Different Types of RAM (Random Access Memory) Explained
What is RAM?
The full form of RAM is Random Access Memory. The information stored in this type of memory is lost when the power supply to the PC or laptop is switched off. The information stored in RAM can be checked with the help of BIOS. It is generally known as the main memory or temporary memory or cache memory or volatile memory of the computer system.
History of RAM
Here, are important landmarks from the history of RAM:
| Type of RAM | Year Invented |
|---|---|
| FPM-(Fast page mode RAM)- | 1990 |
| EDO RAM (Extended data out random access memory) | 1994 |
| SDRAM (Single dynamic RAM) | 1996 |
| RDRAM (Rambus RAM) | 1998 |
| DDR (Double Data Rate) | 2000 |
| DDR2 | 2003 |
| DDR3 | 2007 |
| DDR4 | 2012 |
Types of RAM
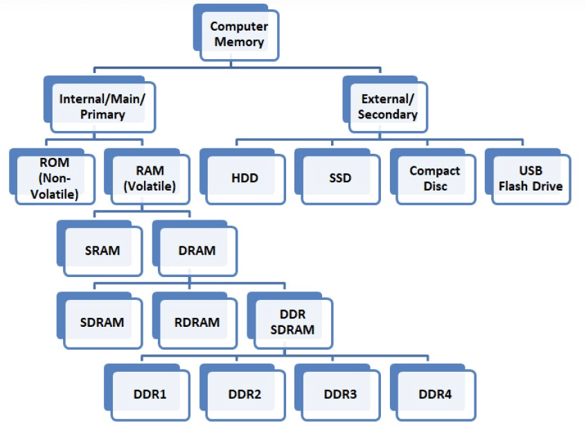
Two main types of RAM are:
- Static RAM
- Dynamic RAM
Static RAM
Static RAM is the full form of SRAM. In this type of RAM, data is stored using the state of a six transistor memory cell. Static RAM is mostly used as a cache memory for the processor (CPU).
Dynamic RAM
DRAM stands for Dynamic Random Access Memory. It is a type of RAM which allows you to stores each bit of data in a separate capacitor within a specific integrated circuit. Dynamic RAM is a standard computer memory of the many modern desktop computers.
This type of RAM is a volatile memory that needs to be refreshed with voltage regularly. Else it loses the information stored on it.
SRAM VS DRAM
| SRAM | DRAM |
|---|---|
| SRAM has lower access time, so it is faster compared to DRAM. | DRAM has higher access time, so it is slower than SRAM. |
| SRAM is costlier than DRAM. | DRAM costs less compared to SRAM. |
| SRAM requires a constant power supply, which means this type of memory which consumes more power. | DRAM offers reduced power consumption because the information is stored in the capacitor. |
| It is a complex internal circuitry, and it offers less storage capacity is available compared to the same physical size of a DRAM memory chip. | It is the small internal circuitry in the one-bit memory cell of DRAM. The large storage capacity is available. |
| SRAM has a low packaging density. | DRAM has a high packaging density. |
Other Important Types of RAM
FPM DRAM

Fast Page Mode Dynamic Random Access Memory is a type of RAM that waits through the entire process of locating a bit of data by column and row and then reading the bit before it begins on the next bit. Max transfer rate is around 176 Mbps.
SDR RAM

SDR RAM is a full form of synchronous dynamic access memory. It has access times between 25 and 10 ns(nanosecond), and they are in DIMM (dual in-line memory module) modules of 168 contacts.
They store data using capacitors using IC’s (Integrated Circuits). On one of its sides, they have terminations, which can be inserted inside of the individual slots for the Motherboard’s memory.
RD RAM

Rambus Dynamic Random Access Memory is a full form of RDRAM. This type of RAM chips works in parallel, which allows you to achieve a data rate of 800 MHz or 1,600 Mbps. It generates much more heat as they operate at such high speeds.
VRAM (Video):

RAM optimized for video adapters is called VRAM. These chips have two ports so that video data can be written to chips at the same time the video adapter regularly reads the memory to refresh the monitor’s current display.
EDO RAM

EDO DRAM is an abbreviation of Extended Data Output Random Access Memory. It doesn’t wait for the completion of the processing of the first bit before continuing to the next one. As soon as the address of the first bit is located, EDO DRAM begins looking for the next bit.
Flash Memory

Flash memory is an electrically erasable and programmable permanent type of memory. It uses a one-transistor memory to store a bit. It offers low power consumption and helps to reduce the cost. It is mainly used in digital cameras, MP3 players, etc.
DDR SDRAM

The full form of DDR SDRAM is Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory. It is just like SDRAM. The only difference between the two is that it has a higher bandwidth, which offers greater speed. It’s maximum transfer rate to L2 cache which is approximately 1,064 Mbps.
Uses of RAM
Here, are important uses of RAM:
- RAM is utilized in the computer as a scratchpad, buffer, and main memory.
- It offers a fast operating speed.
- It is also popular for its compatibility
- It offers low power dissipation
Performance Comparison of RAM Types
| Standard | Time in Market | Internal Rate | Bus Clock(MHZ) | Perfectch | Data rate(MT/s) | Tranfer rate(GB/s) | Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDRAM | 1993 | 100-166 | 100-166 | 1n | 100-166 | 0.8-1.3 | 3.3 |
| DDR | 2000 | 133-200 | 133-200 | 2n | 266-400 | 2.1-3.2 | 2.5/2.6 |
| DDR2 SDRAM | 2003 | 133-200 | 266-400 | 4n | 533-800 | 4.2-6.4 | 1.8 |
| DDR3 | 2007 | 133-200 | 533-800 | 8n | 1066-1600 | 8.5-14.9 | 1.35/1.5 |
| DDR 4 | 2014 | 133-200 | 1066-1600 | 8n | 2133-3200 | 17-21.3 | 1.2 |
Summary
- The full form of RAM is Random Access Memory.
- Two main types of RAM are 1)Static RAM and 2) Dynamic RAM
- Static RAM is the full form of SRAM. In this type of RAM, data is stored using the state of a six transistor memory cell.
- DRAM stands for Dynamic Random Access Memory. It is a type of RAM which allows you to stores each bit of data in a separate capacitor
- FPM DRAM is a full form of Fast Page Mode Dynamic Random Access Memory
- Rambus Dynamic Random Access Memory is an extended form of an RDRAM
- RAM optimized for video adapters is called VRAM.
- EDO DRAM is an abbreviation of Extended Data Output Random Access Memory.
- Flash memory is an electrically erasable and programmable permanent type of memory
- The full form of DDR RAM is Double Data Rate.
- SRAM has lower access time, so it is faster compared to DRAM.
- RAM is utilized in the computer as a scratchpad, buffer, and main memory.
