Test di automazione
Che cos'è il test di automazione?
L'Automation Testing è una tecnica di test del software che utilizza strumenti e script specializzati per eseguire automaticamente casi di test, riducendo la necessità di intervento umano. Migliora l'accuratezza, velocizza l'esecuzione e consente una copertura di test più ampia rispetto ai test manuali.
Integrandosi con le pipeline Agile, DevOps e CI/CD, i test di automazione garantiscono la convalida continua delle modifiche al codice, rilasci più rapidi e una qualità affidabile del software. Sebbene non possano sostituire completamente Test manuale metodi quali test esplorativi o di usabilità, è essenziale per la scalabilità, la coerenza e l'efficienza a lungo termine.
Clicchi Qui. se il video non è accessibile
👉 Iscriviti gratuitamente al progetto di test di automazione in tempo reale
Quali sono i tipi di test di automazione
I test di automazione comprendono diverse categorie, ciascuna delle quali ha uno scopo specifico: garantire la qualità del software. La comprensione di queste tipologie consente ai team di sviluppare strategie di test complete che garantiscano una copertura completa dell'intero stack applicativo, ottimizzando al contempo l'allocazione delle risorse e massimizzando il rilevamento dei difetti.
1. Test unitario
Test unitari convalida singoli componenti o moduli in modo isolato, esaminando funzioni, metodi o classi specifiche senza dipendenze.
2. Test di integrazione
Test d'integrazione verifica la comunicazione tra componenti integrati, API e servizi, assicurando che i moduli funzionino correttamente quando combinati.
3. Test di regressione
Test di regressione garantisce che le nuove modifiche al codice non interrompano le funzionalità esistenti eseguendo suite di test complete sulle applicazioni modificate.
4. Test delle prestazioni
Test delle prestazioni valuta il comportamento del sistema in condizioni di carico, misurando i tempi di risposta, la produttività e i limiti di scalabilità.
5. Test di sicurezza
Test di sicurezza identifica vulnerabilità, difetti di autenticazione e lacune di autorizzazione attraverso scansioni sistematiche e test di penetrazione.
6. Test API
Test dell'API convalida i servizi backend indipendentemente dalle interfacce utente, testando i modelli di richiesta/risposta e la gestione degli errori.
7. Test UI/GUI
Test dell'interfaccia utente automatizza le interazioni con gli elementi grafici, convalidando componenti visivi, layout e flussi di lavoro degli utenti su tutti i dispositivi.
8. Test del fumo
Test del fumo esegue una rapida convalida delle funzionalità critiche dopo le nuove build, determinando la stabilità della build prima di effettuare test approfonditi.
9. Test di accettazione
Test di accettazione convalida i requisiti aziendali attraverso uno sviluppo basato sul comportamento, garantendo che le funzionalità soddisfino le aspettative degli utenti.
10. Test basati sui dati
Test basati sui dati separa la logica di test dai dati di test, consentendo a singoli script di convalidare più scenari utilizzando input diversi.
Perché passare dai test manuali a quelli automatici?

I test manuali sono essenziali per i controlli esplorativi, le informazioni sull'usabilità e la convalida delle nuove funzionalità, ma sono lenti, ripetitivi e soggetti a errori quando vengono scalati. Test di automazione affronta queste limitazioni eseguendo rapidamente le suite di test, garantendo l'accuratezza e riducendo lo sforzo umano nelle attività ripetitive.
Differenza tra test manuali e test di automazione
Ecco un rapido confronto affiancato per aiutarti a capire meglio perché passare dai test manuali a quelli automatizzati è vantaggioso:
| Criteri | Test manuale | Test di automazione |
|---|---|---|
| Velocità di esecuzione | Più lento, richiede sforzo umano per ogni esecuzione del test. | Più veloce, esegue automaticamente grandi suite di test. |
| Precisione | Soggetto a errori umani, stanchezza e disattenzione. | Elevata precisione e coerenza nei cicli di prova. |
| Scalabilità | Difficile da adattare ad applicazioni di grandi dimensioni. | Si adatta facilmente a browser, dispositivi e ambienti. |
| Razionalizzazione dei costi | Minori costi iniziali, maggiori costi delle risorse a lungo termine. | Costi di installazione più elevati, ma costi a lungo termine inferiori (ROI migliore). |
| Copertura del test | Limitato dalla capacità umana e dal tempo. | Ampia copertura con test di regressione, prestazioni e multipiattaforma. |
| migliori casi d'uso | Controlli esplorativi, di usabilità, ad hoc o una tantum. | Regressione, prestazioni, integrazione e casi di test ripetitivi. |
Quali casi di test automatizzare?
