Project Management Life Cycle Phases: What are the stages?
What is a Project Management Life Cycle?
Project Management Life Cycle is a series of essential activities for accomplishing project objectives or targets. It is a framework that includes the stages to transform an idea into reality. Projects may have different dimensions and difficulty levels, but they can be mapped to the Project Management life cycle structure, whatever the project’s size is.
Project Management Life Cycle Phases
The Project Management Lifecycle process is divided into four main parts: Initiation phase, Planning phase, Execution phase and Monitoring, Controlling and Closing phase as shown in the below diagram.

We will look every Project Life Cycle Phases:
Project Initiation Stage
Initiation phase defines those processes that are required to start a new project. The purpose of the project initiation phase is to determine what the project should accomplish.
This phase mainly composed of two main activities
- Develop a Project Charter and
- Identify Stakeholders
All the information related to the project are entered in the Project Charter and Stakeholder Register. When the project charter is approved, the project becomes officially authorized.
Project Charter
The Project Charter defines the project’s main elements
- Project goals
- Project constraints and Problem statements
- Assign project manager
- Stakeholder list
- High-level schedule and budget
- Milestones
- Approvals
This document allows a project manager to utilize organizational resources for the sake of the project. To create a project charter, the inputs required will be enterprise environment factor, business case, agreements, a project statement of work and organizational process assets.
Identifying Stakeholders
A stakeholder can influence the success and failure of the project. To note down the information about the stakeholder, a Stakeholder Register is used.
The stakeholder register will have information like
- Type of stakeholder
- Expectation of stakeholder
- Role in Project ( Business Analyst, Tech architect, Client PM)
- Designation (Director, Business Lead, etc.)
- Type Communication ( Weekly/Monthly)
- Influence on the project ( Partial/Supportive/Influensive)
The other activities involved in initiating process group are:
- Assigning the project manager
- Determining the stakeholder needs, expectations and high-level requirements
- Define the project success criteria
- Identify particular budget for particular stage
- Make sure that the project is aligned with the organizations strategic goal
The stakeholder register and project charter are used as inputs to the other development groups such as planning process group.
Project Planning Stage
Project Planning phase covers about 50% of the whole process. Planning phase determines the scope of the project as well as the objective of the project. It begins with the outputs of initiation phase (charter, preliminary scope statement, and project manager). The output of the planning phase serves as the input for the execution phase.
The important aspects of planning process are
- Planning phase should not be executed before your initial planning is finished
- Until the execution process does not start, you should not stop revising plans
Create Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
For any successful project WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) is important. Following are steps to create WBS.
- Conduct a brainstorm to list all the tasks
- Involve your whole team for brainstorming
- Write down the structure tree of the task also known as WBS (work breakdown structure)
- Further breakdown your top WBS into a hierarchical set of activities, for instance, categories, sub-categories, etc. For example hardware, software, trainee, management teams, etc.
- Define how to record the items into your WBS
- Ask other people – it can be an expert, experienced personnel, etc.
- Granularity- how detailed your task should you have? Estimating cost and time for higher granularity is hard while for lower granularity it will be bogged down with too detailed information
- Granularity should be of right level not too high or not too low
Planning Schedule Management
Plan Scheduling is the process of establishing the procedure, policies and documentation for planning, managing, executing and controlling the project schedule. The inputs in these activities include
- Project management plan
- Project Charter
- Enterprise environmental factors
- Organizational process assets
The output of the Planning Schedule Management includes
- Schedule management plan
Defining Activities
Defining Activities is the procedure for documenting and identifying specific actions to be performed to produce the project deliverables.
In define activities, each work packages is broken down into individual work schedule activities. The inputs of the defining activities include
- Schedule management plan
- Scope baseline
- Enterprise environmental factors
- Organizational process assets
While the outputs of these activities are
- Activity list
- Activity attributes
- Milestone list
Sequence Activities
Sequence activities is nothing but logically organizing the output of “define activities”. It determines the order in which the activities needs to be performed.
The main output from the sequence activity process is “Network Diagram”.
Network diagram is nothing but posting the task on a board in a logical order.
