VLAN Trunking Protocol: What is VTP in Networking & Benefits
What is VLAN?
A VLAN is a custom network that is created from one or more Local Area Networks. It allows a group of devices available in multiple networks to be combined into one logical network. The result becomes a virtual LAN that is administered like a physical LAN. The full form of VLAN is Virtual Local Area Network.
What is VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)?
VTP is a Cisco proprietary protocol is used to exchange VLAN information. This type of protocol was developed to effectively manage the transfer of frames from different VLANs on a single physical line. The full form of VTP is the VLAN Trucking Protocol.
Using VTP, you can synchronize VLAN information (like VLAN name or VLAN ID) with switches into the same VTP domain.
For example, let us consider a large size network with 100 switches. Without VTP protocol, if you try to create a VLAN on each Switch, you need to enter VLAN configuration commands on every Switch!
Trunking protocol VTP allows you to create the VLAN only on a single switch. Similarly, if you want to delete a VLAN, you only require deleting it in one switch. After that, it will automatically circulate to every other switch inside the same VTP domain.
Two important VTP techniques are:
- Frame Filtering: This method examines particular information about each frame (MAC address or layer 3 protocol.
- Frame Tagging: This method places a unique identifier in each frame’s header as it is forwarded throughout the network backbone.
Requirements for VTP protocol
Here are some requirements for VTP to communicate VLAN information between CISCO switches.
- The VTP version needs to be the same on the switches that you want to configure.
- The name of the VTP domain must be the same on the switches.
- Authentication should match if applied.
VTP Components
Here are some important Components of VTP
VTP Domain
VTP domain limits the extent to which configuration change are propagated in the network if an error occurs. At a time switch can be a member of only one VTP domain at a time. Until the VTP domain name is specified, you can’t create or modify VLANs on a VTP server mode. VLAN information is not propagated over the network. This component consists of single or multiple interconnected switches.
VTP Pruning
This component prevents unnecessary flooding of broadcast information from one VLAN across all trunks in the VTP domain. It allows pruning on one VTP server switch in one domain is disabled by default. It is enabled by using the VTP pruning global configuration command.
VTP Advertisements
This VTP mode uses a hierarchy of advertisements to synchronize and distribute VLAN configurations in the network. This component distributes VTP domain name and VLAN configurator changes to VTP-enabled switches.
Request advertisements:
Whenever a request for advertisement needs to be sent to a VTP server in the same VTP domain, at that time VTP server responds by sending a summary advertisement and then a subset advertisement.
Request advertisements are sent when:
- The VTP domain name has been changed.
- A summary advertisement comes with a higher configuration revision number.
- A subset advertisement message is missed.
- When the switch has been reset.
Summary Advertisement:
This type of advertisement component contains the VTP domain name, the current revision number, and other VTP configuration details.
- A VTP Server sends it every 5 minutes.
- Notify VTP enables switches of the current VTP configuration revision number.
- They are sent immediately after a configuration change.
Subnet Advertisement:
A subset of advertisements contains VLAN information:
- Creating/ deleting a VLAN
- Suspending/ revoking a VLAN
- Changing the name of a VLAN
- Changing the MTU of a VLAN
VTP Modes
You can configure Switch in three modes: 1) Server, 2) Client, or 3) Transparent.
- VTP Server: VTP servers help you to advertise the VTP domain VLAN information.
- VTP Client: VTP clients function in the same way as VTP servers. A VTP client also enables you to store the VLAN information for the entire domain when the Switch is on.
- VTP Transparent: Transparent switches help you to forward VTP to VTP clients and also to VTP servers. Whenever Switch is running in the transparent mode, you can create and modify VLANs on that Switch.
| VTP Server | VTP Client | VTP Transparent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create/Modify/Delete VLANs | Yes | No | Only local |
| Synchronizes itself | Yes | Yes | No |
| Forwards advertisements | Yes | Yes | Yes |
How VTP Works?
