. You can further lower the price and save costs drastically.
Step 5) Once we are done looking at the trends and quoting our bid price, click on next.
Configure the Spot instance
Our next step is to configure the instance, in this step of the wizard, we’ll configure instance parameters like VPC, subnets, etc.
Let’s take a look.
Step 1) Allocation Strategy – it determines how your spot request is fulfilled from the AWS’s spot pools. There are two types of strategies:
- Diversified – here, spot instances are balanced across all the spot pools
- Lowest price – here, spot instances are launched from the pool which has lowest price offers
For this tutorial, we’ll select Lowest Price as our allocation strategy.
Step 2) Select the VPC- we’ll select from the list of available VPCs that we have created earlier. We can also create a new VPC in this step.
Step 3) Next we’ll select the security group for the instance. We can select an already existing SG or create a new one.
Step 4) Availability Zone- we’ll select the AZ where we want to place our instance based on our application architecture. We are selecting AZ- us-east-1a.
Step 5) Subnets- we are going to select the subnet from our list of already available list.
Step 6) Public IP- we’ll choose to assign the instance a public IP as soon as it launches. In this step, you can choose if you want AWS to assign it an IP automatically, or you want to do it manually later. You can enable/ disable ‘Auto assign Public IP’ feature here likewise.
Step 7) Key pair- A key pair is a set of public-private keys.
AWS stores the private key in the instance, and you are asked to download the private key. Make sure you download the key and keep it safe and secured; if it is lost you cannot download it again.
After selecting public IP, here we are selecting a key which we already have created in our last tutorial.
Review your Spot instance
Once we are done configuring our spot instance request in the 2 steps earlier in our wizard, we’ll take a look at the overall configuration.
- We can also download a JSON file with all the configurations. Below is our JSON file.
After we are done reviewing, we can proceed with the launching by clicking the Launch button as shown below.
Once we select Launch, we can see a notification about the request getting created.
The spot request creation wizard will close, and the page will automatically direct back to the EC2 Dashboard.
You can see as shown below that the State of our request is ‘open’ which means that it is getting evaluated from the AWS’s side. AWS EC2 will check if the required instance is available in its spot pool.
After a couple of minutes, you can see that the state is changed to ‘active’, and now our spot request is successfully fulfilled. You can note the configuration parameters below.
Summary
Thus, we saw in detail how to create an on-demand EC2 instance in this tutorial. Because it is an on-demand server, you can keep it running when in use and ‘Stop’ it when it’s unused to save on your costs.
You can provision a Linux or Windows EC2 instance or from any of the available AMIs in AWS Marketplace based on your choice of OS platform.
If your application is in production and you have to use it for years to come, you should consider provisioning a reserved instance to drastically save on your CAPEX.
Here, we saw how to create a Spot Instance request successfully by determining our bid price.
Spot instances are a great way to save on costs for instances which are not application critical. A common example would be to create a fleet of spot instances for a task such as image processing or video encoding. In such cases, you can keep a cluster of instances under a load balancer.
If the bid price exceeds the spot price and your instance is terminated from AWS’s side, you can have other instances doing the processing job for you. You can leverage Auto scaling for this scenario. Avoid using Spot instances for business critical applications like databases etc.