For example, you want to start a business in foreign country what will be your list of activities and what will be the order it should be done?
You will perform activities in these order
- Choose a country
- Get business permit
- Hiring a manager
- Buying a property
- Buying the furniture etc.
- Opening the business
Estimating Activity Resources
This stage explains the process of estimating the work effort and resources required to complete the task. The other factor that has to be considered at this stage is the availability of the resources.
While estimating resources, the focus should be on the longest path of the plan (Critical Path), which going to consume more time and money.
You have to estimate resources for two tasks
- Critical tasks
- Floating tasks
Make sure that your critical tasks are accurately estimated (completion time).
There are five inputs used to estimate activity resources
- Schedule Management Plan
- Activity list
- Resource Calendar
- Enterprise environmental factors
- Organizational process assets
The output of this stage is
- Activity resource requirements
- Resource breakdown structure
- Project documents updates
NOTE: All the activity that is done so far (define activities + sequence activities + Estimate activity resources) is going to help in “Develop Schedule.”
Estimating Activity Durations
Estimating Activity Duration is the process of estimating the number of work periods (weeks/months) required to complete the individual task with estimated resources. This step defines how much time an individual task will take to complete.
You cannot calculate activity duration without calculating the work effort and resources required to complete the task. Estimating process should be done in this order
- Estimate work effort first
- Followed by estimating the resources
- Followed by Estimating the duration of task
To estimate activity durations, you need inputs
- Activity list
- Activity attributes
- Resource calendars
- Project scope statement
- Organizational process assets
- Enterprise environmental factors
While there are two main outputs
- Estimate activity durations
- Estimate activity durations-project document updates
This technique is also referred as PERT (Project Evaluation and Review Techniques) estimates.
Develop Schedule
Develop Schedule is the process of analyzing activity sequences, resource requirements, durations and schedule constraints to create the project schedule model. For scheduling each task, three main factors are taken into consideration
- Duration
- Task dependencies
- Constraints
Using these factors project calculates the start date and finish date for each task.
A scheduling software can be used to create a schedule. It generates a schedule model with planned dates for completing project activities.
The input of this tool includes
- Schedule management plan
- Activity list
- Activity attributes
- Project schedule –network diagrams
- Activity resource requirements
- Resource calendars
- Activity duration estimates
- Project scope statement
- Risk register
- Project staff assignments
- Resource breakdown structure
- Enterprise environmental factors
- Organizational process assets
The output from this would be
- Project Schedule
- Project network diagram
- Gantt charts or Bar charts
- Milestone chart
- Schedule baseline
- Scheduled data
- Project document updates
Control Schedule
The last stage of the planning phase is Control Schedule. It is the process of monitoring the status of project activities to update project process and manage changes to the schedule baseline.
If changes are required to the schedule, they must go through the change control process. The schedule should be managed or controlled by manager proactively.
There are four main outputs of control schedule process
- Project management plan
- Schedule baseline
- Schedule management plan
- Project schedule
- Work performance information
- Organizational process assets
There are five outputs of control schedule
- Work performance management
- Organizational process assets updates
- Change request
- Project management plan updates
- Project document updates
Project Execution Stage
The executing phase consists of those activities that are defined in project management plan. This process involves managing stakeholder expectations, coordinating with people and resources, as well as performing other activities related to project deliverables.
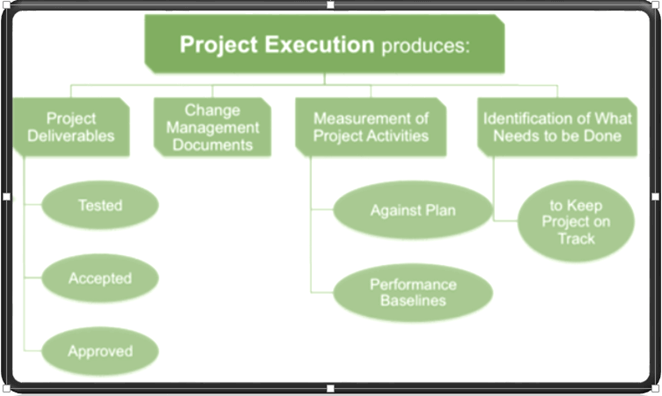
During the execution phase, the result may require re-baselining and updates to existing project requirements. Action taken in execution phase may affect the project management plan or documents.
