PHP Control Structures: If else, Switch Case
What is a control structure?
Code execution can be grouped into categories as shown below
- Sequential – this one involves executing all the codes in the order in which they have been written.
- Decision – this one involves making a choice given a number of options. The code executed depends on the value of the condition.
A control structure is a block of code that decides the execution path of a program depending on the value of the set condition.
Let’s now look at some of the control structures that PHP supports.
PHP IF Else
If… then… else is the simplest control structure. It evaluates the conditions using Boolean logic
When to use if… then… else
- You have a block of code that should be executed only if a certain condition is true
- You have two options, and you have to select one.
- If… then… else if… is used when you have to select more than two options and you have to select one or more
Syntax The syntax for if… then… else is;
<?php
if (condition is true) {
block one
else
block two
}
?>
HERE,
- “if (condition is true)” is the control structure
- “block one” is the code to be executed if the condition is true
- {…else…} is the fallback if the condition is false
- “block two” is the block of code executed if the condition is false
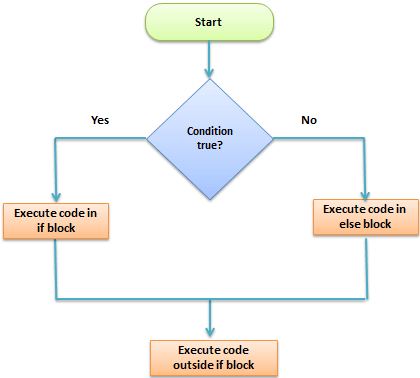
How it works The flow chart shown below illustrates how the if then… else control structure works
Let’s see this in action The code below uses “if… then… else” to determine the larger value between two numbers.
<?php
$first_number = 7;
$second_number = 21;
if ($first_number > $second_number){
echo "$first_number is greater than $second_number";
}else{
echo "$second_number is greater than $first_number";
}
?>
Output:
21 is greater than 7
PHP Switch Case
Switch… case is similar to the if then… else control structure.
It only executes a single block of code depending on the value of the condition.
If no condition has been met then the default block of code is executed.
It has the following basic syntax.
<?php
switch(condition){
case value:
//block of code to be executed
break;
case value2:
//block of code to be executed
break;
default:
//default block code
break;
}
?>
HERE,
- “switch(…){…}” is the control structure block code
- “case value: case…” are the blocks of code to be executed depending on the value of the condition
- “default:” is the block of code to be executed when no value matches with the condition
How it works
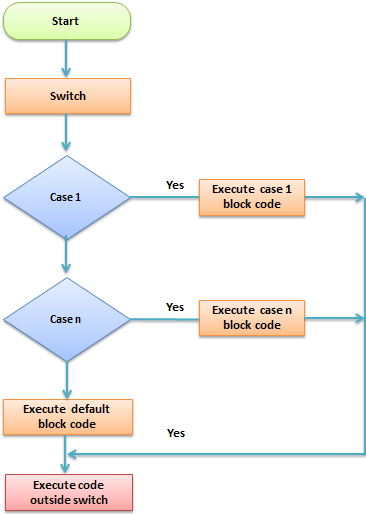
The flow chart shown below illustrates how the switch control structure works
Practical example
The code below uses the switch control structure to display a message depending on the day of the week.
<?php
$today = "wednesday";
switch($today){
case "sunday":
echo "pray for us sinners.";
break;
case "wednesday":
echo "ladies night, take her out for dinner";
break;
case "saturday":
echo "take care as you go out tonight.";
break;
default:
echo "have a nice day at work";
break;
}
?>
Output:
ladies night, take her out for dinner
Summary
- Control structures are used to control the execution of the program
- The if then… else is when you have more than route block of code to execute depending on the value of the condition
- Switch… case is used to when you have a number of block codes, and you only have to execute one of them depending on the value of the set case.