Non tutti i test sono adatti all'automazione. Il valore di Test di automazione consiste nel concentrarsi sui casi che garantiscono il maggiore ritorno sull'investimento, lasciando gli altri all'esecuzione manuale.
✅ Casi di test migliori adatti all'automazione
- Flussi di lavoro ad alto rischio o critici per l'azienda – eventuali guasti in questo caso possono avere gravi ripercussioni sugli utenti o sui ricavi.
- Test di regressione ripetitivi – eseguito frequentemente con ogni build o release.
- Test ad alta intensità di dati – scenari che richiedono grandi set di dati o più combinazioni di input.
- Scenari multi-browser o multi-piattaforma – garantisce la coerenza tra dispositivi e ambienti.
- Processi manuali che richiedono molto tempo – passaggi noiosi che rallentano i cicli di rilascio.
Qual è il processo per eseguire i test di automazione?
L'implementazione dei test di automazione richiede un approccio sistematico che trasformi le operazioni di test manuali in flussi di lavoro automatizzati, efficienti e scalabili. Di seguito, ho fornito il metodo tradizionale. Processo in 5 fasi per eseguire test di automazione:
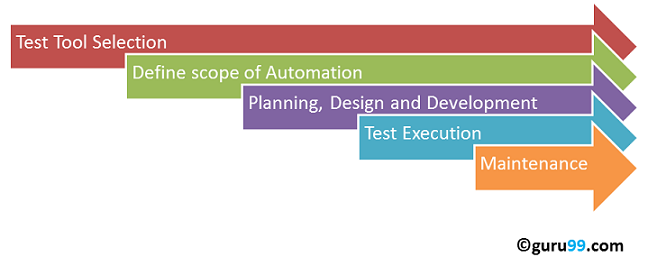
Fase 1: selezione dello strumento di prova
Seleziona l'appropriato strumento di automazione In base alla tecnologia applicativa, alle competenze del team e al budget, la scelta dello strumento giusto determina il successo dell'automazione, incidendo su tutto, dalla velocità di sviluppo ai costi di manutenzione.
Fase 2: definire l'ambito dell'automazione
Determina quali test automatizzare e stabilisci limiti chiari per la tua iniziativa di automazione. Questa pianificazione strategica garantisce il massimo ROI, evitando al contempo le comuni insidie dell'automazione eccessiva o dell'individuazione di aree sbagliate.
Fase 3: Pianificazione, progettazione e sviluppo
Crea il tuo framework di automazione, configura gli ambienti e sviluppa script di test. Questa fase completa trasforma la tua strategia di automazione in suite di test funzionanti che offrono valore immediato.
Fase 4: Esecuzione del test
Esegui test automatizzati in modo efficiente attraverso una pianificazione strategica e l'integrazione con i flussi di lavoro di sviluppo. Una corretta gestione dell'esecuzione garantisce un feedback continuo, ottimizzando al contempo l'utilizzo delle risorse e la copertura dei test.
Passaggio 5: manutenzione
Mantenere la suite di automazione efficiente attraverso aggiornamenti, ottimizzazioni ed espansioni regolari. La manutenzione continua garantisce il successo dell'automazione e il ROI a lungo termine, adattandosi al contempo ai cambiamenti delle applicazioni.
Che cos'è un framework di test di automazione?
Un framework per i test di automazione è come un ricettario per l'automazione dei test: fornisce struttura, linee guida e componenti riutilizzabili che semplificano la creazione e la manutenzione dei test. Consideralo il modello che guida la scrittura, l'organizzazione e l'esecuzione dei test automatizzati.
