Exception Handling in Java
What is Exception in Java?
Exception in Java is an event that interrupts the execution of program instructions and disturbs the normal flow of program execution. It is an object that wraps an error event information that occurred within a method and it is passed to the runtime system. In Java, exceptions are mainly used for indicating different types of error conditions.
There are two types of errors:
- Compile time errors
- Runtime errors
Compile time errors can be again classified again into two types:
- Syntax Errors
- Semantic Errors
Syntax Errors Example:
Instead of declaring int a; you mistakenly declared it as in a; for which compiler will throw an error.
Example: You have declared a variable int a; and after some lines of code you again declare an integer as int a;. All these errors are highlighted when you compile the code.
Runtime Errors Example
A Runtime error is called an Exceptions error. It is any event that interrupts the normal flow of program execution. Example for exceptions are, arithmetic exception, Nullpointer exception, Divide by zero exception, etc. Exceptions in Java are something that is out of developers control.
Click here if the video is not accessible
Why do we need Exception?
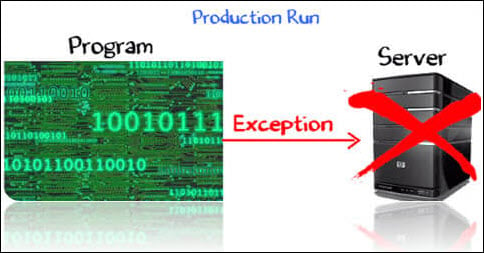
Suppose you have coded a program to access the server. Things worked fine while you were developing the code.
During the actual production run, the server is down. When your program tried to access it, an exception is raised.
How to Handle Exception
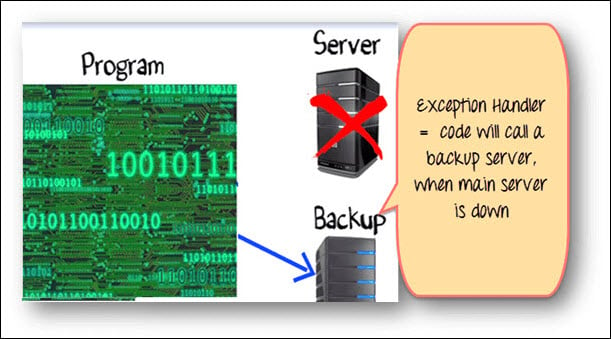
So far we have seen, exception is beyond developer’s control. But blaming your code failure on environmental issues is not a solution. You need a Robust Programming, which takes care of exceptional situations. Such code is known as Exception Handler.
In our example, good exception handling would be, when the server is down, connect to the backup server.
To implement this, enter your code to connect to the server (Using traditional if and else conditions). You will check if the server is down. If yes, write the code to connect to the backup server. Such organization of code, using “if” and “else” loop is not effective when your code has multiple java exceptions to handle.
class connect{
if(Server Up){
// code to connect to server
}
else{
// code to connect to BACKUP server
}
}
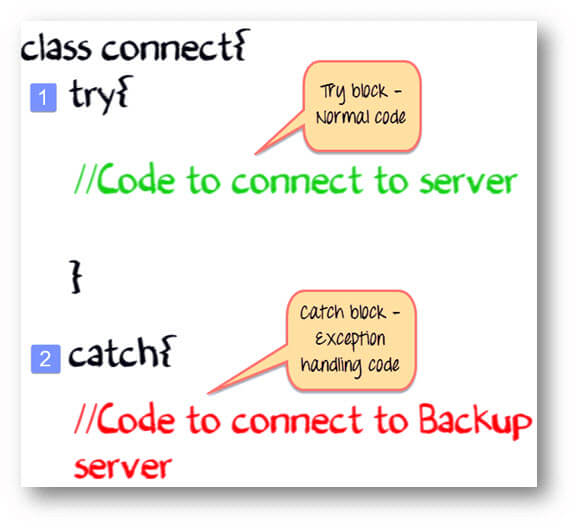
Try Catch Block
Java provides an inbuilt exceptional handling.
- The normal code goes into a TRY block.
- The exception handling code goes into the CATCH block
In our example, TRY block will contain the code to connect to the server. CATCH block will contain the code to connect to the backup server. In case the server is up, the code in the CATCH block will be ignored. In case the server is down, an exception is raised, and the code in catch block will be executed.
