PostgreSQL ALTER Table: ADD Column, Rename Column/Table Examples
The ALTER TABLE command is used to alter the structure of a PostgreSQL table. It is the command used to change the table columns or the name of the table.
Syntax
Here is the syntax for the PostgreSQL ALTER TABLE command:
ALTER TABLE table-name action;
The table-name parameter is the name of the table that you need to change.
The action parameter is the action that you need to perform, such as changing the name of a column, changing the data type of a column, etc.
Description
The ALTER TABLE command changes the definition of an existing table. It takes the following subforms:
- ADD COLUMN: this uses similar syntax as CREATE TABLE command to add a new column to a table.
- DROP COLUMN: for dropping a table column. The constraints and indexes imposed on the columns will also be dropped.
- SET/DROP DEFAULT: Use for removing the default value for a column. However, the change will only apply to the subsequent INSERT statements.
- SET/DROP NOT NULL: Changes whether a column will allow nulls or not.
- SET STATISTICS: For setting the statistics-gathering target for each column for ANALYZE operations.
- SET STORAGE: For setting the mode of storage for a column. This will determine where the column is held, whether inline, or in a supplementary table.
- SET WITHOUT OIDS: Use for removing the old column of the table.
- RENAME: for changing the table name or a column name.
- ADD table_constraint: Use for adding a new constraint to a table It uses the same syntax as CREATE TABLE command.
- DROP CONSTRAINT: Use for dropping a table constraint.
- OWNER: for changing the owner of a table, sequence, index or a view to a certain user.
- CLUSTER: for marking a table to be used for carrying out future cluster operations.
Modifying a column
A column may be modified in a number of ways. Such modifications can be done using the ALTER TABLE command. Let us discuss these:
Adding a New column
To add a new column to a PostgreSQL table, the ALTER TABLE command is used with the following syntax:
ALTER TABLE table-name ADD new-column-name column-definition;
The table-name is the name of the table to be modified.
The new-column-name is the name of the new column to be added.
The column-definition is the data type of the new column.
See the Book table shown below:
The table has two columns, id, and name. We need to add a new column to the table and give it the name author. Just run the following command:
ALTER TABLE Book ADD author VARCHAR(50);
After running the above command, the Book table is now as follows:
The new column was added successfully.
Renaming a Table Column
We can use the ALTER TABLE command to change the name of a column. In this case, the command is used with the following syntax:
ALTER TABLE table-name RENAME COLUMN old-name TO new-name;
The table-name is the name of the table whose column is to be renamed.
The old-name is the old/current name of the column.
The new-name is the new name of the column. Consider the table Book shown below:
Book:
We need the name of the column author to book_author. Here is the command:
ALTER TABLE Book RENAME COLUMN author TO book_author;
After running the command, we can view the structure of the table:
The column name was changed successfully.
Setting a Default Value for a Column
We can set a default value for a column such that even when you don’t specify a value for that column during INSERT operations, the default value will be used. In this case, the ALTER TABLE command can be used with the following syntax:
ALTER TABLE table-name ALTER COLUMN column-name [SET DEFAULT value];
The table-name is the name of the table whose column is to be modified.
The column-name is the name for whose default value is to be set.
The value is the default value for the column.
Consider the Book table given below:
We need to set a default value for the book_author column. We can run the following command:
ALTER TABLE Book ALTER COLUMN book_author SET DEFAULT 'Nicholas Samuel';
Now, let us insert a row into the table:
INSERT INTO Book (id, name) VALUES (6, 'PostgreSQL for Beginners');
Note that we inserted values for only two columns, id and name. However, the default value has been used for book_author column:
Adding a Check Constraint
A check constraint helps in validating the records that are being inserted into a table. We can do this by combining the ALTER TABLE command with the ADD CHECK statement. Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table-name ADD CHECK expression;
The table-name is the name of the table to be altered.
The expression is the constraint to be imposed on the table column.
Let us modify the book_author column of the Book table so that it only accepts the values, Nicholas and Samuel:
ALTER TABLE Book ADD CHECK (book_author IN ('Nicholas', 'Samuel'));
Now, let us try to insert a value other than Nicholas or Samuel into the book_author column of the Book table:
INSERT INTO Book VALUES(7, 'Best PostgreSQL Book', 'Gregory Bush');
The statement will return the following error:
The insert operation failed because we violated the check constraint.
