SAP HANA Architecture, LandScape, Sizing: Complete Tutorial
SAP HANA Database is Main-Memory centric data management platform. SAP HANA Database runs on SUSE Linux Enterprises Server and builds on C++ Language.
SAP HANA Database can be distributed to multiple machines.
SAP HANA Advantages are as mentioned below –
- SAP HANA is useful as it’s very fast due to all data loaded in-Memory and no need to load data from disk.
- SAP HANA can be used for the purpose of OLAP (On-line analytic) and OLTP (On-Line Transaction) on a single database.
SAP HANA Database consists of a set of in-memory processing engines. Calculation engine is main in-memory Processing engines in SAP HANA. It works with other processing engine like Relational database Engine(Row and Column engine), OLAP Engine, etc.
Relational database table resides in column or row store.
There are two storage types for SAP HANA table.
- Row type storage (For Row Table).
- Column type storage (For Column Table).
Text data and Graph data resides in Text Engine and Graph Engine respectively. There are some more engines in SAP HANA Database. The data is allowed to store in these engines as long as enough space is available.
SAP HANA Architecture
Data is compressed by different compression techniques (e.g. dictionary encoding, run length encoding, sparse encoding, cluster encoding, indirect encoding) in SAP HANA Column store.
When main memory limit is reached in SAP HANA, the whole database objects (table, view,etc.) that are not used will be unloaded from the main memory and saved into the disk.
These objects names are defined by application semantic and reloaded into main memory from the disk when required again. Under normal circumstances SAP HANA database manages unloading and loading of data automatically.
However, the user can load and unload data from individual table manually by selecting a table in SAP HANA studio in respective Schema- by right-clicking and selecting the option “Unload/Load”.
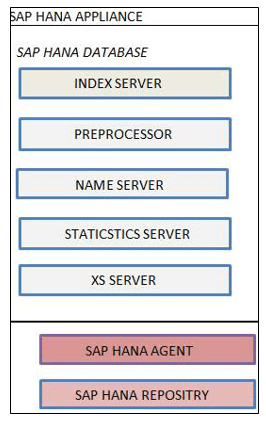
SAP HANA Server consists of
- SAP HANA Index Server SAP HANA Database Main server are index server. Detail of each server is as below-
- It’s the main SAP HANA database component
- It contains actual data stores and the engine for processing the data.
- Index Server processes incoming SQL or MDX statement.
Below is the architecture of Index Server.
SAP HANA Index Server overview
- Preprocessor Server
This server is used in Text Analysis and extracts data from a text when the search function is used.
- Name Server
This Server contains all information about the system landscape. In distributed server, the name server contains information about each running component and location of data on the server. This server contains information about the server on which data exists.
- Statistic Server
Statistic server is responsible for collecting the data related to status, resource allocation / consumption and performance of SAP HANA system.
- XS Server
XS Server contains XS Engine. It allows external application and developers to use SAP HANA database via the XS Engine client. The external client application can use HTTP to transmit data via XS engine for HTTP server.
SAP HANA Landscape
“HANA” mean High Performance Analytic Appliance is a combination of hardware and software platform.
- Due to change in computer architecture, the more powerful computer is available in terms of CPU, RAM, and Hard Disk.
- SAP HANA is the solution for performance bottleneck, in which all data is stored in Main Memory and no need to frequently transfer data from disk I/O to main memory.
Below are SAP HANA Innovation in the field of Hardware/Software.
There are two types of Relational data stores in SAP HANA: Row Store and Column Store.
Row Store
- It is same as Traditional database e.g. (Oracle, SQL Server). The only difference is that all data is stored in row storage area in memory of SAP HANA, unlike a traditional database, where data is stored in Hard Drive.
Column Store
- Column store is the part of the SAP HANA database and manages data in columnar way in SAP HANA memory. Column tables are stored in Column store area. The Column store provides good performance for write operations and at the same time optimizes the read operation.
Read and write operation performance optimized with below two data structure.
Main Storage
Main Storage contains the main part of data. In Main Storage, suitable data compression Method (Dictionary Encoding, Cluster Encoding, Sparse Encoding, Run Length encoding, etc.) is applied to compress data with the purpose to save memory and speed up searches.
- In main storage write operations on compressed data will be costly, so write operation do not directly modify compressed data in main storage. Instead, all changes are written in a separate area in column storage known as “Delta Storage.”
- Delta storage is optimized for a write operation and uses normal compression. The write operations are not allowed on main storage but allowed on delta storage. Read operations are allowed on both storages.
We can manually load data in Main memory by option “Load into Memory” and Unload data from Main memory by “Unload from Memory” option as shown below.
Delta Storage
Delta storage is used for a write operation and uses basic compression. All uncommitted modification in Column table data stored in delta storage.
When we want to move these changes into Main Storage, then use “delta merge operation” from SAP HANA studio as below –
- The purpose of delta merge operation is to move changes, which is collected in delta storage to main storage.
- After performing Delta Merge operation on sap column table, the content of main storage is saved to disk and compression recalculated.
Process of moving Data from Delta to Main Storage during delta merge
There is a buffer store (L1-Delta) which is row storage. So in SAP HANA, column table acts like row store due to L1-delta.
- The user runs update / insert query on the table (Physical Operator is SQL statements.).
- Data first go to L1. When L1 moves data further (L1- Uncommitted data)
- Then data goes to L2-delta buffer, which is column oriented. (L2- Committed data)
- When L2-delta process is complete, data goes to Main storage.
So, Column storage is both Write-optimized and Read-optimized due to L1-Delta and main storage respectively. L1-Delta contains all uncommitted data. Committed data moves to Main Store through L2-Delta. From main store data goes to the persistence layer (The arrow indicating here is a physical operator that send SQL Statement in Column Store). After Processing SQL Statement in Column store, data goes to the persistence layer.
E.g. below is row-based table-
Table data is stored on disk in linear format, so below is format how data is stored on disk for row and column table –
In SAP HANA memory, this table is stored in Row Store on disk as format –

And in Column, data is stored on disk as –

Data is stored column-wise in the linear format on the disk. Data can be compressed by compress technique.
So, Column store has an advantage of memory saving.
SAP HANA Sizing
Sizing is a term which is used to determine hardware requirement for SAP HANA system, such as RAM, Hard Disk and CPU, etc.
The main important sizing component is the Memory, and the second important sizing component is CPU. The third main component is a disk, but sizing is completely dependent on Memory and CPU.
In SAP HANA implementation, one of the critical tasks is to determine the right size of a server according to business requirement.
SAP HANA DB differ in sizing with normal DBMS in terms of –
- Main Memory Requirement for SAP HANA ( Memory sizing is determined by Metadata and Transaction data in SAP HANA)
- CPU Requirement for SAP HANA (Forecast CPU is Estimated not accurate).
- Disk Space Requirement for SAP HANA ( Is calculated for data persistence and for logging data)
The Application server CPU and application server memory remain unchanged.
For sizing calculation SAP has provided various guidelines and method to calculate correct size.
We can use below method-
- Sizing using ABAP report.
- Sizing using DB Script.
- Sizing using Quicksizer Tool.
By using Quicksizer tool, Requirement will be displayed in below format-