Python JSON: 인코딩(덤프), 디코딩(로드) 및 JSON 파일 읽기
JSON이란 무엇입니까? Python?
JSON in Python 에서 영감을 얻은 표준 형식입니다. Java네트워크를 통한 텍스트 형식으로 데이터 교환 및 데이터 전송을 위한 스크립트입니다. 일반적으로 JSON은 문자열 또는 텍스트 형식입니다. API 및 데이터베이스에서 사용할 수 있으며 객체를 이름/값 쌍으로 나타냅니다. JSON은 다음을 의미합니다. Java스크립트 객체 표기법.
Python JSON 구문:
JSON은 키와 값 쌍으로 작성됩니다.
{
"Key": "Value",
"Key": "Value",
}
JSON은 다음과 매우 유사합니다. Python 사전. Python JSON을 지원하며 JSON으로 라이브러리가 내장되어 있습니다.
JSON 라이브러리 Python
'육군 원수'및'간물' 외부 모듈 Python 버전을 유지하다 JSON Python 도서관. JSON 작업 Python 인코딩 및 디코딩과 같은 JSON 관련 작업을 수행하려면 먼저 다음이 필요합니다. import JSON 라이브러리와 이를 위한 .py 파일
import json
JSON에서는 다음 방법을 사용할 수 있습니다. Python 모듈
| 방법 | 기술설명 |
|---|---|
| 우울() | JSON 객체로 인코딩 |
| 덤프() | 파일에 인코딩된 문자열 쓰기 |
| 잔뜩() | JSON 문자열 디코딩 |
| 하중() | JSON 파일을 읽는 동안 디코딩 |
Python JSON으로(인코딩)
JSON 도서관 Python 다음 번역을 수행합니다. Python 기본적으로 객체를 JSON 객체로 변환
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| 딕셔너리 | 목적 |
| 명부 | 배열 |
| 유니 코드 | 끈 |
| 숫자 – int, long | 숫자 - 정수 |
| 뜨다 | 숫자 - 실제 |
| 참된 | 참된 |
| 거짓 | 거짓 |
| 없음 | null로 |
변환 중 Python JSON으로 데이터를 전송하는 것을 인코딩 작업이라고 합니다. 인코딩은 JSON 라이브러리 메서드의 도움으로 수행됩니다. 우울()
JSON 덤프() Python
json.dumps() in Python 사전 객체를 변환하는 방법입니다 Python JSON 문자열 데이터 형식으로 변환합니다. 파싱, 인쇄 등의 작업을 위해 객체가 문자열 형식이어야 할 때 유용합니다.
이제 첫 번째 json.dumps 인코딩 예제를 수행해 보겠습니다. Python:
import json
x = {
"name": "Ken",
"age": 45,
"married": True,
"children": ("Alice","Bob"),
"pets": ['Dog'],
"cars": [
{"model": "Audi A1", "mpg": 15.1},
{"model": "Zeep Compass", "mpg": 18.1}
]
}
# sorting result in asscending order by keys:
sorted_string = json.dumps(x, indent=4, sort_keys=True)
print(sorted_string)
출력:
{"person": {"name": "Kenn", "sex": "male", "age": 28}})
의 예를 보자 Python 동일한 함수를 사용하여 사전의 JSON 파일을 생성하기 위해 파일에 JSON을 작성합니다. 덤프()
# here we create new data_file.json file with write mode using file i/o operation
with open('json_file.json', "w") as file_write:
# write json data into file
json.dump(person_data, file_write)
출력:
표시할 내용이 없습니다… 시스템에 json_file.json이 생성됩니다. 아래 JSON을 파일에 쓰기와 같이 해당 파일을 확인할 수 있습니다. Python 예.
