What is CI/CD? Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery
What is Continuous Integration (CI)?
Continuous Integration is a software development method where team members integrate their work at least once a day. In this method, every integration is checked by an automated build to detect errors. This concept was first introduced over two decades ago to avoid “integration hell,” which happens when integration is put off till the end of a project.
In Continuous Integration after a code commit, the software is built and tested immediately. In a large project with many developers, commits are made many times during a day. With each commit code is built and tested. If the test is passed, build is tested for deployment. If the deployment is a success, the code is pushed to Production. This commit, build, test, and deploy is a continuous process, and hence the name continuous integration/deployment.
What is Continuous Delivery (CD)?
Continuous Delivery is a software engineering method in which a team develops software products in a short cycle. It ensures that software can be easily released at any time. The main aim of continuous delivery is to build, test, and release software with good speed and frequency. It helps you to reduce the cost, time, and risk of delivering changes by allowing for frequent updates in production.
What is the difference between CI and CD?
Development without CI vs. Development with CI
Here are key differences between development using CI or without CI:
| Development without CI | Development with CI |
|---|---|
| Lots of Bugs | Fewer bugs |
| Infrequent commits | Regular commits |
| Infrequent and slow releases | Regular working releases |
| Difficult integration | Easy and Effective Integration |
| Testing happens late | Continuous Integration testing happens early and often. |
| Issue raised are harder to fix | Find and fix problems faster and more efficiently. |
| Poor project visibility | Better project visibility |
Difference between Compilation and Continuous Integration

While compilation only compiles a code, CI does the following activities
DB integration
- Ensure DB and code in sync
- Automated creation of DB and test data.
Code Inspection
- Ensures a healthy codebase
- Identifies problems early and applies best practices
Automated Deployment
- Allows you to release product anytime
- Continually demo-able state and it is works on any machine
Document generation
- Ensure documentation is current
- Removes burned from the developer
- Produces build reports and metrics
Compilation
Compilation is the process the computer takes to convert a high-level programming language code into a machine language that the computer able to understand. It ensures a code compiler on every target platform.
When do I build?
- At every check-in
- Every time a dependency changes
What steps are in continuous integration?

- Ideally, the build should come from the command line and should not depend on an integrated development environment (IDE).
- The build should happen continuously using a dedicated Cl server, not a cron job.
- CI built should be triggered on every check-in and not just at midnight
- The build should provide immediate feedback and Require no developer effort
- Identify key metrics and track them visually. More importantly, act on them immediately
What do you need to conduct CI process?
Here, are the key elements which you need to perform the entire CI process:
- Version Control System (VCS): It offers a reliable method to centralize and preserve changes made to your project over time.
- Virtual Machine: You should have a spare server or at least one virtual machine to build your system.
- Hosted CI Tool Solutions: To avoid servers or virtual machines, you should go for hosted CI tool solutions. This tool helps in the maintenance of the whole process and offers easier scalability.
- Tools: If you select a self-hosted variant, you will need to install one of the many CI tools like Jenkins, TeamCity, Bamboo, GitLab, etc.
How Continuous integration work?
You are surely aware of the old phone Nokia. Nokia used to implement a procedure called nightly build. After multiple commits from diverse developers during the day, the software built every night. Since the software was built only once in a day, it’s a huge pain to isolate, identify, and fix the errors in a large codebase.
Later, they adopted the Continuous Integration approach. The software was built and tested as soon as a developer committed code. If any error is detected, the respective developer can quickly fix the defect.