In parole povere, un framework è un insieme di regole e strumenti che aiutano a creare test automatizzati migliori. Proprio come una casa ha bisogno di fondamenta e struttura prima di aggiungere muri e mobili, i test di automazione necessitano di un framework prima di scrivere gli script di test veri e propri.
Perché hai bisogno di un quadro?
| Senza cornice | Con Framework |
|---|---|
| Scrivi ripetutamente lo stesso codice | Riutilizzare il codice comune nei test |
| I test si interrompono facilmente quando l'applicazione cambia | Aggiornamenti facili quando cambia l'applicazione |
| I diversi membri del team scrivono i test in modo diverso | Tutti seguono gli stessi standard |
| Difficile mantenere e aggiornare i test | I test sono organizzati e gestibili |
Quali sono i diversi tipi di framework di test di automazione
Esploriamo i diversi tipi di framework, partendo dal più semplice al più avanzato. Non preoccuparti: in genere inizierai con quelli più semplici e passerai gradualmente a framework più complessi man mano che acquisisci esperienza.
1. Framework lineare/di registrazione e riproduzione
Il framework più semplice in cui registrare le tue azioni e riprodurle. È come registrare un video di te stesso che le testi e le riproduci.
Come funziona:
Step 1: Open Browser → Record
Step 2: Click Login → Record
Step 3: Enter Username → Record
Step 4: Enter Password → Record
Step 5: Click Submit → RecordStrumento di esempio: Selenium L'IDE registra le azioni del browser e crea automaticamente script di base.
2. Framework modulare/componente
Suddividi l'applicazione in piccoli moduli e crea script separati per ciascuno. Come quando si costruisce con i mattoncini LEGO: ogni blocco è indipendente, ma si combina per creare qualcosa di più grande.
Come funziona:
Module 1: Login Module
├── enterUsername()
├── enterPassword()
└── clickLogin()
Module 2: Search Module
├── enterSearchTerm()
├── clickSearchButton()
└── verifyResults()
Module 3: Checkout Module
├── addToCart()
├── enterShippingDetails()
└── makePayment()Esempio reale: Amazon l'automazione avrebbe moduli separati per Accesso, Ricerca, Carrello, Pagamento, ognuno testato in modo indipendente ma funzionante insieme.
3. Framework basato sui dati
Separa la logica di test dai dati di test. Uno script può testare più scenari utilizzando set di dati diversi, ad esempio utilizzando una ricetta per preparare torte con gusti diversi cambiando gli ingredienti.
Come funziona:
Script di prova (uno script):
def test_login(username, password , expected_result):
enter_username(username)
enter_password(password)
click_login()
verify_result(expected_result)Dati di prova (set multipli):
| Nome utente | Password | Risultato atteso |
|---|---|---|
| valid@email.com | Pass123 | di successo |
| email@non valido | Pass123 | Errore email non valida |
| valid@email.com | Wrongs | Errore password non valida |
| "" | "" | Errore nei campi obbligatori |
Esempio reale: Test di un modulo di registrazione con 50 diversi formati di posta elettronica utilizzando uno script ma 50 righe di dati.
4. Framework basato sulle parole chiave
Utilizza parole chiave semplici per rappresentare le azioni di test. Anche chi non è un programmatore può scrivere test utilizzando queste parole chiave, come se si scrivessero test in un linguaggio semplice.
Come funziona:
Libreria di parole chiave:
OPEN_BROWSER → Opens web browser
NAVIGATE → Goes to URL
CLICK → Clicks element
TYPE → Enters text
VERIFY → Checks resultCaso di prova (senza codice):
| step | Parola chiave | Target | Dati |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | APRI_BROWSER | Chrome | - |
| 2 | NAVIGARE | - | www.amazon.com |
| 3 | CLICCA | Cerca Box | - |
| 4 | TIPO | Cerca Box | Laptop |
| 5 | CLICCA | Pulsante di ricerca | - |
| 6 | VERIFICA | Pagina dei risultati | Computer portatili trovati |
Esempio reale: Gli analisti aziendali scrivono casi di test in Excel utilizzando parole chiave, gli ingegneri dell'automazione li eseguono.
