SOAP Web Services Tutorial: What is SOAP Protocol? EXAMPLE
What is SOAP?
SOAP is an XML-based protocol for accessing web services over HTTP. It has some specification which could be used across all applications.
SOAP is known as the Simple Object Access Protocol, but in later times was just shortened to SOAP v1.2. SOAP is a protocol or in other words is a definition of how web services talk to each other or talk to client applications that invoke them.
SOAP was developed as an intermediate language so that applications built on various programming languages could talk easily to each other and avoid the extreme development effort.
SOAP Introduction
In today’s world, there is huge number of applications which are built on different programming languages. For example, there could be a web application designed in Java, another in .Net and another in PHP.
Exchanging data between applications is crucial in today’s networked world. But data exchange between these heterogeneous applications would be complex. So will be the complexity of the code to accomplish this data exchange.
One of the methods used to combat this complexity is to use XML (Extensible Markup Language) as the intermediate language for exchanging data between applications.
Every programming language can understand the XML markup language. Hence, XML was used as the underlying medium for data exchange.
But there are no standard specifications on use of XML across all programming languages for data exchange. That is where SOAP software comes in.
SOAP was designed to work with XML over HTTP and have some sort of specification which could be used across all applications. We will look into further details on the SOAP protocol in the subsequent chapters.
Advantages of SOAP
SOAP is the protocol used for data interchange between applications. Below are some of the reasons as to why SOAP is used.
- When developing SOAP based Web services, you need to have some of language which can be used for web services to talk with client applications. SOAP is the perfect medium which was developed in order to achieve this purpose. This protocol is also recommended by the W3C consortium which is the governing body for all web standards.
- SOAP is a light-weight protocol that is used for data interchange between applications. Note the keyword ‘light.’ Since SOAP programming is based on the XML language, which itself is a light weight data interchange language, hence SOAP as a protocol that also falls in the same category.
- SOAP is designed to be platform independent and is also designed to be operating system independent. So the SOAP protocol can work any programming language based applications on both Windows and Linux platform.
- It works on the HTTP protocol –SOAP works on the HTTP protocol, which is the default protocol used by all web applications. Hence, there is no sort of customization which is required to run the web services built on the SOAP protocol to work on the World Wide Web.
SOAP Building Blocks
The SOAP specification defines something known as a “SOAP message” which is what is sent to the web service and the client application.
The below diagram of SOAP architecture shows the various building blocks of a SOAP Message.

The SOAP message is nothing but a mere XML document which has the below components.
- An Envelope element that identifies the XML document as a SOAP message – This is the containing part of the SOAP message and is used to encapsulate all the details in the SOAP message. This is the root element in the SOAP message.
- A Header element that contains header information – The header element can contain information such as authentication credentials which can be used by the calling application. It can also contain the definition of complex types which could be used in the SOAP message. By default, the SOAP message can contain parameters which could be of simple types such as strings and numbers, but can also be a complex object type.
A simple SOAP service example of a complex type is shown below.
Suppose we wanted to send a structured data type which had a combination of a “Tutorial Name” and a “Tutorial Description,” then we would define the complex type as shown below.
The complex type is defined by the element tag <xsd:complexType>. All of the required elements of the structure along with their respective data types are then defined in the complex type collection.
<xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="Tutorial Name" type="string"/> <xsd:element name="Tutorial Description" type="string"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType>
- A Body element that contains call and response information – This element is what contains the actual data which needs to be sent between the web service and the calling application. Below is an SOAP web service example of the SOAP body which actually works on the complex type defined in the header section. Here is the response of the Tutorial Name and Tutorial Description that is sent to the calling application which calls this web service.
<soap:Body> <GetTutorialInfo> <TutorialName>Web Services</TutorialName> <TutorialDescription>All about web services</TutorialDescription> </GetTutorialInfo> </soap:Body>
SOAP Message Structure
One thing to note is that SOAP messages are normally auto-generated by the web service when it is called.
