Preemptive and Non-Preemptive Scheduling
Key Differences between Preemptive and Non-Preemptive Scheduling
- In Preemptive Scheduling, the CPU is allocated to the processes for a specific time period, and the non-preemptive scheduling CPU is allocated to the process until it terminates.
- In Preemptive Scheduling, tasks are switched based on priority, while in non-preemptive Scheduling, no switching takes place.
- The preemptive algorithm has the overhead of switching the process from the ready state to the running state, while Non-preemptive Scheduling has no such overhead of switching.
- Preemptive Scheduling is flexible, while Non-preemptive Scheduling is rigid.

What is Preemptive Scheduling?
Preemptive Scheduling is a scheduling method where the tasks are mostly assigned with their priorities. Sometimes it is important to run a task with a higher priority before another lower priority task, even if the lower priority task is still running.
At that time, the lower priority task holds for some time and resumes when the higher priority task finishes its execution.
What is Non-Preemptive Scheduling?
In this type of scheduling method, the CPU has been allocated to a specific process. The process that keeps the CPU busy will release the CPU either by switching context or terminating.
It is the only method that can be used for various hardware platforms. That’s because it doesn’t need specialized hardware (for example, a timer) like preemptive Scheduling.
Non-Preemptive Scheduling occurs when a process voluntarily enters the wait state or terminates.
Preemptive vs Non-Preemptive Scheduling: Comparison Table
Here, are head-to-head comparison Preemptive vs Non-Preemptive Scheduling. The main differences between Preemptive and Non-Preemptive Scheduling in OS are as follows:
| Preemptive Scheduling | Non-preemptive Scheduling |
|---|---|
| A processor can be preempted to execute the different processes in the middle of any current process execution. | Once the processor starts its execution, it must finish it before executing the other. It can’t be paused in the middle. |
| CPU utilization is more efficient compared to Non-Preemptive Scheduling. | CPU utilization is less efficient compared to preemptive Scheduling. |
| Waiting and response time of preemptive Scheduling is less. | Waiting and response time of the non-preemptive Scheduling method is higher. |
| Preemptive Scheduling is prioritized. The highest priority process is a process that is currently utilized. | When any process enters the state of running, the state of that process is never deleted from the scheduler until it finishes its job. |
| Preemptive Scheduling is flexible. | Non-preemptive Scheduling is rigid. |
| Examples: – Shortest Remaining Time First, Round Robin, etc. | Examples: First Come First Serve, Shortest Job First, Priority Scheduling, etc. |
| Preemptive Scheduling algorithm can be pre-empted that is the process can be Scheduled | In non-preemptive scheduling process cannot be Scheduled |
| In this process, the CPU is allocated to the processes for a specific time period. | In this process, CPU is allocated to the process until it terminates or switches to the waiting state. |
| Preemptive algorithm has the overhead of switching the process from the ready state to the running state and vice-versa. | Non-preemptive Scheduling has no such overhead of switching the process from running into the ready state. |
Advantages of Preemptive Scheduling
Here, are pros/benefits of Preemptive Scheduling method:
- Preemptive scheduling method is more robust, approach so one process cannot monopolize the CPU
- Choice of running task reconsidered after each interruption.
- Each event cause interruption of running tasks
- The OS makes sure that CPU usage is the same by all running process.
- In this, the usage of CPU is the same, i.e., all the running processes will make use of CPU equally.
- This scheduling method also improvises the average response time.
- Preemptive Scheduling is beneficial when we use it for the multi-programming environment.
Advantages of Non-preemptive Scheduling
Here, are pros/benefits of Non-preemptive Scheduling method:
- Offers low scheduling overhead
- Tends to offer high throughput
- It is conceptually very simple method
- Less computational resources need for Scheduling
Disadvantages of Preemptive Scheduling
Following are the drawbacks of preemptive scheduling:
- Need limited computational resources for Scheduling
- Takes a higher time by the scheduler to suspend the running task, switch the context, and dispatch the new incoming task.
- The process which has low priority needs to wait for a longer time if some high priority processes arrive continuously.
Disadvantages of Non-Preemptive Scheduling
Here, are cons/drawback of Non-Preemptive Scheduling method:
- It can lead to starvation especially for those real-time tasks
- Bugs can cause a machine to freeze up
- It can make real-time and priority Scheduling difficult
- Poor response time for processes
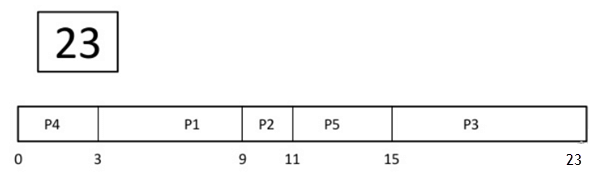
Example of Non-Preemptive Scheduling
In non-preemptive SJF scheduling, once the CPU cycle is allocated to process, the process holds it till it reaches a waiting state or terminated.
Consider the following five processes each having its own unique burst time and arrival time.
| Process Queue | Burst time | Arrival time |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 6 | 2 |
| P2 | 2 | 5 |
| P3 | 8 | 1 |
| P4 | 3 | 0 |
| P5 | 4 | 4 |
Step 0) At time=0, P4 arrives and starts execution.
Step 1) At time= 1, Process P3 arrives. But, P4 still needs 2 execution units to complete. It will continue execution.
Step 2) At time =2, process P1 arrives and is added to the waiting queue. P4 will continue execution.
Step 3) At time = 3, process P4 will finish its execution. The burst time of P3 and P1 is compared. Process P1 is executed because its burst time is less compared to P3.
Step 4) At time = 4, process P5 arrives and is added to the waiting queue. P1 will continue execution.
Step 5) At time = 5, process P2 arrives and is added to the waiting queue. P1 will continue execution.
Step 6) At time = 9, process P1 will finish its execution. The burst time of P3, P5, and P2 is compared. Process P2 is executed because its burst time is the lowest.
Step 7) At time=10, P2 is executing, and P3 and P5 are in the waiting queue.
Step 8) At time = 11, process P2 will finish its execution. The burst time of P3 and P5 is compared. Process P5 is executed because its burst time is lower.
Step 9) At time = 15, process P5 will finish its execution.
Step 10) At time = 23, process P3 will finish its execution.
Step 11) Let’s calculate the average waiting time for above example.
Wait time P4= 0-0=0 P1= 3-2=1 P2= 9-5=4 P5= 11-4=7 P3= 15-1=14 Average Waiting Time= 0+1+4+7+14/5 = 26/5 = 5.2
Example of Pre-emptive Scheduling
Consider this following three processes in Round-robin
| Process Queue | Burst time |
|---|---|
| P1 | 4 |
| P2 | 3 |
| P3 | 5 |
Step 1) The execution begins with process P1, which has burst time 4. Here, every process executes for 2 seconds. P2 and P3 are still in the waiting queue.
Step 2) At time =2, P1 is added to the end of the Queue and P2 starts executing
Step 3) At time=4 , P2 is preempted and add at the end of the queue. P3 starts executing.
Step 4) At time=6 , P3 is preempted and add at the end of the queue. P1 starts executing.
Step 5) At time=8 , P1 has a burst time of 4. It has completed execution. P2 starts execution
Step 6) P2 has a burst time of 3. It has already executed for 2 interval. At time=9, P2 completes execution. Then, P3 starts execution till it completes.
Step 7) Let’s calculate the average waiting time for above example.
Wait time P1= 0+ 4= 4 P2= 2+4= 6 P3= 4+3= 7