SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS: Must Know Differences
Key Differences
- A SaaS model provides cloud-based tools and applications to consumers and businesses, whereas a PaaS model allows them to host, manage, and secure their own applications and IaaS allows organizations to manage their business resources like network, server, and data storage.
- SaaS helps you to eliminate the need to have IT staff download and install applications on each computer, while PaaS provides freedom to build the software without the need to worry about software updates. IaaS delivers cloud computing infrastructure through virtualization technology.
- The SaaS model is used by end users, while developers use PAAS, and network architects use the IaaS model.

What is SaaS and PaaS, IaaS?
SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are the three main categories of cloud computing. You can access all three via an Internet browser or online apps available on desktops, mobile, and tablets. Example, OneDrive enables the team to collaborate online instead of needing to work on one common document and send it between the team members.
What is SaaS?
SaaS (Software as a Service) is a web-based deployment model that makes the software accessible through a web browser. As a user of SaaS software, you don’t need to care where the software is hosted, which operating system it uses, or which programming language it is written in. The SaaS software is accessible from any device with an internet connection.
What is PaaS?
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a framework for application creation and deployment. This cloud computing model scales up or down automatically based on demand. The PaaS Cloud service provider manages the servers, storage, and networking, while the developers manage only the application part.
What is IaaS?
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing service offering on-demand computing, storage, and networking resources. It usually works on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Organizations can purchase resources on-demand and as needed instead of buying the hardware outright. The IaaS cloud vendor hosts the infrastructure components, including the on-premises data center, servers, storage, networking hardware, and the hypervisor or virtualization layer.
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: Differences
Here are the significant differences between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS:
| Parameter | SaaS | PaaS | IaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stands for | Software as a service. | Platform as a service. | Infrastructure as a service. |
| Used by | The end users use it. | Developers use PAAS. | Network architects use it. |
| Access | SAAS gives access to the end user. | PAAS gives access to the runtime environment for deployment and development tools | It provides access to the resources like virtual machines and virtual storage. |
| Model | It is a service model in cloud computing that hosts software. | It is a cloud computing service model that delivers tools that are used for the development of applications. | IaaS is a service model that provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. |
| Technical understanding | No need for technical knowledge. | Some knowledge is required for basic setup. | It requires technical writing. |
| Control is given to developers | Nothing | Data of Application | OS, Runtime, Middleware, etc |
| Abstraction | Complete abstraction | Abstraction of the underlying hardware and software resources. | Only for underlying hardware resources |
| Operational Cost | Minimal | Lower | Highest |
| Portability | No portability | Lower | Best |
| Risk of Vendor Interlock | Highest | Medium | Lowest |
| Examples of Cloud services | Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox, CISCO, MS Office Web, etc. | Windows Azure, Force.com, Google App Engine, OpenShift, Heroku, etc. | AWS, Google Compute Engine, Rackspace, Digital Ocean, VCloud Express, Sun, etc. |
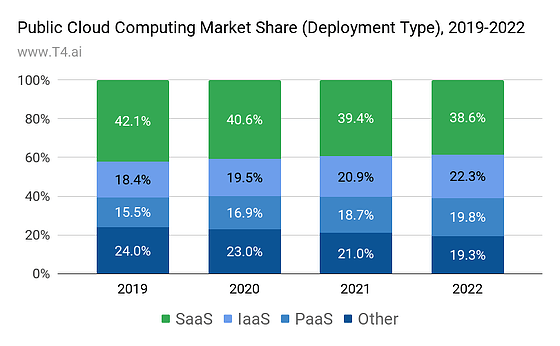
SaaS vs PaaS vs. IaaS market share
You can see how the public cloud computing market share has developed over the years and its projection for 2030. By the end of next year, SaaS will hold 50% of the cloud computing market share. IaaS will hold 28% of the market share, while PaaS will hold 22%.
The trend shows a slight decrease in SaaS and an increase in IaaS and PaaS, which are likely to continue to grow in the coming times.
This trend shows some decrease in SaaS and a slight increase in PaaS and Iaas. This trend is most likely to continue over the next coming years. So, based on that, we can say that even though SaaS has reduced its market share, it remains the dominant cloud computing model and stays the largest cloud service model in terms of cloud spending.
When to use SaaS PaaS and IaaS?
When to use SaaS?
Here are the most common use cases for SaaS:
- Live events are well suited to SaaS models, specific tournaments in live sports, and eSports.
- SaaS helps in delivering applications that can be widely distributed and accessed. For example, Google workspace, Dropbox, Salesforce, CISCO, WebEx, etc.
- Applications such as tax-calculating software are widely used in cloud computing.
- Used by start-ups or small companies that need to launch e-commerce quickly and don’t have time to manage various servers or software issues.
- Short-term projects which need quick, easy, and affordable collaboration.
- SaaS Applications that need both web and mobile access.
When to use PaaS?
Here are the most common use cases for PaaS:
- PaaS is useful for companies developing, running, and managing app interfaces and microservices.
- It is suitable for setting up and managing an organization’s database.
- Using advanced analytics techniques allows you to identify patterns within business data, make predictions, and make more informed business decisions.
- It is also a medium for communication and collaboration, so it features voice, chat, and videos.
- PaaS helps streamline workflows when multiple coders work on the same development project.
- Examples of PaaS are AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku Google App Engine, etc.
When to use IaaS?
Here are the most common use cases for IaaS:
- It is used when you are unsure about new applications’ demands.
- Start-ups and small companies use this technology to avoid spending time and money on purchasing and creating hardware and software.
- Larger companies also prefer this form of cloud computing, as it offers complete control over their applications.
- IaaS allows companies experiencing rapid growth to change hardware and software easily as their needs change.
- It is a helpful model for backing up, storing, and recovering data to manage fluctuating storage needs.
- Many companies are working with Big Data that often use IaaS as it allows them to increase their computing power.
- Because of its stability, IaaS can be a better alternative for complex tasks that include millions of variables or calculations. It might require the use of supercomputers or clusters.
- Users can easily run graphic-intensive applications without latency, as the cloud servers offer superior performance.
- Examples of IaaS are Amazon web service, Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine, etc.
Delivery model of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Here are the Delivery models of each cloud computing model:
SaaS delivery
The SaaS delivery model helps you to eliminate the need for IT staff to download and install applications on each computer. All potential technical issues, like data, middleware, servers, and storage, are managed by SaaS providers. It allows businesses to maintain and support their systems more efficiently.
Pass delivery
The delivery model of PaaS is quite similar to SaaS. The only difference between the two is that PaaS provides a platform for software creation while PaaS is delivered via the web. This cloud computing model allows developers to concentrate on building the software without worrying about software updates, operating systems, storage, or infrastructure. Businesses can also design and develop applications built into the PaaS with special software components.
IaaS delivery
IaaS delivers cloud computing infrastructure through virtualization technology, including servers, networks, operating systems, and storage. These cloud servers are provided to the organization using a dashboard or an API that gives IaaS clients complete control over the entire infrastructure.
It provides the same technology and capabilities as a traditional data center, but you don’t need to maintain or manage all of it. Clients of the IaaS service can access their servers and storage directly, but all of this is outsourced to a “virtual data center” on the cloud.