Difference Between Class and Object in OOPs
Key Differences between Class and Object
- A class is a template for creating objects in a program, whereas the object is an instance of a class.
- A class is a logical entity, while an object is a physical entity.
- A class does not allocate memory space; on the other hand, an object allocates memory space.
- You can declare a class only once, but you can create more than one object using a class.
- Classes can’t be manipulated, while objects can be manipulated.
- Classes don’t have any values, whereas objects have their own values.
- You can create a class using “class” keyword, while hand you can create an object using “new” keyword in Java.

What is Class?
A class is an entity that determines how an object will behave and what the object will contain. In other words, it is a blueprint or a set of instruction to build a specific type of object. It provides initial values for member variables and member functions or methods.
What is Object?
An object is nothing but a self-contained component that consists of methods and properties to make a data useful. It helps you to determines the behavior of the class.
For example, when you send a message to an object, you are asking the object to invoke or execute one of its methods.
From a programming point of view, an object can be a data structure, a variable, or a function that has a memory location allocated. The object is designed as class hierarchies.
Class vs Object – Difference Between Them
Here is the important difference between class and object:
| Class | Object |
|---|---|
| A class is a template for creating objects in program. | The object is an instance of a class. |
| A class is a logical entity | Object is a physical entity |
| A class does not allocate memory space when it is created. | Object allocates memory space whenever they are created. |
| You can declare class only once. | You can create more than one object using a class. |
| Example: Car. | Example: Jaguar, BMW, Tesla, etc. |
| Class generates objects | Objects provide life to the class. |
| Classes can’t be manipulated as they are not available in memory. | They can be manipulated. |
| It doesn’t have any values which are associated with the fields. | Each and every object has its own values, which are associated with the fields. |
| You can create class using “class” keyword. | You can create object using “new” keyword in Java |
Understand the concept of Java Classes and Objects with an example.
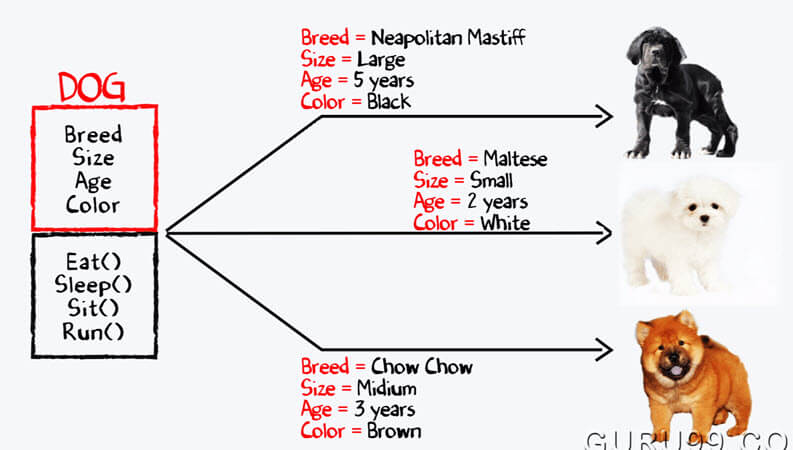
Let’s take an example of developing a pet management system, specially meant for dogs. You will need various information about the dogs like different breeds of the dogs, the age, size, etc.
You need to model real-life beings, i.e., dogs into software entities.
Moreover, the million dollar question is, how you design such software? Here is the solution-
First, let’s do an exercise.
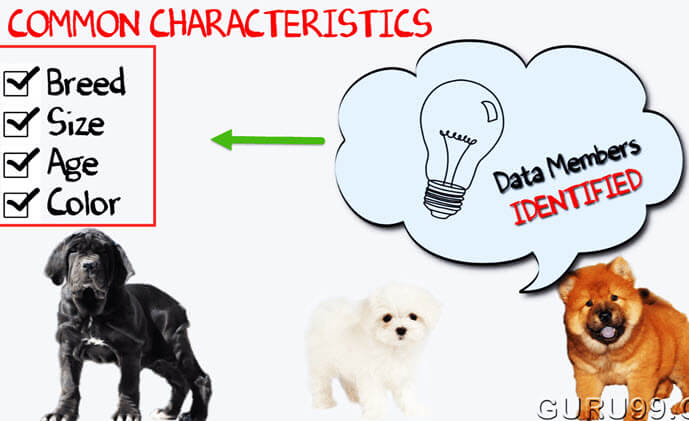
You can see the picture of three different breeds of dogs below.