JSON을 Python (디코딩)
JSON 문자열 디코딩은 내장된 메소드의 도움으로 수행됩니다. json.로드() & json.로드() JSON 라이브러리의 Python. 여기 번역표는 JSON 객체의 예를 보여줍니다. Python 사물 디코딩을 수행하는 데 도움이 되는 Python JSON 문자열.
| JSON | Python |
|---|---|
| 목적 | 딕셔너리 |
| 배열 | 명부 |
| 끈 | 유니 코드 |
| 숫자 - 정수 | 숫자 – int, long |
| 숫자 - 실제 | 뜨다 |
| 참된 | 참된 |
| 거짓 | 거짓 |
| null로 | 없음 |
기본 구문 분석 JSON을 살펴보겠습니다. Python 의 도움으로 디코딩의 예 json.로드 기능,
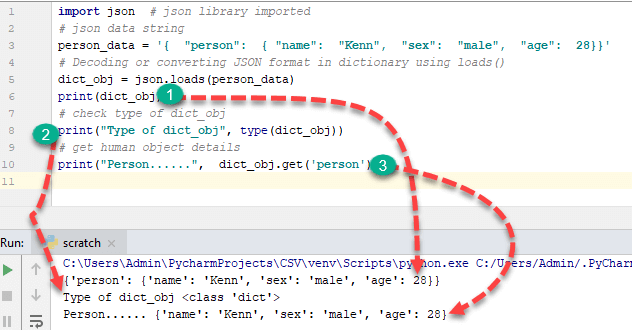
import json # json library imported
# json data string
person_data = '{ "person": { "name": "Kenn", "sex": "male", "age": 28}}'
# Decoding or converting JSON format in dictionary using loads()
dict_obj = json.loads(person_data)
print(dict_obj)
# check type of dict_obj
print("Type of dict_obj", type(dict_obj))
# get human object details
print("Person......", dict_obj.get('person'))
출력:
{'person': {'name': 'Kenn', 'sex': 'male', 'age': 28}}
Type of dict_obj <class 'dict'>
Person...... {'name': 'John', 'sex': 'male'}
JSON 파일 디코딩 또는 JSON 파일 구문 분석 Python
이제 JSON 파일을 읽는 방법을 알아 보겠습니다. Python 과 Python JSON 예를 구문 분석합니다.
알림: JSON 파일 디코딩은 파일 입출력(I/O) 관련 작업입니다. JSON 파일은 프로그램에서 언급한 지정된 위치에 있는 시스템에 존재해야 합니다.
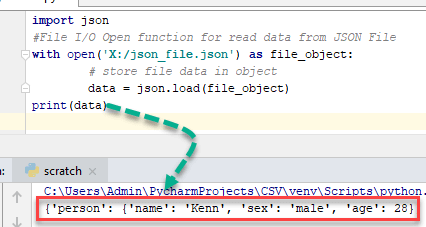
Python JSON 파일 읽기 예:
import json
#File I/O Open function for read data from JSON File
with open('X:/json_file.json') as file_object:
# store file data in object
data = json.load(file_object)
print(data)
여기 데이터 의 사전 객체입니다 Python 위의 읽기 JSON 파일에 표시된 대로 Python 예.
출력:
{'person': {'name': 'Kenn', 'sex': 'male', 'age': 28}}
컴팩트 인코딩 Python
JSON 파일의 크기를 줄여야 하는 경우 다음에서 압축 인코딩을 사용할 수 있습니다. Python.
예,
import json
# Create a List that contains dictionary
lst = ['a', 'b', 'c',{'4': 5, '6': 7}]
# separator used for compact representation of JSON.
# Use of ',' to identify list items
# Use of ':' to identify key and value in dictionary
compact_obj = json.dumps(lst, separators=(',', ':'))
print(compact_obj)
출력:
'["a", "b", "c", {"4": 5, "6": 7}]'
** Here output of JSON is represented in a single line which is the most compact representation by removing the space character from compact_obj **
JSON 코드 형식(예쁜 인쇄)
- 목표는 사람이 이해할 수 있도록 올바른 형식의 코드를 작성하는 것입니다. 예쁜 프린팅의 도움으로 누구나 쉽게 코드를 이해할 수 있습니다.
예:
import json
dic = { 'a': 4, 'b': 5 }
''' To format the code use of indent and 4 shows number of space and use of separator is not necessary but standard way to write code of particular function. '''
formatted_obj = json.dumps(dic, indent=4, separators=(',', ': '))
print(formatted_obj)
출력:
{
"a" : 4,
"b" : 5
}
이를 더 잘 이해하려면 들여쓰기를 40으로 변경하고 출력을 관찰하십시오.
