What is Private Cloud? Examples
What is Private Cloud?
A private cloud is a computing model that offers a secure and dedicated environment for a single business. Private clouds can be hosted within an organization’s data center, at a third-party co-location facility, or by a private cloud provider. This cloud computing model is used exclusively by a particular organization and never shared with other organizations.
Private Cloud provides high data security and privacy. It also prevents third parties from accessing operational and sensitive data. When compared to public clouds, they are generally more expensive. Private Cloud is also known as an internal cloud or corporate cloud.
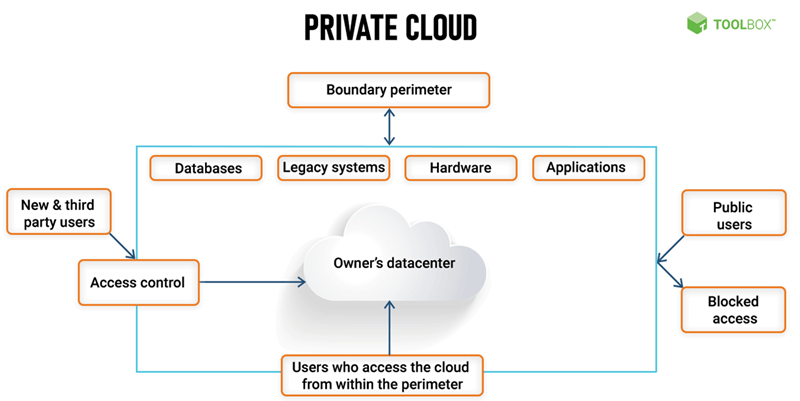
Private Cloud Architecture
Apart from single-tenant design, the private Cloud is based on the same technologies as other cloud computing technologies.
Private cloud architecture aggregates resources in a data center into a single pool of resources. Organizations can increase the efficiency and utilization of their private cloud infrastructure by virtualizing the hardware components. Private cloud solutions enable businesses to architect data centers using software-defined networking (SDN) and virtual machines (VMs).
In this cloud computing model, multiple server locations can be connected to the network, or space can be leased in co-location facilities abroad.
Characteristics of Private Cloud
Here are some important characteristics of the Private Cloud:
- Employees can securely access data around the globe using a device of their choice.
- High availability and redundancy are inherently part of the architecture.
- Gives you better and more direct control over your data.
- Cloud computing is a transformational catalyst for business.
- Offers flexibility in serving up applications.
- Built-in resource usage and audit logging tools.
Types of Private Cloud
There are various ways in which private clouds can be hosted and managed. Each implementation offers its unique functionality and advantages. Here are three types of Private Clouds:
- Virtual Private Cloud: A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a cloud model that offers the benefits of a private cloud using public cloud resources. VPC uses isolated environments within public clouds. VPC allows organizations to run their workloads independently from other users. Virtual logic ensures that users’ computing resources are private even though other organizations share the server.
- Hosted Private Cloud: In this type, the Cloud Service Vendor offers servers used exclusively by a single organization. They manage the network and hardware/software updates for you. The vendors offer a support team, high-demand scalability options, and a user-friendly dashboard to assist in server management.
- Managed: Managed private clouds are private clouds that do not share their infrastructure. It is called a dedicated or single-tenant cloud. Usually, the organization owns the data center and not the cloud provider. Mostly third-party vendor manages this kind of private Cloud. The vendor offers support, upgrades, maintenance, and remote management services in this private Cloud.
Key difference between Public and Private cloud
Here are some important differences between Public and Private Clouds:
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|
| Multiple Clients | Single Client |
| Accessed over the general Internet. | Access is provided with specific boundaries, like firewall settings and VPN, and only employees of the organization can access it. |
| Hosted at Providers Location | Hosted at the Provider or organization’s location. |
| Low Cost | High Security |
Private Cloud Service Providers Example
Here are some popular Private cloud service providers:
AWS: AWS Virtual Private Cloud services allow you to manage your virtual networking environment, including resource placement, connectivity, and security. It enables you to secure and monitor your connection, screen traffic, and restrict instance aces inside your virtual network.
