Inheritance in Java (with Example)
What is Inheritance?
Inheritance is a mechanism in which one class acquires the property of another class. For example, a child inherits the traits of his/her parents. With inheritance, we can reuse the fields and methods of the existing class. Hence, inheritance facilitates Reusability and is an important concept of OOPs.
What is Inheritance in Java?
Java Inheritance is a mechanism in which one class acquires the property of another class. In Java, when an “Is-A” relationship exists between two classes, we use Inheritance. The parent class is called a super class and the inherited class is called a subclass. The keyword extends is used by the sub class to inherit the features of super class. Inheritance is important since it leads to the reusability of code.
Java Inheritance Syntax:
class subClass extends superClass
{
//methods and fields
}
Types of Inheritance in Java
Here are the different types of inheritance in Java:
- Single Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
1. Single Inheritance:
In Single Inheritance one class extends another class (one class only).
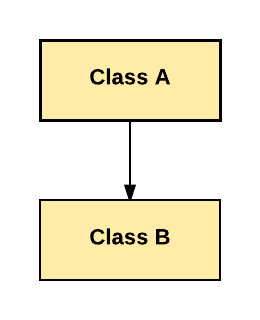
In above diagram, Class B extends only Class A. Class A is a super class and Class B is a Sub-class.
2. Multiple Inheritance:
Multiple Inheritance is one of the inheritance in Java types where one class extending more than one class. Java does not support multiple inheritance.
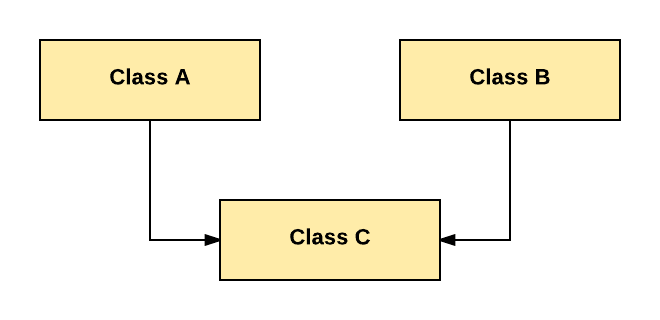
As per above diagram, Class C extends Class A and Class B both.
3. Multilevel Inheritance:
In Multilevel Inheritance, one class can inherit from a derived class. Hence, the derived class becomes the base class for the new class.

As per shown in diagram Class C is subclass of B and B is a of subclass Class A.
4. Hierarchical Inheritance:
In Hierarchical Inheritance, one class is inherited by many sub classes.
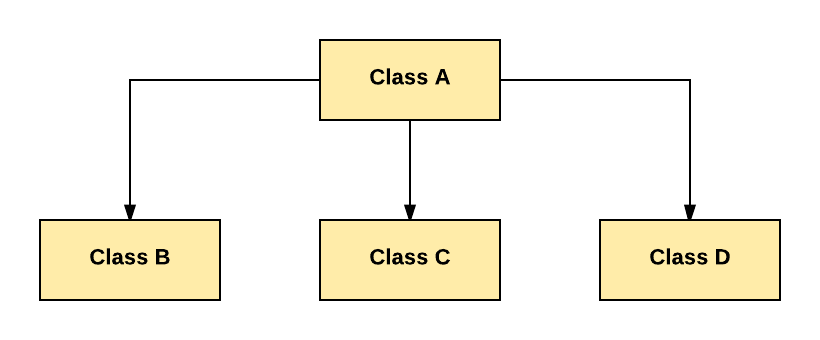
As per above example, Class B, C, and D inherit the same class A.
5. Hybrid Inheritance:
Hybrid inheritance is one of the inheritance types in Java which is a combination of Single and Multiple inheritance.

As per above example, all the public and protected members of Class A are inherited into Class D, first via Class B and secondly via Class C.
Note: Java doesn’t support hybrid/Multiple inheritence
Inheritance in Java Example
Here is an example of inheritance in Java:

class Doctor {
void Doctor_Details() {
System.out.println("Doctor Details...");
}
}
class Surgeon extends Doctor {
void Surgeon_Details() {
System.out.println("Surgen Detail...");
}
}
public class Hospital {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Surgeon s = new Surgeon();
s.Doctor_Details();
s.Surgeon_Details();
}
}
Super Keyword
The super keyword is similar to “this” keyword. The keyword super can be used to access any data member or methods of the parent class. Super keyword can be used at variable, method and constructor level.
Syntax:
super.<method-name>();
Also Check:- this Keyword in Java: What is & How to use with Example
Learn Inheritance in OOP’s with Example
Consider the same banking application from the previous example.
We are supposed to open two different account types, one for saving and another for checking (also known as current).
Let’s compare and study how we can approach coding from a structured and object-oriented programming perspective.
Structural approach: In structured programming, we will create two functions –
- One to withdraw
- And the other for deposit action.
Since the working of these functions remains same across the accounts.
OOP’s approach: While using the OOPs programming approach. We would create two classes.
- Each having implementation of the deposit and withdraw functions.
- This will redundant extra work.
Change Request in Software
Now there is a change in the requirement specification for something that is so common in the software industry. You are supposed to add functionality privileged Banking Account with Overdraft Facility. For a background, overdraft is a facility where you can withdraw an amount more than available the balance in your account.
Structural approach: Using functional approach, I have to modify my withdraw function, which is already tested and baselined. And add a method like below will take care of new requirements.
OOP’s approach: Using OOP’s approach, you just need to write a new class with unique implementation of withdraw function. We never touched the tested piece of code.
Another Change Request
What if the requirement changes further? Like to add credit card account with its own unique requirement of deposits.
Structural approach: Using structural approach you have to change tested piece of deposit code again.
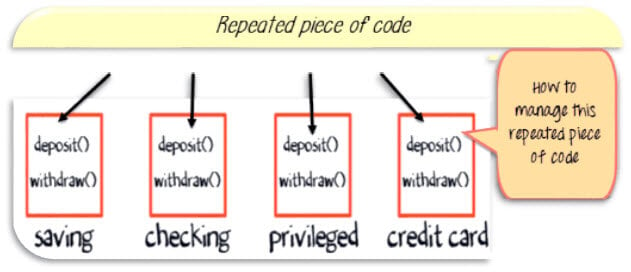
OOP’s approach: But using object-oriented approach, you will just create a new class with its unique implementation of deposit method ( highlighted red in the image below). So even though the structural programming seems like an easy approach initially, OOP’s wins in a long term.
Advantages of Inheritance in OOPs
But one may argue that across all classes, you have a repeated pieces of code.
To overcome this, you create a parent class, say “account” and implement the same function of deposit and withdraw. And make child classes inherited “account” class. So that they will have access to withdraw and deposit functions in account class. The functions are not required to be implemented individually. This is Inheritance in java. .