JSON 코드 주문:
sort_keys 속성 Python dumps 함수의 인수는 JSON의 키를 오름차순으로 정렬합니다. sort_keys 인수는 부울 속성입니다. 참이면 정렬이 허용되고 그렇지 않으면 허용되지 않습니다. 다음을 통해 이해해 보겠습니다. Python 문자열을 JSON으로 정렬하는 예입니다.
예,
import json
x = {
"name": "Ken",
"age": 45,
"married": True,
"children": ("Alice", "Bob"),
"pets": [ 'Dog' ],
"cars": [
{"model": "Audi A1", "mpg": 15.1},
{"model": "Zeep Compass", "mpg": 18.1}
],
}
# sorting result in asscending order by keys:
sorted_string = json.dumps(x, indent=4, sort_keys=True)
print(sorted_string)
출력:
{
"age": 45,
"cars": [ {
"model": "Audi A1",
"mpg": 15.1
},
{
"model": "Zeep Compass",
"mpg": 18.1
}
],
"children": [ "Alice",
"Bob"
],
"married": true,
"name": "Ken",
"pets": [
"Dog"
]
}
열쇠의 나이를 관찰할 수 있듯이 자동차, 어린이 등은 오름차순으로 배열됩니다.
복합 객체 인코딩 Python
복합 객체에는 두 가지 다른 부분이 있습니다.
- 실제 부분
- 허수부
예: 3 +2i
복잡한 객체의 인코딩을 수행하기 전에 변수가 복잡한지 아닌지 확인해야 합니다. 인스턴스 메서드를 사용하여 변수에 저장된 값을 확인하는 함수를 만들어야 합니다.
객체가 복잡하거나 인코딩에 적합한지 확인하기 위한 특정 함수를 만들어 보겠습니다.
import json
# create function to check instance is complex or not
def complex_encode(object):
# check using isinstance method
if isinstance(object, complex):
return [object.real, object.imag]
# raised error using exception handling if object is not complex
raise TypeError(repr(object) + " is not JSON serialized")
# perform json encoding by passing parameter
complex_obj = json.dumps(4 + 5j, default=complex_encode)
print(complex_obj)
출력:
'[4.0, 5.0]'
복잡한 JSON 객체 디코딩 Python
JSON에서 복잡한 객체를 디코딩하려면 JSON 문자열에 복잡한 객체가 포함되어 있는지 확인하는 object_hook 매개변수를 사용합니다. 문자열을 JSON으로 이해해 보겠습니다. Python 예,
import json
# function check JSON string contains complex object
def is_complex(objct):
if '__complex__' in objct:
return complex(objct['real'], objct['img'])
return objct
# use of json loads method with object_hook for check object complex or not
complex_object =json.loads('{"__complex__": true, "real": 4, "img": 5}', object_hook = is_complex)
#here we not passed complex object so it's convert into dictionary
simple_object =json.loads('{"real": 6, "img": 7}', object_hook = is_complex)
print("Complex_object......",complex_object)
print("Without_complex_object......",simple_object)
출력:
Complex_object...... (4+5j)
Without_complex_object...... {'real': 6, 'img': 7}
JSON 직렬화 클래스 JSONEncoder 개요
JSONEncoder 클래스는 모든 직렬화에 사용됩니다. Python 인코딩을 수행하는 동안 개체. 여기에는 세 가지 인코딩 방법이 포함되어 있습니다.
- 기본값(o) – 서브클래스에서 구현되고 직렬화 객체를 반환합니다. o 목적.
- 인코딩(o) – JSON 덤프와 동일 Python 메소드는 JSON 문자열을 반환합니다. Python 데이터 구조.
- iterencode(오) – 문자열을 하나씩 표현하고 객체 o를 인코딩합니다.
JSONEncoder 클래스의 encode() 메소드를 사용하면 어떤 것도 인코딩할 수 있습니다. Python 아래 그림과 같은 객체 Python JSON 인코더 예시.