Renaming a Table
Here is the syntax for the ALTER TABLE command for renaming a table:
ALTER TABLE table-name RENAME TO new-table-name;
The table-name is the current name of the table.
The new-table-name is the new name to be assigned to the table.
For example, let us change the name of the Book table to Books:
ALTER TABLE Book RENAME TO Books;
Using pgAdmin
Now let’s see how these actions can be performed using pgAdmin.
Adding a New column
To accomplish the same through pgAdmin, do this:
Step 1) Login to your pgAdmin account.
Step 2)
- From the navigation bar on the left- Click Databases.
- Click Demo.
Step 3) Type the query in the query editor:
ALTER TABLE Book ADD author VARCHAR(50);
Step 4) Click the Execute button.
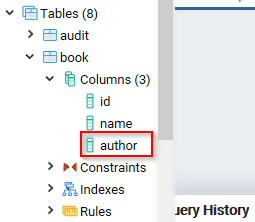
Step 5) To check whether the column was added, do the following:
- Click Databases from the left navigation.
- Expand Demo.
- Expand Schemas.
- Expand Public.
- Expand Tables.
- Expand book.
- Expand Columns.
The column should have been added, as shown below:
Renaming a Table Column
To accomplish the same through pgAdmin, do this:
Step 1) Login to your pgAdmin account.
Step 2)
- From the navigation bar on the left- Click Databases.
- Click Demo.
Step 3) Type the query in the query editor:
ALTER TABLE Book RENAME COLUMN author TO book_author;
Step 4) Click the Execute button.
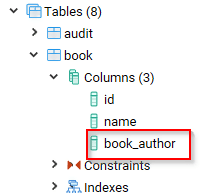
Step 5) To check whether the change was successful, do the following:
- Click Databases from the left navigation.
- Expand Demo.
- Expand Schemas.
- Expand Public.
- Expand Tables.
- Expand book.
- Expand Columns.
The columns should now be as follows:
The column was changed successfully.
Setting a Default Value for a Column
To accomplish the same through pgAdmin, do this:
Step 1) Login to your pgAdmin account.
Step 2)
- From the navigation bar on the left- Click Databases.
- Click Demo.
Step 3) Type the query in the query editor:
ALTER TABLE Book ALTER COLUMN book_author SET DEFAULT 'Nicholas Samuel';
Step 4) Click the Execute button.
Step 5) To test, run the following command on the query editor:
INSERT INTO Book (id, name) VALUES (6, 'PostgreSQL for Beginners')
Step 6) Now, we can query the table to check whether the default value was inserted in the book_author column:
Adding a Check Constraint
To accomplish the same through pgAdmin, do this:
Step 1) Login to your pgAdmin account.
Step 2)
- From the navigation bar on the left- Click Databases.
- Click Demo.
Step 3) Type the query in the query editor:
ALTER TABLE Book ADD CHECK (book_author IN ('Nicholas', 'Samuel'))
Step 4) Click the Execute button.
Step 5) To test this, do the following:
- Type the following query on the query editor:
INSERT INTO Book VALUES(7, 'Best PostgreSQL Book', 'Gregory Bush');
- Click the Execute button.
It will return the following:
Renaming a Table
To accomplish the same through pgAdmin, do this:
Step 1) Login to your pgAdmin account.
Step 2)
- From the navigation bar on the left- Click Databases.
- Click Demo.
Step 3) Type the query in the query editor:
ALTER TABLE Book RENAME TO Books;
Step 4) Click the Execute button.
Step 5) To check whether the table was renamed, do the following:
- Click Databases from the left navigation.
- Expand Demo.
- Expand Schemas.
- Expand Public.
- Expand Tables.
The table was renamed successfully.
Summary
- The ALTER TABLE statement is used to modify the structure of the table.
- The ALTER TABLE command takes various forms depending on the task that you need to perform.
- The structure can be the table columns or the table itself.
- We can use this statement to change the name of a table.
- The ALTER TABLE command can be used to set the default value of a column.
- The statement can be used to validate the values that are entered into a table column.