5. Framework ibrido
Combina le migliori funzionalità di più framework. Come un coltellino svizzero, contiene tutti gli strumenti necessari in un unico pacchetto.
Come funziona:
Hybrid Framework Structure:
├── Modular Components (Reusable Functions)
├── Data-Driven Capability (External Test Data)
├── Keyword Library (For Non-Technical Users)
├── Page Objects (UI Element Organization)
└── Reporting (Detailed Test Reports)Esempio reale: La maggior parte delle aziende utilizza framework ibridi che combinano progettazione modulare, test basati sui dati e funzionalità basate su parole chiave.
6. Quadro di sviluppo guidato dal comportamento (BDD)
Scrivi test in un linguaggio semplice e comprensibile a tutti: professionisti, sviluppatori e tester. I test sono come storie utente.
Come funziona:
Scenario di prova (in inglese semplice):
cetriolino
Feature: Shopping Cart
Scenario: Add product to cart
Given I am on the product page
When I click "Add to Cart" button
Then the product should be in my cart
And the cart count should show "1"Dietro le quinte (Codice):
python
@given('I am on the product page')
def open_product_page()
browser.navigate_to('product-page')
@when('I click "Add to Cart" button')
def click_add_to_cart():
browser.click('add-to-cart-button')Strumenti popolari: Cucumber, SpecFlow, comportarsi
Esempio reale: Netflix potrebbe usare BDD per testare "Dato che sono un utente premium, quando cerco contenuti 4K, dovrei vedere film 4K".
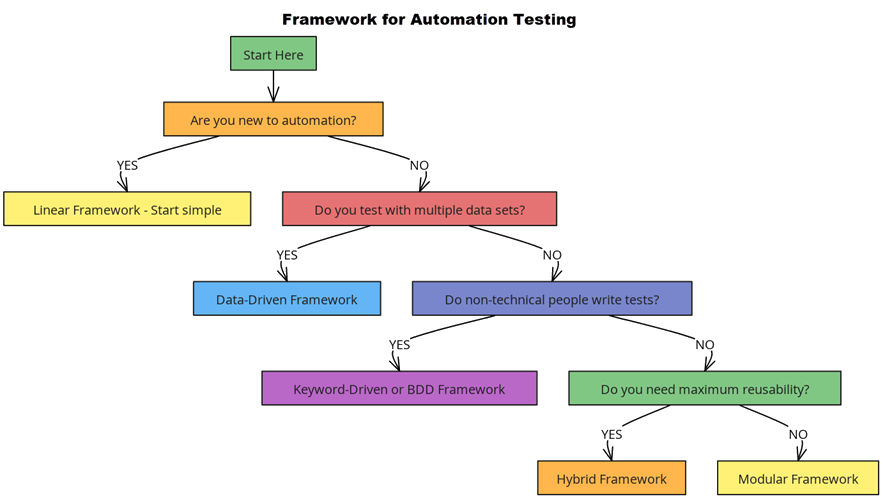
Come selezionare il framework giusto per i test di automazione?
Di seguito ho fornito un diagramma di flusso decisionale per spiegare gli scenari migliori per scegliere il framework giusto:
✅ COSE DA FARE:
- Inizia semplice: Inizia con una struttura di base, evolvi gradualmente
- Seguire gli standard: Denominazione coerente, struttura delle cartelle
- Controllo della versione: Usa Git fin dal primo giorno
- Documenta tutto: Gli altri dovrebbero comprendere il tuo quadro
- Refactoring regolare: Migliorare continuamente la qualità del codice
❌ COSE DA NON FARE:
- Sovra-ingegnerizzazione: Non creare funzionalità di cui non hai ancora bisogno
- Valori hardcoded: Utilizzare invece i file di configurazione
- Ignora manutenzione: Aggiorna il framework con le modifiche dell'applicazione
- Saltare Revopinioni: Ricevi feedback dai membri del team
- Dimentica l'allenamento: Assicurarsi che il team sappia come utilizzare il framework
Come scegliere lo strumento giusto per i test di automazione?