# import JSONEncoder class from json
from json.encoder import JSONEncoder
colour_dict = { "colour": ["red", "yellow", "green" ]}
# directly called encode method of JSON
JSONEncoder().encode(colour_dict)
출력:
'{"colour": ["red", "yellow", "green"]}'
JSON 역직렬화 클래스 JSONDecoder 개요
JSONDecoder 클래스는 모든 데이터의 역직렬화에 사용됩니다. Python 디코딩을 수행하는 동안 개체. 여기에는 세 가지 디코딩 방법이 포함되어 있습니다.
- 기본값(o) – 하위 클래스에서 구현되고 역직렬화된 객체를 반환합니다. o 목적.
- 디코드(o) – json.loads() 메소드 반환과 동일 Python JSON 문자열 또는 데이터의 데이터 구조.
- raw_decode(o) - 대표하다 Python 하나씩 사전화하고 객체 o를 디코딩합니다.
JSONDecoder 클래스의 decode() 메서드를 사용하면 아래와 같이 JSON 문자열을 디코딩할 수도 있습니다. Python JSON 디코더의 예.
import json
# import JSONDecoder class from json
from json.decoder import JSONDecoder
colour_string = '{ "colour": ["red", "yellow"]}'
# directly called decode method of JSON
JSONDecoder().decode(colour_string)
출력:
{'colour': ['red', 'yellow']}
URL에서 JSON 데이터 디코딩: 실제 사례
지정된 URL에서 CityBike NYC(자전거 공유 시스템)의 데이터를 가져옵니다(https://gbfs.citibikenyc.com/gbfs/2.3/gbfs.json) 사전 형식으로 변환합니다.
Python 파일에서 JSON 로드 예:
참고:- 요청 라이브러리가 이미 설치되어 있는지 확인하십시오. Python, 그렇지 않은 경우 터미널 또는 CMD를 열고 다음을 입력하십시오.
- (에 대한 Python 3 이상) pip3 설치 요청
import json
import requests
# get JSON string data from CityBike NYC using web requests library
json_response= requests.get("https://gbfs.citibikenyc.com/gbfs/2.3/gbfs.json")
# check type of json_response object
print(type(json_response.text))
# load data in loads() function of json library
bike_dict = json.loads(json_response.text)
#check type of news_dict
print(type(bike_dict))
# now get stationBeanList key data from dict
print(bike_dict['stationBeanList'][0])
출력:
<class 'str'>
<class 'dict'>
{
'id': 487,
'stationName': 'E 20 St & FDR Drive',
'availableDocks': 24,
'totalDocks': 34,
'latitude': 40.73314259,
'longitude': -73.97573881,
'statusValue': 'In Service',
'statusKey': 1,
'availableBikes': 9,
'stAddress1': 'E 20 St & FDR Drive',
'stAddress2': '',
'city': '',
'postalCode': '',
'location': '',
'altitude': '',
'testStation': False,
'lastCommunicationTime': '2018-12-11 10:59:09 PM', 'landMark': ''
}
JSON 라이브러리와 관련된 예외 Python:
- 클래스 json.JSONDecoder오류 디코딩 작업과 관련된 예외를 처리합니다. 그리고 이것은 다음의 하위 클래스입니다. 값 오류.
- 예외 - json.JSONDecoderError(msg, 문서)
- 예외 매개변수는 다음과 같습니다.
- msg - 형식화되지 않은 오류 메시지
- doc – 구문 분석된 JSON 문서
- pos – 문서가 실패했을 때 문서의 인덱스를 시작합니다.
- lineno – 라인 번호 표시는 pos에 해당합니다.
