Blockchain Testing Tutorial
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a shared database store continuously growing list of records, called blocks. Each block contains a hash of the previous block and a timestamp.
In this tutorial, you will learn:
- What is Blockchain?
- Features of Blockchain includes
- Type of Blockchain
- Main Components of a blockchain
- Advantages of Blockchain
- Challenges in Blockchain Testing
- Phases of Blockchain Testing 7
- Key Testing Types on Blockchain Application 10
- Blockchain Testing Tools 10
Features of Blockchain includes
- Decentralized System: Beneficial in Various Industries like finance, real estate Etc.
- Better Security: Uses multiple nodes to complete and authenticate transactions
- Authenticity: Allows the unique algorithm to process data
- Increased Capacity: Increases the capacity of the entire Network
Type of Blockchain
Here are three types of Blockchain :
Consortium Blockchain:
Multiple organizations will have access and authority over the Network. It’s fully decentralized System
Public Blockchain:
In this type of blockchain testing, everyone has access to the Network and can take part in Consensus. Its Decentralized System.
Private Blockchain:
Only Single organizations will have access and authority over the Network. It’s a partially decentralized system.
| Public | Private | Consortium | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Access |
|
|
|
| Participants |
|
|
|
| Security |
|
|
|
| Transaction Speed |
|
|
|
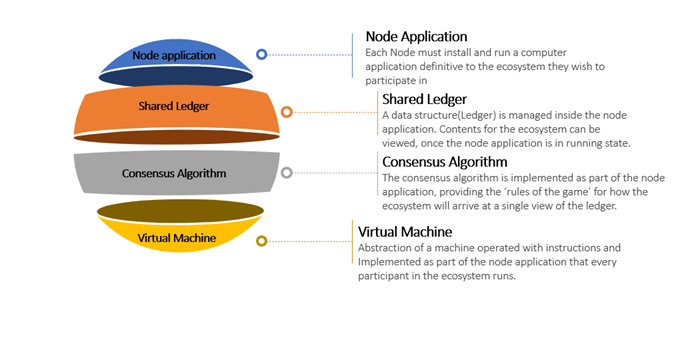
Main Components of a blockchain
Node Application
Each Node must install and run a computer application definitive to the ecosystem they wish to participate in
Shared Ledger
A data structure(ledger) is managed inside the node application. Contents for the ecosystem can be viewed once the node application is in running state.
Consensus Algorithm
The consensus algorithm is implemented as part of the node application, providing the ‘rules of the game’ for how the ecosystem will arrive at a single view of the ledger.
Virtual Machine
Abstraction of a machine operated with instructions and Implemented as part of the node application that every participant m the ecosystem runs.
How Does Blockchain Work?

Advantages of Blockchain
- Time-Saving: Blockchain reduces transaction time from days to minutes. The Transaction solution is faster because it does not demand verification by a central authority.
- Cost-Effective: Blockchain Transactions less handling. Participants can exchange items of value directly. Blockchain removes duplication of effort because participants have access to a shared ledger.
- Increase Security: Blockchain’s security protection against fraud, and cybercrime.
Challenges in Blockchain Testing
- Understanding the Technology– Blockchain is a new technology and understanding the technology with domain knowledge is very important in testing Blockchain Application
- Lack of Blockchain Testing Tools– Blockchain-based applications testing is all about tools. Selecting the right tool as per application is one of the important decisions.
- Defining Test Strategy– Like any application, designing Test Strategy for Blockchain application. It is one of the biggest challenge as Test Strategy demands in-depth knowledge and understanding of the technology and application.
- Block and Chain Size– Along with standard Testing, tools, and the best practices in place, Testing for block size and chain size is also important. Blockchain applications may get fail without proper validation of block size and chain size.
- Integration Testing– As there are multiple components involved in the Blockchain application, integration testing should be done properly and frequently to test that all the components are properly integrated to avoid any failures.
- Performance and Load-Failing to test for performance and load testing gives little or no insight into how the Blockchain application performs in both production as well as under specific workloads and network conditions.
- Security– Securing the data should be the most important in the Blockchain Application. Blockchain can be part of various sectors like Health, finance, etc. any type of malicious attacks can impact the Blockchain application
Phases of Blockchain Testing

Initiation Phase:
- Understanding Blockchain Architecture: In this phase, we understand and analyze the Business and functional requirements. This describes the behavior of the application and how the user will interact with the application
- Full Test Strategy Designing: During this phase, we describe the testing approach for testing an application. This should be done in detail so that every objective are fully covered.
Design Phase:
- Test case Creation: In this phase, the QA team writes the test cases with proper steps. These Testcases are reviewed by Business Analyst(BA).
- Test Data Creation: In this phase, test data is created or extracted from the previous environment against business requirements. Test data can be created manually or using automation tools.
- Environment Setup: In this step, the testing environment is configured as the need for Business or application
- Performance Metrics: Performance Metrics represent the information in terms of performance of application, System or the components
Testing Phase:
- API Testing: In API testing, we ensure that the interaction between applications in the blockchain ecosystem is as expected
- Block Testing: All the blocks on the Network should be tested individually to ensure proper cooperation.
- Functional Testing: In Functional Testing, we evaluate the work of various functional parts of the Blockchain (e.g., smart contracts).
- Performance Testing: Details like network latency based on block size, network size, expected transaction size, and how long a query takes to return the output with the specialized authentication protocol
- Security Testing: In this, we ensure that the application is vulnerable to attacks and Systems can protect the data and is capable of handling malicious attacks, etc.
- Integration Testing: In Integration testing, we ensure that all the components of the application are integrated properly and performing the actions appropriately
- Smart Contract Testing: Smart Contract testing is about performing detailed functional testing of business logic and process.
Report Phase:
- Project Summary Report: Describe the overall overview of project details, project dates, cost, and Task Details
- Smart Contract Testing Report: This report describes the details of Smart contract, data, and rules processing
- Security Testing Report: Shows Vulnerable information in a formal document for the client and higher management. The report contains the date of testing, test data, and Summary of the vulnerabilities found
- performance testing Report: This report shows the details regarding the performance of applications like speed, scalability, reliability, etc.
Key Testing Types on Blockchain Application
Functional Testing
Functional Testing plays an important role in Blockchain Testing as it helps in evaluating business requirements, processes, and effectiveness of use cases. Below are the components that can be tested as part of functional Testing: 1) Block Size and Chain Size 2) Adding a Block 3) Data Transmission
Integration Testing
Blockchain application work in multiple environments. So, it is important to test inter-system connections
Performance Testing:
It helps in identifying hardware and software bottlenecks in advance. This can also help you figure out the potential costs of running the application in the cloud or other environments.
Node Testing
All diverse nodes on the Network must be tested independently to ensure smooth cooperation.
API testing:
Application Programming Interface tests the interaction between applications in the blockchain ecosystem. API Testing ensures that requests and responses are formatted and operated properly.
Blockchain Testing Tools
Here, are some import Blockchain Testing tools:
1)Ethereum Tester:
It is an open-source testing library available on GitHub repo. It is easy to set up with manageable API support for various Testing requirements.
2) Ganache:
It is earlier known as Testrpc, is the widely used library for testing Ethereum contracts locally. It works by spinning up a kind of mock Blockchain that gives you access to accounts you can use for Testing.
3) Hyperledger Composer:
Hyperledger Composer is an open-source tool that helps developers to build blockchain applications. Using this tool, we can perform mainly three types of testing: interactive testing, automated unit, and system testing. If you’re interested in learning how to build blockchain applications and work with tools like Hyperledger Composer, check out this guide on how to become a blockchain developer to kickstart your journey in this exciting field.