La scelta del giusto strumento di test di automazione è fondamentale per il successo del progetto. La decisione dovrebbe basarsi su tipo di applicazione, competenza del team, esigenze di scalabilità e ROI a lungo termine.
Fattori chiave da considerare:
- Allineamento tecnologico e supporto linguistico: Assicurati che lo strumento sia adatto al tipo di applicazione (web, mobile, ecc.) e supporti i linguaggi di programmazione preferiti dal tuo team (ad esempio, Java, Python, JavaCopione).
- Multipiattaforma e scalabilità: Scegli strumenti che offrano un'ampia copertura su browser, dispositivi e sistemi operativi e che siano scalabili per test a livello aziendale con esecuzione parallela.
- Integrazione CI/CD e DevOps: Cerca una compatibilità perfetta con i tuoi strumenti di pipeline come Jenkins, GitHub Actions o GitLab per abilitare test continui.
- Usabilità e supporto della comunità: Dare priorità a strumenti con interfacce intuitive, documentazione solida e community attive o supporto da parte dei fornitori per ridurre la curva di apprendimento e velocizzare la risoluzione dei problemi.
- Reporting, costi e licenze: Scegli soluzioni che forniscano dashboard e analisi approfondite e che bilancino i vincoli di budget con modelli di licenza: open source vs commerciale.
8 migliori strumenti di test di automazione
Un'ampia gamma di strumenti supporta i test di automazione, ognuno dei quali si adatta a diversi ambienti e requisiti di test. La scelta dello strumento giusto dipende dal tipo di applicazione, dallo stack tecnologico, dal budget e dalle competenze del team.
1) Prova sigma
Prova sigma è una moderna piattaforma di test di automazione basata su cloud che consente ai team di creare ed eseguire test su applicazioni web, mobile, API e desktop utilizzando semplici prompt in inglese con agenti di intelligenza artificiale. È progettata per adattarsi alle pratiche di test continuo in ambienti Agile e DevOps, semplificando i flussi di lavoro di garanzia della qualità senza la complessità dei tradizionali framework di scripting.
Caratteristiche:
- Creazione di test senza codice per un'automazione più rapida: Questa funzionalità consente di creare test automatizzati utilizzando semplici comandi in inglese, senza dover scrivere codice complesso. L'ho utilizzata per accelerare lo sviluppo dei test e consentire una più ampia collaborazione tra team, consentendo sia ai membri tecnici che a quelli non tecnici di contribuire in modo efficiente alle attività di garanzia della qualità.
- Test multi-applicazione in un'unica piattaforma: Testsigma fornisce un supporto completo per test web, mobile, API e desktop da un'unica interfaccia unificata. Questo mi ha aiutato a consolidare il mio stack di test ed eliminare il sovraccarico dovuto alla gestione di più strumenti e framework separati.
- Esecuzione parallela su più browser e dispositivi: Permette di eseguire test simultaneamente su diversi browser, dispositivi e sistemi operativi su larga scala. Ho trovato questa funzionalità preziosa per accelerare i cicli di test e garantire un comportamento coerente delle applicazioni in diversi ambienti utente.
- Auto-riparazione basata sull'intelligenza artificiale e manutenzione intelligente: La piattaforma utilizza algoritmi intelligenti per adattare automaticamente i test quando cambiano gli elementi dell'interfaccia utente, riducendo i costi di manutenzione. Ho utilizzato questa funzionalità per ridurre al minimo le interruzioni dei test durante i cicli di sviluppo rapidi e mantenere stabili le suite di automazione attraverso frequenti aggiornamenti delle applicazioni.
- Integrazioni complete CI/CD e DevOps: Testsigma si integra perfettamente con le più diffuse pipeline di CI/CD, sistemi di controllo delle versioni e strumenti di tracciamento dei bug. Consiglio di sfruttare queste integrazioni per integrare i test continui nel flusso di lavoro di sviluppo e abilitare cicli di feedback rapidi.