Whenever a client application calls a method in the web service, the web service will automatically generate a SOAP message which will have the necessary details of the data which will be sent from the web service to the client application.
As discussed in the previous topic of this SOAP tutorial, a simple SOAP Message has the following elements –
- The Envelope element
- The header element and
- The body element
- The Fault element (Optional)
Let’s look at an example below of a simple SOAP message and see what element actually does.

- As seen from the above SOAP message, the first part of the SOAP message is the envelope element which is used to encapsulate the entire SOAP message.
- The next element is the SOAP body which contains the details of the actual message.
- Our message contains a web service which has the name of “Guru99WebService”.
- The “Guru99Webservice” accepts a parameter of the type ‘int’ and has the name of TutorialID.
Now, the above SOAP message will be passed between the web service and the client application.
You can see how useful the above information is to the client application. The SOAP message tells the client application what is the name of the Web service, and also what parameters it expects and also what is the type of each parameter which is taken by the web service.
SOAP Envelope Element
The first bit of the building block is the SOAP Envelope.
The SOAP Envelope is used to encapsulate all of the necessary details of the SOAP messages, which are exchanged between the web service and the client application.
The SOAP envelope element is used to indicate the beginning and end of a SOAP message. This enables the client application which calls the web service to know when the SOAP message ends.
The following points can be noted on the SOAP envelope element.
- Every SOAP message needs to have a root Envelope element. It is absolutely mandatory for SOAP message to have an envelope element.
- Every Envelope element needs to have at least one soap body element.
- If an Envelope element contains a header element, it must contain no more than one, and it must appear as the first child of the Envelope, before the body element.
- The envelope changes when SOAP versions change.
- A v1.1-compliant SOAP processor generates a fault upon receiving a message containing the v1.2 envelope namespace.
- A v1.2-compliant SOAP processor generates a Version Mismatch fault if it receives a message that does not include the v1.2 envelope namespace.
Below is an SOAP API example of version 1.2 of the SOAP envelope element.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope" SOAP-ENV:encodingStyle=" http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
<soap:Body>
<Guru99WebService xmlns="http://tempuri.org/">
<TutorialID>int</TutorialID>
</Guru99WebService>
</soap:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
The Fault message
When a request is made to a SOAP web service, the response returned can be of either 2 forms which are a successful response or an error response. When a success is generated, the response from the server will always be a SOAP message. But if SOAP faults are generated, they are returned as “HTTP 500” errors.
The SOAP Fault message consists of the following elements.
- <faultCode>– This is the code that designates the code of the error. The fault code can be either of any below values
- SOAP-ENV:VersionMismatch – This is when an invalid namespace for the SOAP Envelope element is encountered.
- SOAP-ENV:MustUnderstand – An immediate child element of the Header element, with the mustUnderstand attribute set to “1”, was not understood.
- SOAP-ENV:Client – The message was incorrectly formed or contained incorrect information.
- SOAP-ENV:Server – There was a problem with the server, so the message could not proceed.
- <faultString> – This is the text message which gives a detailed description of the error.
- <faultActor> (Optional)– This is a text string which indicates who caused the fault.
- <detail>(Optional) – This is the element for application-specific error messages. So the application could have a specific error message for different business logic scenarios.
Example for Fault Message
An example of a fault message is given below. The error is generated if the scenario wherein the client tries to use a method called TutorialID in the class GetTutorial.
The below fault message gets generated in the event that the method does not exist in the defined class.
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/1999/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/1999/XMLSchema">
<SOAP-ENV:Body>
<SOAP-ENV:Fault>
<faultcode xsi:type="xsd:string">SOAP-ENV:Client</faultcode>
<faultstring xsi:type="xsd:string">
Failed to locate method (GetTutorialID) in class (GetTutorial)
</faultstring>
</SOAP-ENV:Fault>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
Output:
When you execute the above code, it will show the error like “Failed to locate method (GetTutorialID) in class (GetTutorial)”
SOAP Communication Model
All communication by SOAP is done via the HTTP protocol. Prior to SOAP, a lot of web services used the standard RPC (Remote Procedure Call) style for communication. This was the simplest type of communication, but it had a lot of limitations.