Stop here right now! List down the differences between them.
Some of the differences you might have listed out maybe breed, age, size, color, etc. If you think for a minute, these differences are also some common characteristics shared by these dogs. These characteristics (breed, age, size, color) can form a data members for your object.
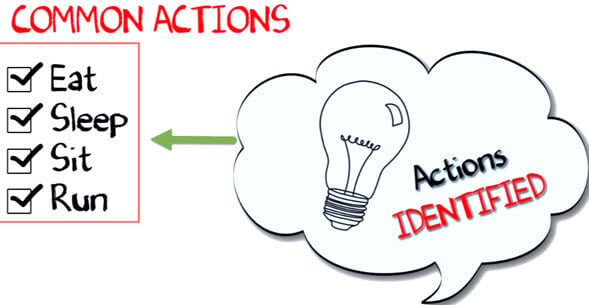
Next, list out the common behaviors of these dogs like sleep, sit, eat, etc. So these will be the actions of our software objects.
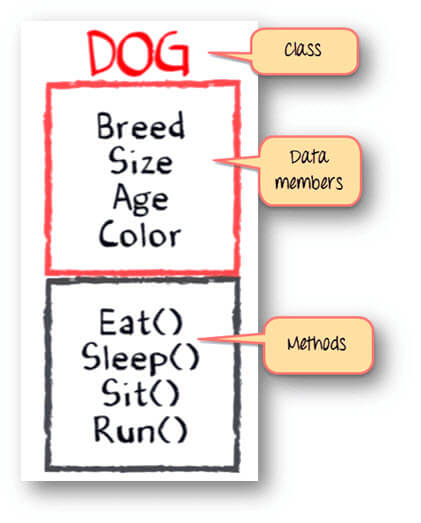
So far we have defined following things,
- Class: Dogs
- Data members or objects: size, age, color, breed, etc.
- Methods: eat, sleep, sit and run.
Now, for different values of data members (breed size, age, and color) in Java class, you will get different dog objects.
You can design any program using this OOPs approach.
Classes and Objects in Java
In the below program, we have declared a class called Dog. We have defined an object of the class called “maltese” using a new keyword. In the last statement System.out.println(maltese.getInfo()); we are displaying dog information like Breed, Size, Age, Color, etc.
// Class Declaration
class Dog {
// Instance Variables
String breed;
String size;
int age;
String color;
// method 1
public String getInfo() {
return ("Breed is: "+breed+" Size is:"+size+" Age is:"+age+" color is: "+color);
}
}
public class Execute{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog maltese = new Dog();
maltese.breed="Maltese";
maltese.size="Small";
maltese.age=2;
maltese.color="white";
System.out.println(maltese.getInfo());
}
}
Output:
Breed is: Maltese Size is: Small Age is:2 color is: white
Types of Class
Following are the important types of class:
Derived Classes and Inheritance
A derived class is a class which is created or derived from other remining class. It is used for increasing the functionality of base class. This type of class derives and inherits properties from existing class. It can also add or share/extends its own properties.
Superclasses:
A superclass is a class from which you can derive many sub classes.
Subclasses:
A subclass is a class that derives from superclass.
Mixed classes
A mixed class is one more functionality that helps you to inherit the properties of one class to another. It uses a subset of the functionality of class, whereas a derive class uses the complete set of superclass functionality.
Uses of Class
Here are the important uses of class:
- Class is used to hold both data variables and member functions.
- It enables you to create user define objects.
- Class provides a way to organize information about data.
- You can use class to inherit the property of other class.
- Classes can be used to take advantage of constructor or destructor.
- It can be used for a large amount of data and complex applications.
Use of Object
Here are the important uses of an object
- It helps you to know the type of message accepted and the type of returned responses.
- You can use an object to access a piece of memory using an object reference variable.
- It is used to manipulate data.
- Objects represent a real-world problem for which you are finding a solution.
- It enables data members and member functions to perform the desired task.