Vantaggi
Svantaggi
Prezzi:
- Prezzo: Prezzi personalizzati forniti direttamente da Testsigma in base all'utilizzo, alle funzionalità e alla struttura del team
- Prova gratuita: Prova gratuita di 14 giorni
Prova gratuita di 14 giorni
2. Selenium
Uno strumento open source per il test delle applicazioni web. Supporta più browser, piattaforme e linguaggi come Java, Pythone C#. Ideale per test di regressione e cross-browser.
link: https://www.selenium.dev/downloads/
3. Appium
Un framework open source per il test delle app mobili su Android e iOS. Consente di scrivere test nei linguaggi di programmazione più diffusi e supporta app native, ibride e web.
link: https://appium.io/docs/en/2.0/quickstart/install/
4. Cypress
Uno strumento moderno per i test front-end. Fornisce test rapidi e affidabili per JavaApplicazioni web basate su script con debug integrato e ricaricamento in tempo reale.
link: https://docs.cypress.io/app/get-started/install-cypress
5. Drammaturgo
Uno strumento di test cross-browser di MicrosoftSupporta l'esecuzione parallela su Chromium, Firefoxe WebKit, rendendolo ideale per la scalabilità.
link: https://playwright.dev/docs/intro
6. TestNG
Un framework di test per Java Supporta test unitari, funzionali e di integrazione. Offre funzionalità avanzate come annotazioni, esecuzione parallela e reporting dettagliato.
link: https://testng.org/download.html
7. JMeter
Uno strumento Apache principalmente per test di prestazioni e carico. Simula più utenti e valuta la stabilità dell'applicazione sotto stress.
link: https://jmeter.apache.org/download_jmeter.cgi
8. Jenkins
Un server di automazione utilizzato per l'integrazione continua e la distribuzione continua (CI/CD). Si integra con diversi strumenti di test per un feedback e una distribuzione continui.
link: https://www.jenkins.io/download/
9. Cucumber
Uno strumento di sviluppo guidato dal comportamento (BDD). Consente di scrivere casi di test in sintassi Gherkin leggibile, colmando il divario tra team aziendali e tecnici.
link: https://cucumber.io/docs/installation/
Prova oggi stesso i migliori strumenti di test di automazione
migliori pratiche per i test di automazione
Seguire le best practice garantisce maggiore affidabilità, manutenibilità e ROI dagli sforzi di automazione:
- Ambito strategico e selezione degli strumenti: Concentrati sull'automazione di casi di test stabili e di alto valore utilizzando strumenti allineati al tuo stack tecnologico e agli obiettivi del progetto.
- Quadro normativo e standard: Adottare framework scalabili (basati sui dati, basati sulle parole chiave, ibridi) e applicare pratiche di codifica pulite e coerenti per la manutenibilità.
- Manutenzione dei dati di test e degli script: Gestisci dati di test riutilizzabili e sicuri e aggiorna regolarmente gli script per riflettere le funzionalità dell'applicazione in evoluzione.
- Integrazione CI/CD ed esecuzione parallela: Integra l'automazione nelle pipeline Agile/DevOps ed esegui test contemporaneamente su più piattaforme per un feedback e una copertura più rapidi.
- Approccio equilibrato e monitoraggio delle metriche: Combina l'automazione con i test manuali per ottenere informazioni sull'usabilità e monitora le metriche chiave per ottimizzare le prestazioni e l'efficacia
Quali sono i vantaggi dell'utilizzo dei test di automazione?

I test di automazione offrono numerosi vantaggi che li rendono essenziali nello sviluppo software moderno:
- Velocità e scalabilità: Esegue le suite di test più velocemente dei test manuali e supporta esecuzioni parallele su browser, piattaforme e dispositivi.
- Copertura e accuratezza: Convalida diversi scenari con risultati coerenti, riducendo al minimo l'errore umano e massimizzando l'affidabilità.
- Efficienza e riutilizzabilità: Riduce lo sforzo a lungo termine tramite script riutilizzabili e abbassa i costi complessivi dei test nonostante l'investimento iniziale di configurazione.
- CI/CD e rilevamento precoce: Si integra perfettamente con le pipeline DevOps per consentire test continui e rilevare bug nelle prime fasi del ciclo di sviluppo.
- Reporting e produttività: Offre dashboard dettagliate per analisi rapide e consente ai tester di concentrarsi su test esplorativi e di alto valore.