HPE: It provides Software-drive infrastructure with leading partner cloud stacks that enable you to deliver IT services and solutions. They provide the best private cloud solutions through IT automation, AI-driven operations, and compliance with leading cloud stacks.
Google Private Cloud: Google Private Cloud can auto-configure your virtual topology, prefix ranges for your subnets, and network policies, or you may configure them yourself. Communication between organizations can be configured privately without bandwidth bottlenecks or single points of failure. You can configure a VPC network to be shared across several projects in your organization.
Azure: A private cloud comprises only computing resources for business or organization. The private Cloud can be physically at your company’s on-site data center, or a third-party service provider can host it. Azure Private Cloud offers hybrid cloud solutions. It protects hybrid cloud workloads against threats with streamlined security.
Dell: Dell’s Microsoft Hyper-VCloud Fast Track program is a comprehensive approach to cloud computing. This private cloud solution combines Microsoft software, consolidated guidance, and validated configurations with Dell hardware technology, including computing power, network, storage architectures, and value-added software components.
Best Practices of Private Cloud
Here are the best practices of the Private Cloud Model:
- Select a hyper-scale private cloud provider that offers managed services
- Establish robust policies for backup and disaster recovery
- Private cloud storage should be interoperable with other cloud computing environments
- Try to bring uniformity into your application and hardware stack
- Leverage PaaS to speed up your cloud application roadmap
Challenges of Private Cloud
Here are some challenges that you would like to face while implementing a Private Cloud:
- Up-front costs: Private clouds hosted on-site require substantial capital at an initial level to bring value to the organization. The hardware demands to run a private cloud can be costly and require an expert cloud engineer to set up, manage and maintain.
- Capacity utilization: An organization cannot always maximize capacity utilization under this cloud computing model. It will help you if you realize that an under-used cloud deployment may cost massive damage to your business.
- Scalability: Sometimes, the business needs additional computing power from the private Cloud. So, it takes extra effort and cost to scale up the private Cloud’s available resources. It takes longer to scale a virtual machine or request additional resources from a public cloud provider.
Other Challenges:
- Legal Clause, which might prohibit complete outsourcing.
- Indemnification & ensuring the availability of records for multiple years. It requires precise data handling.
- Business secrecy issues force you to own the hosting infrastructure.
- Audit concerns.
Advantages of Private Cloud
Here are some essential pros/benefits of Private Cloud:
- It offers better performance with improved speed and storage space capacity.
- Private clouds can be operated in a completely isolated environment that offers an additional layer of security.
- It helps you to save time and money by eliminating conventional IT obstacles.
- You can reallocate IT infrastructure resources quickly with this solution.
- Offers greater visibility into security and access control.
- Ensured compliance with regulatory standards was fully enforced.
- You can have complete control over hardware and software.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
Here are some important cons/drawbacks of Private Cloud:
- The up-front cost is higher than a public cloud because setting up and maintaining hardware resources are costly.
- Private Cloud is only accessible within the organization, so the area of operations is limited.
- Private clouds can be scaled only within the capacity of internally hosted resources.
- You need a skilled cloud computing expert to manage and operate cloud services.
Is a Private Cloud more secure Compared to Public Cloud?
A Private Cloud can be more secure than a public cloud. This cloud model is protected by firewalls and can be accessed through private, secure networks instead of the general Internet. A business’s private cloud control can also facilitate regulatory compliance and governance.
But the catch is that organizations should proactively apply updates and security patches to their software/hardware stack. If not properly managed, the private Cloud could be exposed to security risks that otherwise would have been fixed by the managed support in a public cloud environment. As long as an organization does not remain complacent about security, the private Cloud can offer many advantages to any organization.
Summary
- A private cloud is a computing model that offers a secure and dedicated environment for a single business.
- Three widely used Private clouds are 1) Virtual, 2) Managed, and 3) Private Cloud.
- AWS, Azure, HPE, and Dell are examples of some popular Private Cloud providers.
- It is important to select a hyper-scale private cloud provider that offers managed services.
- Private clouds hosted on-site require substantial capital at an initial level to bring value to the organization.
- Security & privacy is one of the biggest pros of cloud computing.
- The up-front cost is higher than a public cloud because setting up and maintaining hardware resources are costly.