So, this is how the exception is handled in Java.
Syntax for using try & catch
try{
statement(s)
}
catch (exceptiontype name){
statement(s)
}
Example
Step 1) Copy the following code into an editor
class JavaException {
public static void main(String args[]){
int d = 0;
int n = 20;
int fraction = n/d;
System.out.println("End Of Main");
}
}
Step 2) Save the file & compile the code. Run the program using command, java JavaException
Step 3) An Arithmetic Exception – divide by zero is shown as below for line # 5 and line # 6 is never executed
Step 4) Now let’s see examine how try and catch will help us to handle this exception. We will put the exception causing the line of code into a try block, followed by a catch block. Copy the following code into the editor.
class JavaException {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int d = 0;
int n = 20;
try {
int fraction = n / d;
System.out.println("This line will not be Executed");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("In the catch Block due to Exception = " + e);
}
System.out.println("End Of Main");
}
}
Step 5) Save, Compile & Run the code.You will get the following output
As you observe, the exception is handled, and the last line of code is also executed. Also, note that Line #7 will not be executed because as soon as an exception is raised the flow of control jumps to the catch block.
Note: The AritmeticException Object “e” carries information about the exception that has occurred which can be useful in taking recovery actions.
Java Exception class Hierarchy
After one catch statement executes, the others are bypassed, and execution continues after the try/catch block. The nested catch blocks follow Exception hierarchy.
- All exception classes in Java extend the class ‘Throwable’. Throwable has two subclasses, Error and Exception
- The Error class defines the exception or the problems that are not expected to occur under normal circumstances by our program, example Memory error, Hardware error, JVM error, etc
- The Exception class represents the exceptions that can be handled by our program, and our program can be recovered from this exception using try and catch block
- A Runtime exception is a sub-class of the exception class. The Exception of these type represents exception that occur at the run time and which cannot be tracked at the compile time. An excellent example of same is divide by zero exception, or null pointer exception, etc
- IO exception is generated during input and output operations
- Interrupted exceptions in Java, is generated during multiple threading.
Example: To understand nesting of try and catch blocks
Step 1) Copy the following code into an editor.
class JavaException {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
int d = 1;
int n = 20;
int fraction = n / d;
int g[] = {
1
};
g[20] = 100;
}
/*catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("In the catch block due to Exception = "+e);
}*/
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("In the catch block due to Exception = " + e);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("In the catch block due to Exception = " + e);
}
System.out.println("End Of Main");
}
}
Step 2) Save the file & compile the code. Run the program using command, java JavaException.
Step 3) An ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException is generated. Change the value of int d to 0. Save, Compile & Run the code.
Step 4) An ArithmeticException must be generated.
Step 5) Uncomment line #10 to line #12. Save, Compile & Run the code.
Step 6) Compilation Error? This is because Exception is the base class of ArithmeticException Exception. Any Exception that is raised by ArithmeticException can be handled by Exception class as well.So the catch block of ArithmeticException will never get a chance to be executed which makes it redundant. Hence the compilation error.
Java Finally Block
The finally block is executed irrespective of an exception being raised in the try block. It is optional to use with a try block.
try {
statement(s)
} catch (ExceptiontType name) {
statement(s)
} finally {
statement(s)
}
In case, an exception is raised in the try block, finally block is executed after the catch block is executed.
Example
Step 1) Copy the following code into an editor.
class JavaException {
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
int d = 0;
int n =20;
int fraction = n/d;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("In the catch block due to Exception = "+e);
}
finally{
System.out.println("Inside the finally block");
}
}
}
Step 2) Save, Compile & Run the Code.
Step 3) Expected output. Finally block is executed even though an exception is raised.
Step 4) Change the value of variable d = 1. Save, Compile and Run the code and observe the output.Bottom of Form
Summary
- An Exception is a run-time error which interrupts the normal flow of program execution.Disruption during the execution of the program is referred as error or exception.
- Errors are classified into two categories
- Compile time errors – Syntax errors, Semantic errors
- Runtime errors- Exception
- A robust program should handle all exceptions and continue with its normal flow of program execution. Java provides an inbuilt exceptional handling method
- Exception Handler is a set of code that handles an exception. Exceptions can be handled in Java using try & catch.
- Try block: Normal code goes on this block.
- Catch block: If there is error in normal code, then it will go into this block