Now in this SOAP API tutorial, let’s consider the below diagram to see how this communication works. In this example, let’s assume the server hosts a web service which provided 2 methods as
- GetEmployee – This would get all Employee details
- SetEmployee – This would set the value of the details like employees dept, salary, etc. accordingly.
In the normal RPC style communication, the client would just call the methods in its request and send the required parameters to the server, and the server would then send the desired response.
The above communication model has the below serious limitations
- Not Language Independent – The server hosting the methods would be in a particular programming language and normally the calls to the server would be in that programming language only.
- Not the standard protocol – When a call is made to the remote procedure, the call is not carried out via the standard protocol. This was an issue since mostly all communication over the web had to be done via the HTTP protocol.
- Firewalls – Since RPC calls do not go via the normal protocol, separate ports need to be open on the server to allow the client to communicate with the server. Normally all firewalls would block this sort of traffic, and a lot of configuration was generally required to ensure that this sort of communication between the client and the server would work.
To overcome all of the limitations cited above, SOAP would then use the below communication model
- The client would format the information regarding the procedure call and any arguments into a SOAP message and sends it to the server as part of an HTTP request. This process of encapsulating the data into a SOAP message was known as Marshalling.
- The server would then unwrap the message sent by the client, see what the client requested for and then send the appropriate response back to the client as a SOAP message. The practice of unwrapping a request sent by the client is known as Demarshalling.
Practical SOAP Example
Now in this SoapUI tutorial, let’s see a practical SOAP example,
Probably one of the best ways to see how SOAP messages get generated is to actually see a web service in action.
This topic will look at using the Microsoft.Net framework to build an ASMX web service. This type of web service supports both SOAP version 1.1 and version 1.2.
ASMX web services automatically generate the Web Service Definition Language (WSDL) document. This WSDL document is required by the calling client application so that the application knows what the web service is capable of doing.
In our example, we are going to create a simple web service, which will be used to return a string to the application which calls the web service.
This web service will be hosted in an Asp.Net web application. We will then invoke the web service and see the result that is returned by the web service.
Visual Studio will also show us what the SOAP message being passed between the web service and the calling application.
The first pre-requisite to setup our Web service application which can be done by following the below steps.
Please ensure that you have Visual Studio 2013 installed on your system for this example.
Step 1) The first step is to create an empty ASP.Net Web application. From Visual Studio 2013, click on the menu option File->New project.
Once you click on the New Project option, Visual Studio will then give you another dialog box for choosing the type of project and to give the necessary details of the project. This is explained in the next step.
Step 2) In this step,
- Ensure to first choose the C# web template of ASP.NET Web application. The project has to be of this type in order to create SOAP services project. By choosing this option, Visual Studio will then carry out the necessary steps to add required files which are required by any web-based application.
- Give a name for your project which in our case has been given as webservice.asmx. Then ensure to give a location where the project files will be stored.
Once done you will see the project file created in your solution explorer in Visual Studio 2013.
Step 3) In this step,
We are going to add a Web service file to our project
- First Right-click on the project file as shown below
- Once you right-click on the project file, you have the chance to choose the option “Add->Web Service(ASMX) to add a web service file. Just provide a name of Tutorial Service for the web service name file.
Step 4) Add the following code to your Tutorial Service asmx file.
Code Explanation:
- This line of code provides a name for your web service file. This is an important step because it gives way for the client application to call the web service via the name of the web service.
- Normally a class file is used to encapsulate the functionality of a web service. So the class file will have the definition of all the web methods which will provide some functionality to the client application.
- Here [WebMethod] is known as an attribute which describes a function. The subsequent step creates a function called “Guru99WebService”, but with the inclusion of this step of adding a [WebMethod] attribute makes sure that this method can be invoked by a client application. If this attribute is not in place, then the method can never be called by a client application.