- 콜론 – pos에 해당하지 않는 열
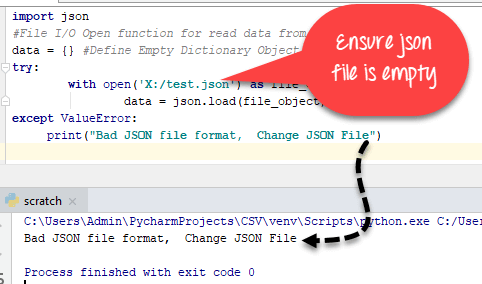
Python 파일에서 JSON 로드 예:
import json
#File I/O Open function for read data from JSON File
data = {} #Define Empty Dictionary Object
try:
with open('json_file_name.json') as file_object:
data = json.load(file_object)
except ValueError:
print("Bad JSON file format, Change JSON File")
무한과 NaN Numbers in Python
JSON 데이터 교환 형식(RFC – Request For Comments)은 무한 또는 Nan 값을 허용하지 않지만 제한은 없습니다. Python- Infinite 및 Nan 값 관련 작업을 수행하는 JSON 라이브러리. JSON이 INFINITE 및 Nan 데이터 유형을 받으면 리터럴로 변환합니다.
예,
import json
# pass float Infinite value
infinite_json = json.dumps(float('inf'))
# check infinite json type
print(infinite_json)
print(type(infinite_json))
json_nan = json.dumps(float('nan'))
print(json_nan)
# pass json_string as Infinity
infinite = json.loads('Infinity')
print(infinite)
# check type of Infinity
print(type(infinite))
출력:
Infinity <class 'str'> NaN inf <class 'float'>
JSON 문자열의 반복 키
RFC는 키 이름이 JSON 객체에서 고유해야 한다고 지정하지만 필수는 아닙니다. Python JSON 라이브러리는 JSON에서 반복되는 개체에 대한 예외를 발생시키지 않습니다. 반복되는 모든 키-값 쌍을 무시하고 그 중 마지막 키-값 쌍만 고려합니다.
- 예,
import json
repeat_pair = '{"a": 1, "a": 2, "a": 3}'
json.loads(repeat_pair)
출력:
{'a': 3}
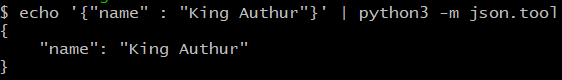
JSON이 포함된 CLI(명령줄 인터페이스) Python
json.tool JSON 예쁜 인쇄 구문을 검증하기 위한 명령줄 인터페이스를 제공합니다. CLI의 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
$ echo '{"name" : "Kings Authur" }' | python3 -m json.tool
출력:
{
"name": " Kings Authur "
}
JSON의 장점 Python
- 컨테이너와 값 사이를 쉽게 뒤로 이동할 수 있습니다(JSON에서 Python 및 Python JSON으로)
- 인간이 읽을 수 있는 (Pretty-print) JSON 객체
- 데이터 처리에 널리 사용됩니다.
- 단일 파일에는 동일한 데이터 구조가 없습니다.
JSON의 구현 제한 사항 Python
- JSON 범위의 역직렬 변환기 및 숫자 예측
- JSON 문자열의 최대 길이와 JSON 배열, 객체 중첩 수준입니다.
Python JSON 치트 시트
| Python JSON 함수 | 기술설명 |
|---|---|
| json.dumps(person_data) | JSON 객체 생성 |
| json.dump(person_data, file_write) | 파일 I/O를 사용하여 JSON 파일 생성 Python |
| Compact_obj = json.dumps(데이터, 구분 기호=(',',':')) | 구분 기호를 사용하여 JSON 개체에서 공백 문자를 제거하여 JSON 개체를 압축합니다. |
| formatted_obj = json.dumps(dic, indent=4, 구분 기호=(',', ': ')) | 들여쓰기를 사용하여 JSON 코드 형식 지정 |
| sorted_string = json.dumps(x, 들여쓰기=4, sort_keys=True) | JSON 객체 키를 알파벳순으로 정렬 |
| complex_obj = json.dumps(4 + 5j, 기본값=complex_encode) | Python JSON의 복합 객체 인코딩 |
| JSONEncoder().encode(color_dict) | 직렬화를 위해 JSONEncoder 클래스 사용 |
| json.loads(data_string) | JSON 문자열 디코딩 Python json.loads() 함수를 사용하는 사전 |
| json.loads('{“__complex__”: true, “real”: 4, “img”: 5}', object_hook = is_complex) | 복잡한 JSON 객체 디코딩 Python |
| JSONDecoder().decode(color_string) | JSON 디코딩을 사용하여 Python 역직렬화를 통해 |