JUnit @Ignore Test Annotation with Example
Sometimes you may require not to execute a method/code or Test Case because coding is not done fully. For that particular test, JUnit provides @Ignore annotation to skip the test.
What is JUnit @Ignore test annotation
The @Ignore test annotation is used to ignore particular tests or group of tests in order to skip the build failure.
@Ignore annotation can be used in two scenarios as given below:
- If you want to ignore a test method, use @Ignore along with @Test annotation.
- If you want to ignore all the tests of class, use @Ignore annotation at the class level.
You can provide the reason for disabling a test in the optional parameter provided by @Ignore annotation.
It will help other developers working on the same piece of code, to understand “why a particular test is disabled?” When the issue of that particular test is fixed, you can simply enable it by removing @Ignore annotation.
Junit Test Example – Ignore
As discussed in above definition, you can use @Ignore annotation to ignore a test or group of the test.
Let’s understand it using simple example and in below given scenarios:
- Creating a simple test class without ignoring a test.
- Ignore a test method using @Ignore annotation.
- Ignore a test method using @Ignore annotation with proper reason.
- Ignore all test method using @Ignore annotation.
Creating a simple test class without ignoring a test
Let’s create a simple Java class which prints two types of message.
- First method prints a simple message and
- The second method prints a “hi” message
JUnitMessage.java
package guru99.junit;
public class JUnitMessage {
private String message;
public JUnitMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String printMessage(){
System.out.println(message);
return message;
}
public String printHiMessage(){
message="Hi!"+ message;
System.out.println(message);
return message;
}
}
JunitTestExample.java
Let’s create a JUnit test class to test JUnitMessage.java.
In this JUnit test class,
- First test, named “testJUnitMessage()” tests “printMessage()” method of above class.
- Similarly the second test, named “testJUnitHiMessage” tests “testJUnitHiMessage” of above class.
package guru99.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.junit.Test;
public class JunitTestExample {
public String message = "Guru99";
JUnitMessage junitMessage = new JUnitMessage(message);
@Test
public void testJUnitMessage() {
System.out.println("Junit Message is printing");
assertEquals(message, junitMessage.printMessage());
}
@Test
public void testJUnitHiMessage() {
message="Hi!" +message;
System.out.println("Junit Hi Message is printing ");
assertEquals(message, junitMessage.printHiMessage());
}
}
TestRunner.java
Let’s create a test runner class to execute JunitTestExample.java
package guru99.junit;
import org.junit.runner.JUnitCore;
import org.junit.runner.Result;
import org.junit.runner.notification.Failure;
public class TestRunner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Result result = JUnitCore.runClasses(JunitTestExample.class);
for (Failure failure : result.getFailures()) {
System.out.println(failure.toString());
}
System.out.println("Result=="+result.wasSuccessful());
}
}
Output:
Print statement on console:
Junit Hi Message is printing
Hi!Guru99
Junit Message is printing
Guru99
Ignore a test method using @Ignore annotation
Let’s create ignore test to disable a test in above example. For this, you need to use @Ignore in the method, you want to skip.
Let’s do it for testJUnitMessage() of JunitTestExample.java
JunitTestExample.java
package guru99.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.junit.Ignore;
import org.junit.Test;
public class JunitTestExample {
public String message = "Guru99";
JUnitMessage junitMessage = new JUnitMessage(message);
@Ignore
@Test
public void testJUnitMessage() {
System.out.println("Junit Message is printing ");
assertEquals(message, junitMessage.printMessage());
}
@Test
public void testJUnitHiMessage() {
message="Hi!" +message;
System.out.println("Junit Hi Message is printing ");
assertEquals(message, junitMessage.printHiMessage());
}
}
Output:
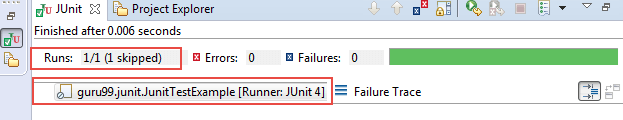
Let’s execute and verify the output of above example.
Below output shows that one test is skipped (disabled), see as marked below:
Print statement on console:
Junit Hi Message is printing
Hi!Guru99
Using @ ignore annotation with Condition
Let’s take the example of how to ignore a test and define the reason for ignoring along with it. As discussed above, to provide a reason you have one optional parameter in @Ignore annotation where you can provide the reason statement.
JunitTestExample.java
package guru99.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.junit.Ignore;
import org.junit.Test;
public class JunitTestExample {
public String message = "Guru99";
JUnitMessage junitMessage = new JUnitMessage(message);
@Ignore("not yet ready , Please ignore.")
@Test
public void testJUnitMessage() {
System.out.println("Junit Message is printing ");
assertEquals(message, junitMessage.printMessage());
}
@Test
public void testJUnitHiMessage() {
message="Hi!" +message;
System.out.println("Junit Hi Message is printing ");
assertEquals(message, junitMessage.printHiMessage());
}
}
Output:
Same as above.
Ignore all test methods using @Ignore annotation.
As discussed above to ignore all the tests in class, you need to use @Ignore annotation at the class level.
Let’s modify above example to understand how to ignore all the tests:
package guru99.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.junit.Ignore;
import org.junit.Test;
@Ignore
public class JunitTestExample {
public String message = "Guru99";
JUnitMessage junitMessage = new JUnitMessage(message);
@Test
public void testJUnitMessage() {
System.out.println("Junit Message is printing ");
assertEquals(message, junitMessage.printMessage());
}
@Test
public void testJUnitHiMessage() {
message="Hi!" +message;
System.out.println("Junit Hi Message is printing ");
assertEquals(message, junitMessage.printHiMessage());
}
}
Output :
Print statement on console:
As both the tests skipped by using @Ignore at class level so no statement would be printed on the console.
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned how to ignore a single test, group of test or all tests by using @Ignore annotation.
@Ignore annotation can be used in two scenarios as given below:
- If you want to ignore a test method, use @Ignore along with @Test annotation.
- If you want to ignore all the tests of class, use @Ignore annotation at the class level.
You also learned how to provide a statement to make understand other developer, why a particular test is disabled.