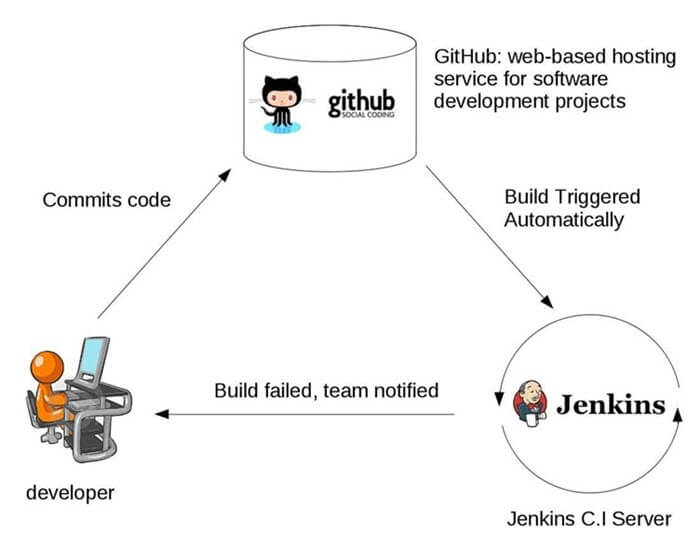
Features of CI
Here, are important features and benefits of Continuous Integration:
- Allows you to maintain just a single source repository
- You can test the clone of the production CI environment
- The built environment should be close to the production environment.
- One of the advantages of continuous integration is Constant availability of a current build
- The complete process of build and testing and deployment should be visible to all the stack holders.
Why Use CI?
Here are important reasons for using Continuous Integration:
- Helps you to build better quality software
- CI process helps to scale up headcount and delivery output of engineering teams.
- CI allows software developers to work independently on features in parallel.
- Helps you to conduct repeatable testing
- Increase visibility enabling greater communication
- Helps develop a potentially shippable product for fully automated build
- Helps you to reduced risks by making deployment faster and more predictable
- immediate feedback when issue arrives
- Avoid last-minute confusion at release date and timing
Best practices of using CI Systems
Here, are some important best practices while implementing
- Commit Early and Commit Often never Commit Broken Code
- Fix build failures immediately
- Act on metrics
- Build-in every target environment Create artifacts from every build
- The build of the software need to be carried out in a manner so that it can be automated
- Do not depend on an IDE
- Build and test everything when it changes
- The database schema counts as everything
- Helps you to find out key metrics and track them visually
- Check-in often and early
- Stronger source code control
- Continuous integration is running unit tests whenever you commit code
- Automate the build and test everyone
- Keep the build fast with automated deployment
Disadvantages of CI
Here, are cons/drawbacks of Continuous Integration process:
- Initial setup time and training is required to get acquainted with Cl server
- Development of suitable test procedures is essential
- Well-developed test-suite required many resources for Cl server
- Conversion of familiar processes
- Requires additional servers and environments
- Waiting times may occur when multiple developers want to integrate their code around the same time
Tools for CI process
Here, are some most essential CI/CD tools:
Jenkins
Jenkins is an open-source continuous integration software. It is written using the Java programming language. It facilitates real-time testing and reporting on isolated changes in a more massive codebase. This software helps developers to quickly find and solve defects in their codebase & automate testing of their builds.
Bamboo
Bamboo is a continuous integration build server that performs – automatic build, test, and releases in a single place. It works seamlessly with JIRA software and Bitbucket. Bamboo supports many languages and technologies such as CodeDeply, Docker, Git, SVN, Mercurial, AWS, and Amazon S3 buckets.
TeamCity
TeamCity is a Continuous Integration server that supports many powerful features. It maintains a CI server healthy and stable even when no builds are running. It provides better code quality for any project
Summary
- Continuous Integration definition: Continuous integration is a software development method where members of the team can integrate their work at least once a day
- CI/CD meaning combination of Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment.
- Development without CI creates lots of bugs whereas Development with CI offers Fewer bugs
- Important activities of Continuous Integration are 1) DB integration, 2) Code Inspection, 3) Automated Deployment, Document generation, and Compilation.
- The build should happen continuously using a dedicated Cl server, not a cron job.
- Important elements of CI are 1) Version Control System 2) Virtual Machine 3) Host CI Tool solutions 4) Tools
- Continuous Integration system allows you to maintain just a single source repository
- CI/CD process helps you to build better quality software
- The most important best practices of Azure Continuous Integration process is to Commit Early and Commit Often never Commit Broken Code
- The major drawback of the CI/CD pipeline process is that well-developed test-suite required many resources for Cl server
- Jenkins, Bambook, and Team City are some useful AWS Continuous Integration tools.