Direct and Manage Project Execution
This stage consumes most of the project cost, time, and resources as this is the process that produce project deliverables.
There are four inputs to Direct and Manage Project Execution
- Project Management Plan
- Approved change request
- EEFs (Enterprise Environmental Factors)
- OPAs (Organizational Process Assets)
While there are five outputs
- Deliverables
- Work performance data
- Change request
- Project Management plan updates
- Project documents updates
During this stage, expert’s judgments, meetings, and reporting KPI (Key Performance Indicators) are of prime importance.
Performing Quality Assurance
Performing Quality Assurance is the process of auditing the quality requirements and the results from quality control measurements. It is the process of recording and monitoring results of the quality activities to assess performance. Various tools like control charts, cost-benefit analysis, flowcharting, run charts, scatter diagrams, inspection & reviews, etc., can be used for this process.
The main input to this is
- Project management plan
- Quality metrics
- Quality control measurements
- Work performance information
While, the output of this is
- Change request
- Project management plan updates
- Project document updates
- Organizational process assets updates
Acquiring Project Team
During the execution phase, project team acquiring takes place, this is because it is more likely that individuals with different skill set will be required during the process.
There are three main inputs to acquire project team
- Roles and responsibilities
- Project organization chart
- Staffing management plan
While there are three outputs
- Project staff assignments
- Resource calendars
- Project management plan updates
Develop Project Team
The majority of human resource processes involves in executing process, developing project team is also a part of it. The main purpose of developing project team is to improve the overall performance of team members. This stage must start early on in the project.
The inputs in project development team include
- Human resource management plan
- Project staff assignments
- Resource calendars
Output of this process include
- Team performance assessments
- EEFs Updates
Manage project team
Managing project team is one of the important parts of project management. It is the most complex area of project management because many times managers would not be in direct contact with team members, in such situation to analyze their performance and deciding their remuneration becomes difficult.
There are five inputs to manage project team process
- Project staff assignments
- Team performance assessments
- Performance reports
- Project management plan
- Organizational process assets
There are four main outputs
- Organizational process assets updates
- Enterprise environmental factors updates
- Change request
- Project management plan updates
Manage Communications
Out of three communication attributes, one falls in the execution process. In communication management program, there are three main communication aspects that need to monitor.
- Project team members to the project manager
- Project managers to the program manager
- Program manager to stakeholders or other sponsors
The input of managing communications include
- Communications management plan
- Work performance reports
- EEFs
- OPAs
The output of this stage would be
- Project communications
- Project management plan updates
- Project documents updates
- OPAs updates
Conduct Procurements
In this stage, there are two main roles involved the buyer and the seller. During the procurement process the activities involved are
- Issue the bid package to potential sellers
- Hold bidder conferences
- Evaluate potential seller proposals
- Select the winning seller proposals
The output of the procurement process include
- Project management plan
- Conduct procurement documents
- Source selection criteria
- Qualified seller list
- Seller proposals
- Project documents
- Make or buy decisions
- Partnership agreement (teaming agreement)
- Organizational process assets
While, you will have six outputs
- Selected sellers
- Procurement contract award
- Resource calendars
- Change requests
- Project management plan updates
Manage Stakeholder Engagement
This stage includes actively managing stakeholders throughout the project. To avoid unexpected project delay or abandoning the project in between, stakeholder expectation is identified and quickly resolved.
There are five inputs to manage stakeholder process
- Stakeholder register
- Stakeholder management strategy
- Project management plan
- Issue log
- Change log
- Organizational process assets
The output of this process include
- Organizational process assets updates
- Change request
- Project management plan updates
- Project documentation updates
Project Phase Review
At the end of execution phase, project phase review is done. It helps you to document in following activities
- Document the result of your project management review
- Inform the sponsor about the progress of the project
- Identifying any risk or issues that impacted the project
- Shows deliverable to stakeholder produced during the project
- Seek approval to proceed to the next phase
Project Monitoring and Controlling & Closing Stage
After execution phase, to check the project is on right track, monitoring and controlling phase becomes active. During this phase various changes and reviews to enhance the project performance is done.