- Here we are defining a function called ‘Guru99WebService’ which will be used to return a string to the calling client application. This function is a web service which can be called by any client application.
- We are using the return statement to return the string “This is a Guru99 Web service” to the client application.
If the code is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
Output:
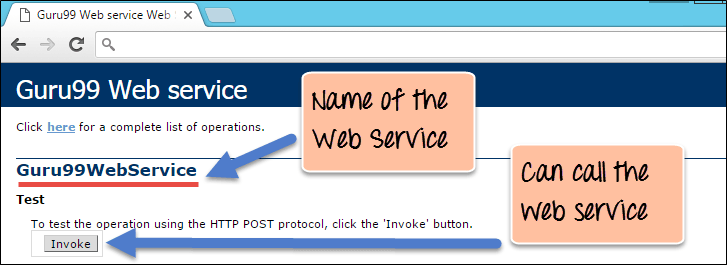
- The output clearly shows that the name of our web service is “Guru99 Web Service” which is the result of giving a name for our web service.
- We can also see that we can to invoke the web service. If we click the Invoke button, we will get the below response in the web browser.
The above output,
- It clearly shows that by invoking the web method, the string “This is a Guru99 Web service” is returned.
- Visual Studio also allows you to view the SOAP message request and response which is generated when the above web service is called.
The SOAP request which is generated when the web service is called is shown below.
Code Explanation:
- The first part of the SOAP message is the envelope element which is what was discussed in the prior chapters. This is the encapsulating element which is present in every SOAP message.
- The SOAP Body is the next element and contains the actual details of the SOAP message.
- The third part is the element which specifies that we want to call the service which is called ‘Guru99WebService.’
<soap:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<soap:Body>
<Guru99WebServiceResponse xmlns="http://tempuri.org/">
<Guru99WebServiceResult>string</Guru99WebServiceResult>
</Guru99WebServiceResponse>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
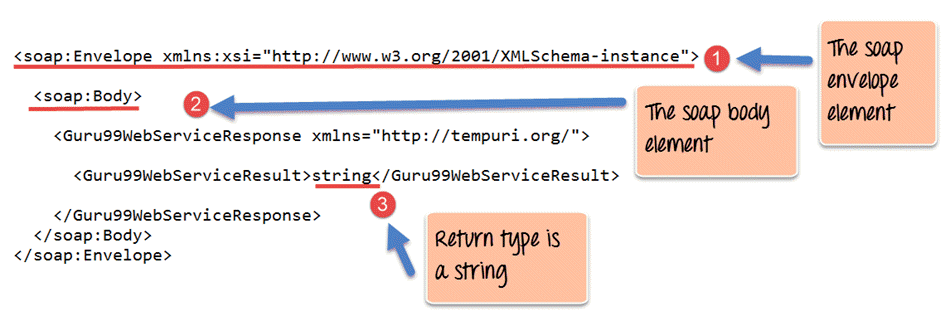
Code Explanation:
- The first part of the SOAP message is the envelope element which is what was discussed in the prior chapters. This is the encapsulating element which is present in every SOAP message.
- The SOAP Body is the next element and contains the actual details of the SOAP message.
- The interesting part you will see now is the ‘string’ attribute. This tells the client application that the web service being called returns an object of the type string. This is very useful because if the client application which otherwise would not know what the web service returns.
Summary
- SOAP is a protocol which is used to interchange data between applications which are built on different programming languages.
- SOAP is built upon the XML specification and works with the HTTP protocol. This makes it a perfect for usage within web applications.
- The SOAP building blocks consist of a SOAP Message. Each SOAP message consists of an envelope element, a header, and a body element.
- The envelope element is the mandatory element in the SOAP message and is used to encapsulate all of the data in the SOAP message.
- The header element can be used to contain information such as authentication information or the definition of complex data types.
- The body element is the main element which contains the definition of the web methods along with any parameter information if required.