Defect Management Process in Software Testing
What is Defect Management Process?
Defect Management is a systematic process to identify and fix bugs. A defect management cycle contains the following stages 1) Discovery of Defect, 2) Defect Categorization 3) Fixing of Defect by developers 4) Verification by Testers, 5) Defect Closure 6) Defect Reports at the end of project
This topic will guide you on how to apply the defect management process to the project Guru99 Bank website. You can follow the below steps to manage defects.
Step 1) Discovery
In the discovery phase, the project teams have to discover as many defects as possible, before the end customer can discover it. A defect is said to be discovered and change to status accepted when it is acknowledged and accepted by the developers
In the above scenario, the testers discovered 84 defects in the website Guru99.
Let’s have a look at the following scenario; your testing team discovered some issues in the Guru99 Bank website. They consider them as defects and reported to the development team, but there is a conflict –
In such case, as a Test Manager, what will you do?
B) Test Manager takes the role of judge to decide whether the problem is defect or not
C) Agree with the development team that is not a defect
In such case, a resolution process should be applied to solve the conflict, you take the role as a judge to decide whether the website problem is a defect or not.
Step 2) Categorization
Defect categorization help the software developers to prioritize their tasks. That means that this kind of priority helps the developers in fixing those defects first that are highly crucial.
Defects are usually categorized by the Test Manager –
Let’s do a small exercise as following
Drag & Drop the Defect Priority Below| 1) The website performance is too slow |
|
| 2) The login function of the website does not work properly |
|
| 3) The GUI of the website does not display correctly on Mobile devices |
|
| 4) The website could not remember the user login session |
|
| 5) Some links doesn’t work |
|
Here are the recommended answers
| No. | Description | Priority | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
The website performance is too slow |
High |
The performance bug can cause huge inconvenience to user. |
|
2 |
The login function of the website does not work properly |
Critical |
Login is one of the main function of the banking website if this feature does not work, it is serious bugs |
|
3 |
The GUI of the website does not display correctly on mobile devices |
Medium |
The defect affects the user who use Smartphone to view the website. |
|
4 |
The website could not remember the user login session |
High |
This is a serious issue since the user will be able to login but not be able to perform any further transactions |
|
5 |
Some links doesn’t work |
Low |
This is an easy fix for development guys and the user can still access the site without these links |
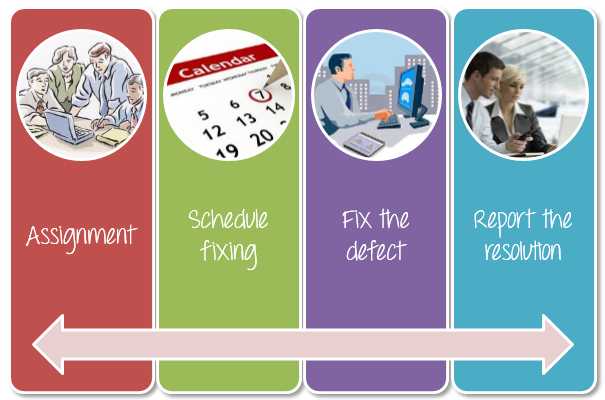
Step 3) Defect Resolution
Defect Resolution in software testing is a step by step process of fixing the defects. Defect resolution process starts with assigning defects to developers, then developers schedule the defect to be fixed as per priority, then defects are fixed and finally developers send a report of resolution to the test manager. This process helps to fix and track defects easily.
You can follow the following steps to fix the defect.
- Assignment: Assigned to a developer or other technician to fix, and changed the status to Responding.
- Schedule fixing: The developer side take charge in this phase. They will create a schedule to fix these defects, depend on the defect priority.
- Fix the defect: While the development team is fixing the defects, the Test Manager tracks the process of fixing defect compare to the above schedule.
- Report the resolution: Get a report of the resolution from developers when defects are fixed.
Step 4) Verification
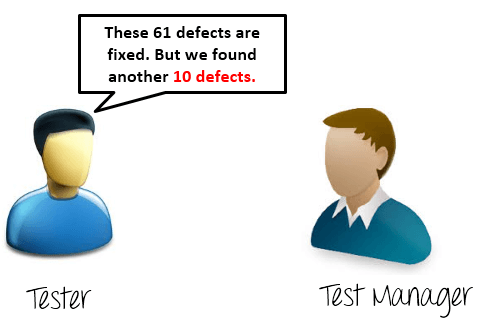
After the development team fixed and reported the defect, the testing team verifies that the defects are actually resolved.
For example, in the above scenario, when the development team reported that they already fixed 61 defects, your team would test again to verify these defects were actually fixed or not.
Step 5) Closure
Once a defect has been resolved and verified, the defect is changed status as closed. If not, you have send a notice to the development to check the defect again.
Step 6) Defect Reporting
Defect Reporting in software testing is a process in which test managers prepare and send the defect report to the management team for feedback on defect management process and defects’ status. Then the management team checks the defect report and sends feedback or provides further support if needed. Defect reporting helps to better communicate, track and explain defects in detail.
The management board has right to know the defect status. They must understand the defect management process to support you in this project. Therefore, you must report them the current defect situation to get feedback from them.
Why do you need Defect Management Process?
Your team found bugs while testing the Guru99 Banking project.
After a week the developer responds –
In next week the tester responds
As in the above case, if the defect communication is done verbally, soon things become very complicated. To control and effectively manage bugs you need a defect lifecycle.
Important Defect Metrics
Back the above scenario. The developer and test teams have reviews the defects reported. Here is the result of that discussion
How to measure and evaluate the quality of the test execution?
This is a question which every Test Manager wants to know. There are 2 parameters which you can consider as following
In the above scenario, you can calculate the defection rejection ratio (DRR) is 20/84 = 0.238 (23.8 %).
Another example, supposed the Guru99 Bank website has total 64 defects, but your testing team only detect 44 defects i.e. they missed 20 defects. Therefore, you can calculate the defect leakage ratio (DLR) is 20/64 = 0.312 (31.2 %).
Conclusion, the quality of test execution is evaluated via following two parameters
The smaller value of DRR and DLR is, the better quality of test execution is. What is the ratio range which is acceptable? This range could be defined and accepted base in the project target or you may refer the metrics of similar projects.
In this project, the recommended value of acceptable ratio is 5 ~ 10%. It means the quality of test execution is low. You should find countermeasure to reduce these ratios such as
- Improve the testing skills of member.
- Spend more time for testing execution, especially for reviewing the test execution results.
FAQs
Click here if the video is not accessible