Monitor and Control Project Work
This stage involves tracking, reviewing and regulating the progress in order to meet the objective of the project. It also ensures that the deliverables are according to the project management plan. The main focus of this step is to identify any changes made from the point of project management plan to determine appropriate preventive action.
The inputs for this stage include
- Project management plan
- Performance reports
- Cost forecasts
- Schedule forecasts
- Validate changes
- Enterprise environmental factors
- Organizational process assets
While the output includes
- Change requests
- Project management plan updates
- Project document updates
Perform Integrated Change Control
It is one of the most important process of project management. It is in this stage where the impact of any change is assessed against the project. If a change in this stage occurs at any one part of a project, the whole project will be assessed. It is better to implement changes at an early stage of the project, because as the project progresses, the cost of implementing changes also increases.
The input of this stage includes
- Project management plan
- Work performance reports
- Change requests
- EEFs
- OPAs
While the outputs are
- Approved change requests
- Change log
- Project management plan updates
- Project document updates
Validate Scope
Validating scope involves verifying whether the deliverables meet the customer acceptance criteria. The external checking with the customer or stakeholders are part of Validating Scope Management.
The inputs for validating scope includes
- Project management plan
- Requirements
- Documentation
- Requirements traceability matrix
- Verified deliverables
- Work performance data
While the output of the scope validation includes
- Accepted deliverables
- Change requests
- Work performance information
- Project document updates
Control Scope
Control scope ensures that it is the only work identified as being in scope that is delivered. The actual result is compared against the scope baseline and ensures that all of the approved scope is in fact being delivered.
The inputs to control scope process includes
- Project management plan
- Work performance information
- Requirement documentation
- Requirements traceability matrix
- Organizational process assets
While the output includes
- Work performance measurements
- Organizational process assets updates
- Change requests
- Project management plan updates
- Project document updates
Control Schedule
Control Schedule process helps you in many ways. It helps you to capture current schedule status, determine the variance from the schedule baseline, understand the nature of the variance and respond by taking appropriate action.
If changes are needed to the schedule then they must go through the change control process, the change should be re-evaluated and only then it should be used to update the schedule baseline.
There are four main inputs to the control schedule
- Project management plan
- Schedule baseline
- Schedule management plan
- Project schedule
- Work performance information
- Organizational process assets
The output includes
- Work performance measurements
- Organizational process assets updates
- Change requests
- Project management plan updates
- Project document updates
Control Cost
Control cost is comparing baseline cost for each deliverable against the actual cost. The cost baseline should change only in response to a change request that has gone through the Perform Integrated Change Control process. Control cost ensures that your project stay within funding limitations.
The inputs for the Control Cost include
- Project management plan
- Project funding requirements
- Work performance information
- Control Cost Organizational process assets
The output for this include
- Earned value work performance measurements
- Earned value budget forecasts in control costs
- Change requests
- Project management plan updates
- Project document updates
- Organizational process assets updates
Control Quality
The control quality ensures that the project and product are delivered with the quality management plan. It ensures that whether the work is performed correctly. The major output of the control quality is Quality management plan. While the other information that will be helpful are
- Existing flowchart
- Upper and lower control and specification limits contained within the control charts
- Information is referenced such as sample criteria, sampling numbers, measurements and variable sampling
- Quality metrics- it is a standard measurement to meet the quality requirements
- It ensures that the proper steps are being followed in order to comply with aspects such as process, policies or regulations
There are four main outputs from the perform quality control process:
- Integrated change control
- Approved change requests
- Approved change requests review
- Validated changes
Control Communications
Control communication ensures that the right information reaches to the stakeholder. Control communication information includes inputs, tools and techniques and output that belong to this process.