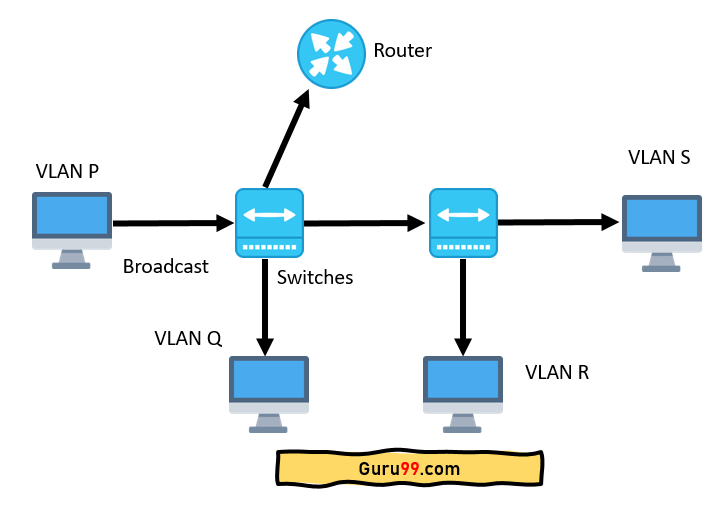
In the diagram above, you can see each switch has two VLANs.
Step 1) On the first switch, VLAN P and VLAN Q are sent through a single port (trunked) to the router and another port to the second switch.
Step 2) VLAN R and VLAN S are trunked from the second switch to the first switch and then the router’s first switch. This trunk can carry traffic from all four VLANs connections.
Step 3) The trunk link from the first switch to the router should be carried to all four VLANs.
Step 4) VLAN P that needs to get to a computer on VLAN Q (or VLAN R or VLAN S) must travel from the switch to the router and return to the switch.
Advantages of VTP
Here are the important pros/benefits of VTP:
- Helps you to separate the network into smaller network VLAN management.
- It allows you to track and monitoring of VLANs accurately.
- Plug-and-play configuration when adding new VLANs.
- VLAN configuration consistency across the network.
- Accurate tracking and monitoring of VLANs.
- Provide dynamic reporting of added VLANs across a network.
- Offers simplify the management of the VLAN database across multiple switches.
- VLAN management on switches like adding, deleting, and renaming VLANs.
- Configurations are consistent and have fewer errors
- Reduce VLAN management.
VTP Configuration Guidelines
Here are some important VTP Configuration Guidelines
- You need to check for incompatible VTP versions and password related issues.
- Incorrect name of VTP mode
- All switches are set to VTP client mode.
VTP Versions
Three types of VTP versions are V1, V2, and V3.
Among the first two versions are similar except that V2 adds support for token ring VLANs.
V3 adds the following features:
- Enhanced authentication
- Support for extended VLANs (1006 to 4094).
- VTP versions 1 and 2 helps you propagate only VLANs 1 to 1005.
- Support for private VLAN
- VTP primary server and VTP secondary servers
- VTP mode off, which disables VTP.
- V3 version offers backward compatibility.
- VTP v3 version can be configured on a per-port basis.
- Protection from unintended database overrides during the insertion of new switches.
- Provide the option of clear text or hidden password protection.
- Configuration option on a per-port which base instead of only a global scheme.
- Optimized resource handling and a more efficient transfer of information.
Summary
- A VLAN is a custom network that is created from one or more Local Area Networks.
- VTP is a Cisco proprietary protocol which is used to exchange VLAN information.
- Important VTP components are 1) VTP domain 2) VTP Pruning, 3) VTP Advertisements.
- Three types of VTP modes are: 1) Server, 2) Client, or 3) Transparent.
- The biggest advantage of VTP is that it helps you to sperate the network into smaller network VLAN management.
- It is important to check for incompatible VTP versions and password related issues.
- V3 version offers backward compatibility and provides optimized resource handling and a more efficient transfer of information.