Quali sono le sfide e i limiti dei test di automazione?
Sebbene siano potenti, i test di automazione presentano delle sfide che devono essere considerate:
- Installazione e costi generali: Richiede un investimento iniziale in strumenti, infrastrutture e risorse qualificate, con una configurazione che richiede molto tempo e ritarda il ROI iniziale.
- Lacune nel giudizio umano: L'automazione non può sostituire completamente i test esplorativi, di usabilità o visivi; l'intuizione umana rimane essenziale per la convalida dell'esperienza utente.
- Rischi di manutenzione e affidabilità: Frequenti aggiornamenti degli script, limitazioni degli strumenti e potenziali falsi positivi/negativi possono erodere la fiducia e richiedere uno sforzo continuo
Ricorda: L'automazione dovrebbe integrare, non sostituire, i test manuali, garantendo un approccio equilibrato per la garanzia della qualità.
Come funziona l'automazione dei test negli ambienti Agile e Enterprise?
I test di automazione sono essenziali per i flussi di lavoro Agile e DevOps, poiché consentono rilasci rapidi, rilevamento precoce dei bug e distribuzione continua. Le suite di test vengono eseguite con ogni build per garantire stabilità e accelerare i cicli di sprint.
Elementi chiave della strategia:
- Framework scalabili: Supporta grandi suite di test, esecuzione multipiattaforma e test basati su cloud.
- Squadre collaborative: Definire i ruoli tra gli architetti QA, sviluppo e automazione all'interno dei team Agile.
- Governance e metriche: Applicare standard di codifica, controllo delle versioni e monitorare KPI quali copertura, percentuali di difetti e ROI.
- Formazione continua: Migliorare le competenze dei team in strumenti come Appium e drammaturgo per rimanere in testa.
- Test bilanciati: Combina l'automazione con test esplorativi e di usabilità per una copertura completa.
Come implementare i test di automazione nelle pipeline CI/CD?
L'integrazione dell'automazione in CI/CD garantisce che ogni modifica al codice venga convalidata in modo tempestivo e coerente prima della distribuzione.
Passaggi chiave per l'implementazione:
- Seleziona strumenti compatibili – Integrare framework come Selenium, Cypress, o drammaturgo con Strumenti CI / CD come Jenkins, GitHub Actions o GitLab CI.
- Configurare le suite di test – Organizzare test di regressione, integrazione e unitari da eseguire automaticamente dopo ogni commit o richiesta pull.
- Abilita esecuzione parallela – Esegui test simultaneamente su più browser e ambienti per ridurre i tempi di compilazione.
- Shift-Test sinistro – Includere test automatizzati in una fase iniziale del ciclo di sviluppo per un feedback più rapido.
- Reporting continuo – Generare dashboard con percentuali di superamento/fallimento, tendenze dei difetti e copertura dei test.
Esempio: Un team DevOps configura una pipeline in Jenkins per attivare test unitari a ogni commit, test di regressione ogni notte e test end-to-end completi prima della distribuzione in produzione. Gli errori vengono automaticamente notificati agli sviluppatori, impedendo al codice difettoso di raggiungere gli utenti.
Questo approccio migliora fiducia nella distribuzione, accelera le versioni e riduce i difetti di post-produzione, rendendo l'automazione un componente fondamentale delle moderne pipeline CI/CD.
Domande Frequenti
Sintesi
I test di automazione sono diventati indispensabili per lo sviluppo software moderno, consentendo rilasci più rapidi, maggiore precisione e maggiore scalabilità rispetto ai metodi manuali. Sebbene non possa sostituire completamente i test condotti da personale umano, come i controlli esplorativi e di usabilità, fornisce una solida base per un controllo di qualità affidabile e ripetibile.
Le organizzazioni che adottano una strategia di test bilanciata, che combina l'automazione con l'intuizione umana, raggiungeranno consegna più rapida, costi ridotti e qualità del software migliorataCon la crescita dell'adozione dell'intelligenza artificiale, i test di automazione evolveranno dall'esecuzione basata su regole a sistemi intelligenti e consapevoli del contesto che migliorano costantemente con i dati.