Control communication can be in any format, it can be
- Trending data
- Tabulated information
- S-curve
- Dashboard formats
- Use histogram
In control communication process, work information is taken from various other processes, and the performance report is used as an input for various monitoring and managing processes. The main deliverables from the control communication process is the performance record.
Control Risks
Throughout the project cycle, risk analysis is a continuous process. It is important that you continuously analyze, identify and respond to risks. The activities include in control risk are
- Tracking existing risks
- Monitoring residual risks
- Identifying new risks
- Implementing risk response plans
- Continuously evaluating risk process
The input for control risk are
- Risk register
- Work performance information
- Performance reports
- Reserve analysis
- Risk Audits
The output for the control risk are
- Updating risk register
- Risk management plan
Control Procurements
Out of four procurement plan, the third process of procurement falls in Monitoring & Executing process group. This stage involves monitoring the vendor’s performance and ensuring that all contract requirements are being met.
The control procurement process involves verifying
- Whether goods or service being delivered
- Whether it is delivered on time
- Whether invoice charged is for correct quantity
- Whether all conditions of the contract being met
- Whether the relationship between buyer or seller are managed properly
The major input for procurement process are
- Project management plan
- Procurement documents
- Agreements
- Approved change requests
- Work performance reports
- Work performance data
The output for procurements are
- Work performance information
- Change requests
- Project management plan updates
- Project document updates
- OPAs updates
Control Stakeholder Management
Many project stumble due to inadequate management of stakeholders. If the stakeholders are managed properly, there are more chances for project success. In this process, we monitor the current engagement level of stakeholders and take actions accordingly.
The input and output for all these activities include
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
| Plan Stakeholder Management | Work performance information |
| Issue log | Change requests |
| Work performance data | Project management plan updates |
| Project documents | Project documents updates |
| OPAs updates |
Closing- Phase
Closing phase is the process that performs a controlled shut down of the project at the end. In a project, there are three closure activities that are going on
- Closure of the product- Getting the customer to accept the final deliverables, if the project is external
- Closure of the project- This include formally closing of administrative procedures, updating project documents and archiving those databases & documents
- Closure of the resource behind the project- The financial closure of the project, resources assigned to the project should be returned
The inputs for this process include
- Project Management Plan
- Accepted Deliverables
- OPAs
The output of this process include
- Final output, service or result transition
- OPAs updates
Close Procurements
For each project development life cycle phase- planning, executing, monitoring and controlling & closing there is one procurement process. The final closing procurement is done as per the contract between the seller and buyer.
The closing activities and deliverables include:
-
Project performance reviews including management of risks and issuesUpdated project management plan to reflect actual resultsFinal reports distributed to appropriate stakeholders
The input for closing procurement include
- Project management plan
- Procurement documents
While the output include
- Closed procurement
- OPAs updates
Project Management Ethic of code and conduct
In the end, you will come across project management ethic of code and conduct which deals various human behavioral aspects such as
- Responsibility
- Respect
- Fairness
- Honesty
- Cultural Competence
This code is practiced to induce the confidence and bring a common frame of behavior in the project manager.
Summary
Initiation phase defines those processes that are required to start a new project. It defines what project should accomplish in due course of time.
The initiation phase mainly composed of two main activities
- Develop a Project Charter
- Identify Stakeholders
The stakeholder register and project charter are also useful in other process groups of project management like planning process.
Planning phase determines the scope as well as the objective of the project. It involves creating a set of plans that guides you through the execution and closure phases of the project.
The executing phase consists of those activities that are defined in project management plan. It is the longest phase of the project life cycle and consumes maximum energy and resources. Action taken in execution phase may affect the project management plan or documents.
Key tasks in execution project life cycle phases are
- Execute Project Management Plans
- Direct and Manage Project Execution
- Execute Task Assignments
- Conduct Progress Status Meetings, etc.
During the execution phase, the result may require re-baselining and updates to existing project requirements.
Monitoring and controlling stage ensures that the deliverables are according to the project management plan before closing phase.
The main focus of this phase is to identify any changes made from the point of project management plan to determine preventive action against any unexpected result.
Closing phase is the process that performs a controlled shut down of the project at the end.
Summarize this post with:


