PostgreSQL LIKE, Not Like, Wildcards (%, _ ) Examples
The PostgreSQL LIKE operator helps us to match text values against patterns using wildcards. It is possible to match the search expression to the pattern expression.
If a match occurs, the LIKE operator returns true. With the help of LIKE operator, it is possible to use wildcards in the WHERE clause of SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT or DELETE statements.
Wild cards
There are only two wildcards that can be used together with
- Percent sign (%)
- Underscore (_)
The percent sign (%) is used to represent zero, one, or many characters or numbers.
The underscore wildcard (_) is used to represent one character or number. These symbols can also be combined. If the LIKE operator is not used together with these two signs, it will act like the equals operator.
Syntax
Here is the syntax for the LIKE operator:
expression LIKE pattern [ ESCAPE 'escape-character' ]
The expression is a character expression like a column or field.
The pattern is a character expression with pattern matching.
The escape-character is an optional parameter. It allows for testing of literal instances of wildcard characters such as % and _. If it is not provided, the \ will be used as the escape character.
Using % wildcard
As we stated earlier, the % sign matches zero, one or more characters or numbers. Consider the following table:
Book:
We want the book whose name is like “Lear…” to get that result, we can run the following command:
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name LIKE 'Lear%';
This will return the following:
The book was found.
Let us search for a book “by” in its name:
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name LIKE '%by%';
This will return the following:
Using _ wildcard
As we stated earlier, the _ sign represents one character or number. It can be used as shown below:
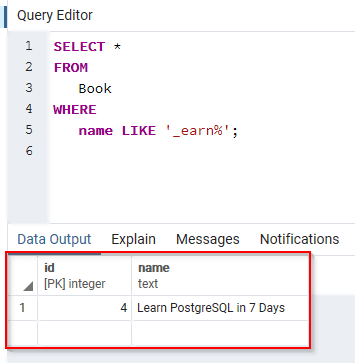
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name LIKE '_earn%';
This returns the following:
Here is another example:
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name LIKE '%Beginner_';
This returns the following:
Using NOT Operator
When the LIKE operator is combined with the NOT operator, any row that does not match the search pattern is returned. For example, to see a book whose name does not begin with “post”, we can run the following command:
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name NOT LIKE 'Post%';
This returns the following:
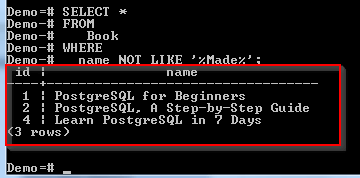
Only one book met the search condition. Let us see the list of books name who don’t have a word “Made”:
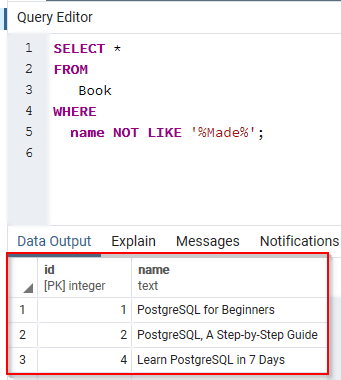
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name NOT LIKE '%Made%';
This returns the following:
3 rows met the search condition.
Using pgAdmin
Now let’s see how the actions can be performed using pgAdmin.
Using % wildcard
Step 1) Login to your pgAdmin account.
Step 2)
- From the navigation bar on the left- Click Databases.
- Click Demo.
Step 3) Type the query in the query editor:
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name LIKE 'Lear%';
Step 4) Click the Execute button.
It should return the following:
To search for a book “by” in its name:
Step 1) Type the following command in the query editor:
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name LIKE '%by%';
Step 2) Click the Execute button.
It should return the following:
Using _ wildcard
Step 1) Login to your pgAdmin account.
Step 2)
- From the navigation bar on the left- Click Databases.
- Click Demo.
Step 3) Type the query in the query editor:
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name LIKE '_earn%';
Step 4) Click the Execute button.
It should return the following:
Step 5) To run the second example:
- Type the following query in the query editor:
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name LIKE '%Beginner_';
- Click the Execute button.
It should return the following:
Using NOT Operator
Step 1) Login to your pgAdmin account.
Step 2)
- From the navigation bar on the left- Click Databases.
- Click Demo.
Step 3) To see all books whose names don’t start with “Post”, type the query in the query editor:
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name NOT LIKE 'Post%';
Step 4) Click the Execute button.
It should return the following:
To see the list of books whose names don’t have the word “Made”:
Step 1) Type the following query in the query editor:
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE name NOT LIKE '%Made%';
Step 2) Click the Execute button.
It should return the following:
Summary
- The PostgreSQL LIKE is used in matching text values against patterns using wildcards.
- The LIKE clause allows us to use wildcards in SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, or DELETE statements.
- The % wildcard matches one or more values. The values can be numbers or characters.
- The _ wildcard matches exactly one value. The value can be a character or a number.
- The LIKE operator can be combined with the NOT operator to return any row that does not match the search pattern.